Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Standard Capital Asset Pricing Model
Uploaded by
Pedro Martín López LiraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Standard Capital Asset Pricing Model
Uploaded by
Pedro Martín López LiraCopyright:
Available Formats
FRM® PREPARATION COURSE
THE STANDARD CAPITAL
ASSET PRICING MODEL
[01.FRM.09]
FRM SPREADSHEETS
1.FRM.09a. - Portfolio Curve.xls
1.FRM.09.b. - Diversification.xls
1.FRM.09.c. - Efficient Porfolio.xls
1.FRM.09.d. - CML SML
FOUNDATIONS OF RISK MANAGEMENT
FRM®
FRM Program Manual
The Standard Capital Asset Pricing Model
After completing this reading the FRM candidate should be able to:
Understand the derivation and components of the CAPM.
Describe the assumptions underlying the CAPM.
Interpret the capital market line.
Apply the CAPM in calculating the expected return on an asset.
Interpret beta and calculate the beta of a single asset or portfolio.
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 2
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Portfolio Possibilities Curve and Efficient Portfolio
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 3
FRM®
Portfolio Theory
Portfolio Expected Return
Key Formula
The return of a portfolio with two or more assets is the weighted sum
of the individual returns
For example, with two assets
E(RP) = wA E(RA) + wB E(RB)
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 4
FRM®
Portfolio Theory
Portfolio Variance
and Volatility
2
.
2
Key Formulas
Variance of a portfolio of two (or more) assets
σ2p= wA2 σ2A + wB2 σ2B + 2 wAwB Cov (RA,RB)
σ2p= wA2 σ2A + wB2 σ2B + 2 wAwB ρA,B σA σB
– It is not the weighted average of asset volatilities (as for portfolio
returns)
– This is due to the interaction between assets (correlation)
Volatility = σ=
2
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 5
FRM®
Portfolio Theory
Correlation and Diversification
FRM Spreadsheet: Porfolio Curve
Correlation = ρA,B = Cov (RA,RB) / σA σB , where ρ [-1;+1]
Diversification benefits
.
The lower the correlation (ρ
close to -1) the greater the
diversification (lower risk)
The higher the correlation (ρ
close to +1), the lower the
benefit of diversification
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 6
FRM®
Portfolio Theory
Correlation and Diversification
FRM Spreadsheet: Porfolio Curve
How the Portfolio Possibilities Curve changes according to
different levels of correlation
If there is no diversification,
(ρ = 1) the Portfolio
Possibilities Curve is a
straight line
The more convex the line is,
the higher the diversification
benefits (lower correlation)
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 7
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Derivation of the CAPM
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 8
FRM®
Assumptions of the CAPM
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
Key Assumptions
No transaction costs
Assets are infinitely divisible
Investment horizon is one single period
There are no taxes
Markets are perfectly competitive
Investors decisions are based on expected portfolio return and risk
Short-selling allowed
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 9
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Portfolio Possibilities Curve and Efficient Portfolio
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 10
Portfolio Possibilities Curve and FRM®
Efficient Portfolio
Risk and Return Combinations
FRM Spreadsheet: Efficient Porfolio
w(A)=80% E(Rp) = 80%*5% + 20%*3% = 4,60%
w(B)=20% σp = ( 80%^2*10%^2 + 20%^2*8%^2 +
+ 2(-0,4)*80%*20%*10%*8% = 7,50%)
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 11
Portfolio Possibilities Curve and FRM®
Efficient Portfolio
The Portfolio with the Smallest Variance
FRM Spreadsheet: Efficient Porfolio
Portfolio with the smallest variance among all portfolio
combinations (the portfolio possibilities curve)
Left-most point on the
portfolio possibilities
curve
2-assets portfolio
w1= [σ22 – ρ1,2 σ1σ2] / [σ12 + σ22 - 2 ρ 1,2σ1σ2]
w2 = 1- w1
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 12
Portfolio Possibilities Curve and FRM®
Efficient Portfolio
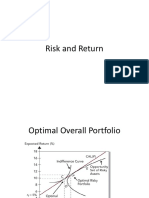
Efficient Frontier
Less risky portfolios for each level of return
All portfolios located UNDER the dotted red line are inefficient
100% Asset A, 0% Asset B
0% Asset A, 100% Asset B
Markowitz Efficient portfolios = all the combinations located ABOVE
dotted line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 13
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Portfolio Possibilities Curve and Efficient Portfolio
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 14
FRM®
Capital Market Line
Finding the Efficient Portfolio
Markowitz Porftolio
Efficient Portfolio = Market Portfolio
– The one that maximizes the Sharpe Ratio
Sharpe Ratio = [E(RP) – Rf] / σp
– The Market Portfolio is one of the portfolios located on the
Efficient Frontier
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 15
FRM®
Capital Market Line
Finding the Efficient Portfolio With Short Sales
FRM Spreadsheets: CML SML
CAPM model allows short selling
Efficient Frontier shape
─ It expands up to the right side of the graph
With short sales
the curve moves
to the right
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 16
FRM®
Capital Market Line
Finding the Efficient Portfolio
FRM Spreadsheets: CML SML
Vol (P) = √ ( 60%2 * 10%2 + 40%2 * 8%2 + 2* 0,2 * 40% * 60% *
10% * 8% ) = 7,34%
Sharpe = 4,20% - 1% / 7,34% = 0,4358
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 17
FRM®
Capital Market Line
Efficient Frontier with Risk Free Asset
FRM Spreadsheet: CML SML
Capital Market Line
– When a risk free asset is
combined with the Market
Portfolio, the resulting
risk/return combinations
will lie on a straight line
tangent to the Efficient
Frontier
This straight line is known as Capital Market Line (CML)
The point of tangency is the Market Portfolio
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 18
FRM®
Capital Market Line
Market Portfolio and CML
Key Concepts
Combining the
Market Portfolio
(the most efficient
portfolio) with the Portfolio possibilities curve
risk free asset
gives us the CML
(Capital Market
Line)
E ( RM ) RF ) E ( RM ) RF )
E ( Ri ) RF i Slope of CML Sharpe Ratio
M M
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 19
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Portfolio Possibilities Curve and Efficient Portfolio
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 20
FRM®
Market Beta and Market Premium
Diversifiable and Systematic Risk
Key Concepts
Diversifiable Risk
– The part of the volatility of a single security’s returns that is
uncorrelated with the volatility of the market portfolio
Systematic Risk
– The part of the volatility of a single security’s returns that is
correlated with the volatility of the market portfolio
When a risky security is added to a well-diversified (efficient)
portfolio, the portfolio’s risk is only affected by the systematic risk of
that security
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 21
FRM®
Market Beta and Market Premium
Market Beta
Units of Systematic Risk
The Systematic Risk (Market Risk) of a security is measured by its
beta (β)
Units of Market Risk which a single security represents
It depends on the covariance between the security and the market
portfolio
Beta, β = Cov (Ri, Rm) / σ2m
– Portfolio Beta is the weighted average of individual securities
Betas
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 22
FRM®
Market Beta and Market Premium
Market Premium
Price of Systematic Risk
For each unit of market risk (β, beta), investors can expect to receive a
premium over risk free return
Premium per unit of market risk [E(RM) – RF]
– E(RM): Market Portfolio Return
– RF: Risk Free asset return
Total premium for an investment is calculated as
Units of Risk x Price of Risk: β [E(RM) – RF]
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 23
FRM®
Key Learning Objetives
1 Portfolio Theory
1 Assumpions of the CAPM
2 Portfolio Possibilities Curve and Efficient Portfolio
3 Capital Market Line
4 Market Beta and Market Premium
5 Security Market Line
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 24
FRM®
Security Market Line
Beta, Market Premium and SML
Key Concepts
Equation of the Security Market Line (SML)
– With efficient diversification, there is no extra expected return for
bearing diversifiable risk
Expected return in equilibrium
Expected return of any security is the
riskless rate of interest plus the market
price of risk times the amount of risk in
the security or portfolio
E(Ri) = RF + βi [E(RM) – RF]
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 25
FRM®
Security Market Line
Beta, Market Premium and SML
FRM Spreadsheet: CML SML
Beta = 0,763 = 0,005 / (7,84%^2)
E(Rp) = 3,59%= 1% + 0,763 * (4,40% - 1%)
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 26
FRM®
FRM Questions
CAPM Assumptions
Sample Question
Which of the following is CORRECT regarding the capital asset pricing model (CAPM)? The
CAPM:
A) assumes there are taxes and transactions costs.
B) assumes investors prefer lower risk given a level of return.
C) applies to non-normally distributed returns.
D) assumes that investors’ expectations regarding risk and return are not identical, but
normally distributed.
CORRECT: B
The CAPM assumes that: investors are risk adverse, there are no taxes or transaction
costs, returns are normally distributed, investors’ expectations for risk and return are
identical.
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 27
FRM®
FRM Questions
Security Market Line
Sample Question
Which of the following statements about the security market line (SML) is least accurate?
A) The market portfolio consists of all risky assets.
B) Securities that plot above the SML are undervalued.
C) The risk-free rate defines where the SML intersects the vertical axis.
D) Securities that plot on the SML have no intrinsic value to the investor.
CORRECT: D
Securities that fall on the SML are properly priced. They have value to an investor in that
they still earn a return.
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 28
FRM®
FRM Questions
Portfolio Variance
Sample Question
Consider a portfolio with 40% invested in asset X and 60% invested in asset Y. The mean
and variance of return on X are 0 and 25 respectively. The mean and variance of return on Y
are 1 and 121 respectively. The correlation coefficient between X and Y is 0.3. What is the
nearest value for portfolio volatility?
a. 9.51%
b. 8.60%
c. 13.38%
d. 7.45%
CORRECT: D
σ2p= wA2 σ2A + wB2 σ2B + 2 wAwB ρA,B σA σB
σ2p = 0,4^2 *25 +0,6^2 * 121 + 2*0,4*0,6*0,3*5*11 = 55,48
σp = (55,48)^0,5 = 7,45
THE STANDARD CAPITAL ASSET PRICING MODEL 29
You might also like
- Part 3 - CAPM (IPM)Document26 pagesPart 3 - CAPM (IPM)Rakib HasanNo ratings yet
- Financial Engineering Portfolio Theory: Linda PontaDocument17 pagesFinancial Engineering Portfolio Theory: Linda PontaDavid BusinelliNo ratings yet
- An Option Greeks Primer: Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using ExcelFrom EverandAn Option Greeks Primer: Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using ExcelNo ratings yet
- Portfolio TheoryDocument10 pagesPortfolio TheorysingarajusarathNo ratings yet
- BKM Chapter 9Document4 pagesBKM Chapter 9Ana Nives RadovićNo ratings yet
- Asset Pricing ModelsDocument60 pagesAsset Pricing ModelsCharlyNo ratings yet
- Security Market Line: Presented by Ujjayini DasDocument13 pagesSecurity Market Line: Presented by Ujjayini Dasd-fbuser-42356381No ratings yet
- Sessions 7&8Document20 pagesSessions 7&8Bhavya JainNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument16 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Modelisteaq ahamedNo ratings yet
- Sapm Unit 3Document13 pagesSapm Unit 3pm2640047No ratings yet
- FF6121 Investments: Week 7Document54 pagesFF6121 Investments: Week 7朱艺璇No ratings yet
- Capital Market Theory PPT - 022357Document16 pagesCapital Market Theory PPT - 022357Pira KhanNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) and The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)Document26 pagesStudy Notes Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) and The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)alok kundaliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - CAPMDocument19 pagesLecture 10 - CAPMroBinNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis and Portfolio ManagementDocument14 pagesSecurity Analysis and Portfolio ManagementSaptarshi RayNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (Rohit)Document20 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model (Rohit)agrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Capital Market TheoryDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Capital Market TheoryEmijiano Ronquillo100% (1)
- CH 9 Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument25 pagesCH 9 Capital Asset Pricing ModelShantanu ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Risk ManagementDocument36 pagesFoundations of Risk ManagementNg Win WwaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio ManagementDocument6 pagesPortfolio ManagementAbhijit SinghNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Finance - 1Document27 pagesAdvanced - Finance - 1pierre.besnardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Multifactor Value at RiskDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - Multifactor Value at RiskVishwajit GoudNo ratings yet
- Slide 7Document17 pagesSlide 7Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing Theory: Prof. Karim MimouniDocument22 pagesCapital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing Theory: Prof. Karim MimouniSpUnky RohitNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)Document4 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)glamm glowwNo ratings yet
- CAPM Derivation20151007141002Document6 pagesCAPM Derivation20151007141002Akshay KumarNo ratings yet
- CAPM Index ModelsDocument14 pagesCAPM Index ModelsSalia Tobias MwinenkumaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Models of Risk and ReturnDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - The Models of Risk and ReturnTú Anh Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document16 pagesChapter 8MOHAMAD ZAIM BIN IBRAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- 11 - Modern Based Factor ModelsDocument23 pages11 - Modern Based Factor ModelsmuzammalNo ratings yet
- #01 Session1Document36 pages#01 Session1YisraelaNo ratings yet
- Lezione 4Document42 pagesLezione 4gio040700No ratings yet
- Portfolio Theories-Markowitz Optimization Model and The Sharpe Index ModelDocument18 pagesPortfolio Theories-Markowitz Optimization Model and The Sharpe Index ModelkenarnyNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument43 pagesTopic 5: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelHuy PhanNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Theory Capital Asset Pricing TheoryDocument29 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Theory Capital Asset Pricing Theoryagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- 08 Iapm9e PPT - ch08Document42 pages08 Iapm9e PPT - ch08Runalen EncarguesNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Investasi Pertemuan 5Document44 pagesManajemen Investasi Pertemuan 5fitria mulyawati pNo ratings yet
- 04 CapmDocument25 pages04 CapmDaniel RisticNo ratings yet
- Session 5 and 6Document28 pagesSession 5 and 6Kaushal MadhyaniNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing TheoryDocument25 pagesCapital Asset Pricing and Arbitrage Pricing TheoryBen CannonNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Theories IIDocument30 pagesRisk and Return Theories IISajid ChishtiNo ratings yet
- The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument45 pagesThe Capital Asset Pricing ModelL SNo ratings yet
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Gareth MylesDocument26 pagesInvestment Analysis and Portfolio Management: Gareth MyleshoalongkiemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Portfolio Risk and Return Part IIDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Portfolio Risk and Return Part IILaura StephanieNo ratings yet
- 4 - Portfolio TheoryDocument22 pages4 - Portfolio TheorySIDDHARTH SNNo ratings yet
- CapmDocument43 pagesCapmVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Seminar 05Document17 pagesSeminar 05api-3695734No ratings yet
- BF2 Lecture3 MFMDocument43 pagesBF2 Lecture3 MFMDuc Tao ManhNo ratings yet
- Cfa Chapter 9 Problems: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument7 pagesCfa Chapter 9 Problems: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelFagbola Oluwatobi Omolaja100% (1)
- The Capm: Dong Lou London School of Economics LSE Summer SchoolDocument39 pagesThe Capm: Dong Lou London School of Economics LSE Summer SchoolAryan PandeyNo ratings yet
- CAPM Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesCAPM Lecture NotesNaailah نائلة MaudarunNo ratings yet
- CAPM: A General Equilibrium Theory of Asset Pricing: Equation For CMLDocument15 pagesCAPM: A General Equilibrium Theory of Asset Pricing: Equation For CMLHalimah SheikhNo ratings yet
- Factor Models of Asset ReturnsDocument55 pagesFactor Models of Asset ReturnsBaigalmaa NyamtserenNo ratings yet
- Capital Market TheoryDocument11 pagesCapital Market TheoryRajeshwari SharmaNo ratings yet
- L1 R50 HY NotesDocument7 pagesL1 R50 HY Notesayesha ansariNo ratings yet
- D - Tutorial 7 (Solutions)Document10 pagesD - Tutorial 7 (Solutions)AlfieNo ratings yet
- CAPMDocument45 pagesCAPMkokmunwai717No ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) : RiskDocument26 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) : RiskKrisi ManNo ratings yet
- Elements of Retail StrategyDocument27 pagesElements of Retail StrategyShagufta Khan83% (6)
- Final Examination Principles of Finance (DPF 24153)Document9 pagesFinal Examination Principles of Finance (DPF 24153)USHA PERUMALNo ratings yet
- Fashion Merchandising: Alondra Galloza P. 7Document17 pagesFashion Merchandising: Alondra Galloza P. 7The GadiatorNo ratings yet
- B1 Free Solving (May 2019) - Set 1Document5 pagesB1 Free Solving (May 2019) - Set 1paul sagudaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Published Business Accounts and RatiosDocument12 pagesInterpreting Published Business Accounts and RatiosAlfie_Armstrong100% (1)
- PDF 20220309 202747 0000Document8 pagesPDF 20220309 202747 0000princesschaves laurenteNo ratings yet
- BS Option Pricing Basics PDFDocument38 pagesBS Option Pricing Basics PDFPankaj Dayani100% (1)
- Marginal Costing: Pooja Gupta Singla PietDocument32 pagesMarginal Costing: Pooja Gupta Singla PietPOOJA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Corruption and FDIDocument10 pagesCorruption and FDIShuchi Goel100% (1)
- Human Capital Theory, The Power of Transnational Companies and A Political Response in Relation To Education and Economic DevelopmentDocument6 pagesHuman Capital Theory, The Power of Transnational Companies and A Political Response in Relation To Education and Economic DevelopmentJ. Félix Angulo RascoNo ratings yet
- The Five Foundations of EconomicsDocument30 pagesThe Five Foundations of EconomicsJayson Maesa BaisaNo ratings yet
- LEAP Beta 1 PagerDocument1 pageLEAP Beta 1 PagerDheeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Feasible Study Glove FactoryDocument27 pagesFeasible Study Glove Factorybeckoy17No ratings yet
- The Product Life Cycle: Analysis and Applications Issues: George S. DayDocument8 pagesThe Product Life Cycle: Analysis and Applications Issues: George S. Daymariaflorina91No ratings yet
- IMC MarathonDocument4 pagesIMC MarathonarlynneNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Job Costing CH4Document8 pagesSample Questions Job Costing CH4angelbear2577100% (1)
- Business Combination Handout RRDocument19 pagesBusiness Combination Handout RRMulugeta NiguseNo ratings yet
- Truck Europe Q1 2023 JPMorgan 280423Document10 pagesTruck Europe Q1 2023 JPMorgan 280423keshav.mundhraNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Chapter 4 NotesDocument11 pagesBusiness Economics Chapter 4 NotesMadesh KuppuswamyNo ratings yet
- (PPT) Ch.7 - Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsDocument44 pages(PPT) Ch.7 - Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsazizkhonNo ratings yet
- Amazon and Walmart On Collision CourseDocument27 pagesAmazon and Walmart On Collision CourseSaloni PatilNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesSYLLABUS Managerial EconomicsSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- CMO VP Marketing Branding in United States Resume Alvan ChaneyDocument3 pagesCMO VP Marketing Branding in United States Resume Alvan ChaneyAlvanChaneyNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Beer Customer Satisfaction in The Breweries Industry: A Case Study of The East African Breweries Limited in KenyaDocument94 pagesFactors Affecting Beer Customer Satisfaction in The Breweries Industry: A Case Study of The East African Breweries Limited in KenyaRonaldNo ratings yet
- Amazon Go PresentationDocument76 pagesAmazon Go PresentationAbinaya Santhakumar100% (1)
- Chapter 6: Land Rights and The Law in Tanzania: Institutional Issues and ChallengesDocument51 pagesChapter 6: Land Rights and The Law in Tanzania: Institutional Issues and ChallengesRANDAN SADIQNo ratings yet
- FINAL Standard Chartered BankDocument9 pagesFINAL Standard Chartered BanknareshmanglaniNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Customer-Linking Marketing Capabilities Using Marketing AnalyticsDocument11 pagesEnhancing Customer-Linking Marketing Capabilities Using Marketing Analyticsumar sohailNo ratings yet
- List of Companies PDFDocument25 pagesList of Companies PDFNitin GuptaNo ratings yet