Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Method
Uploaded by
Phạm Trà MyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Method
Uploaded by
Phạm Trà MyCopyright:
Available Formats
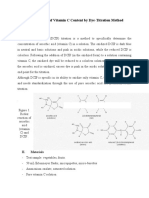
Title: “Determination of vitamin C content (Titration method with 2,6
dichlorophenolindophenol-2,6-DCIP)
Method
1. Preparation:
First, determine the concentration correction factor (f) of the 2,6 DCTP solution. A 5ml aliquot
of pure vitamin, which had been diluted in 2% H2SO4, and 2.5 ml of a solution of satutamin
Oxalatamon were transferred into a 50 ml triangular flask (designated as flask 1). Afterward, the
above mixture was titrated with a 2.6 DCIP solution (analytical) until a stable pink color
persisted for 1 minute and recorded as a1ml. A 5 ml aliquot of pure vitamin, which had been
diluted in a 2% H2SO4 solution, was transferred into a 50 ml triangular flask (designated as flask
2) using a micropipette. A few crystals of KI and 5 drops of starch indicator solution were added
to flask 2. Flask 2 was titrated with 0,001N KIO3 solution until the solution turned blue and
recorded the volume as b1ml. The coefficient f of the 2,6 DCIP solution used in the analysis was
calculated according to the formula: f=b1/a1.
The mass of tangerines was accurately weighed to 10g and then placed in a mortar, where they
were ground in 5% metaphosphoric acid (or 1% HCl). Subsequently, the mixture was thoroughly
shaken, filtered, and the resulting vitamin C filtrate was collected for subsequent analysis.
2. Reaction procedure
Experimental sample:
A micropipette was used to transfer 10ml of the filtered analytical vitamin C solution and 5ml of
saturated oxalate monohydrate into a clean, dry 50ml triangular flask (designated as flask 3). The
flask 3 was titrated with 2,6 DCIP solution (analytical) until a stable pink color persisted for 1
minute.
Control sample:
A pipette was used to transfer 10ml of 1% HCl solution and 5ml of saturated oxalate
monohydrate into a clean, dry 50ml triangular flask (designated as flask 4). The flask 4 was
titrated with 2,6 DCIP solution (analytical) until a stable pink color persisted for 1 minute.
You might also like
- CHM256 ProcedureDocument4 pagesCHM256 ProcedureMUHAMMAD AIDEED RODZINo ratings yet
- Lab 8-Determination of Vitamin C Content by Dye-TitrationDocument3 pagesLab 8-Determination of Vitamin C Content by Dye-TitrationDũng Nguyễn ViệtNo ratings yet
- University of Zululand Faculty of Science and Agriculture: Metabolism (Sbch212) Practical ManualDocument16 pagesUniversity of Zululand Faculty of Science and Agriculture: Metabolism (Sbch212) Practical ManualNomceboNo ratings yet
- Appendix-1 Estimation of Total CarbohydrateDocument46 pagesAppendix-1 Estimation of Total CarbohydrateRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Digestible Crude Protein Pepsin ActivityDocument3 pages5.2 Digestible Crude Protein Pepsin Activitypavan patelNo ratings yet
- 17 Chapter 3 (B)Document11 pages17 Chapter 3 (B)arianooshpNo ratings yet
- Alkaloid, Tanin, Flavonoid and Saponin AnalysisDocument7 pagesAlkaloid, Tanin, Flavonoid and Saponin AnalysisNiken Ayu PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Manual Bt35lDocument14 pagesBiochemistry Lab Manual Bt35ldrugdrugNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document6 pagesActivity 2MARKUS GERARD REYESNo ratings yet
- Manual 4Document11 pagesManual 4ChaithraMalluNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Lidocaine: Chemistry 212 LaboratoryDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Lidocaine: Chemistry 212 LaboratoryNuteLLa Gaming (EFL)No ratings yet
- 149 D30004 PDFDocument8 pages149 D30004 PDFMeldaNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Gluten Formal ReportDocument3 pagesIsolation of Gluten Formal ReportReg LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Action of Saliva and HCL in 2 Carbohydrate SolutionsDocument4 pagesInvestigation of Action of Saliva and HCL in 2 Carbohydrate SolutionsSathYa NatHanNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane Assignment NarayananDocument17 pagesSugarcane Assignment NarayanannarayananNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron in Dietary Supplements For CHM 122.2Document3 pagesSpectrophotometric Determination of Iron in Dietary Supplements For CHM 122.2Angeline RabuyoNo ratings yet
- Advanced PH Analysis Practical Lab3 MetforminDocument2 pagesAdvanced PH Analysis Practical Lab3 Metforminknowlegebook6No ratings yet
- Experiment # 01: Calculations Related To Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesExperiment # 01: Calculations Related To Organic ChemistryAbdullah JavedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument20 pagesCarbohydrates LabChristian Dave MativoNo ratings yet
- Sop For Vitamin K3Document3 pagesSop For Vitamin K3Ganesh KashinathNo ratings yet
- Sop For Vitamin k3Document3 pagesSop For Vitamin k3Ganesh KashinathNo ratings yet
- Enzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food LabDocument21 pagesEnzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food Labmasre semagnNo ratings yet
- Ni EDTADocument1 pageNi EDTARahul ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsIago CarballoNo ratings yet
- Lab 11Document3 pagesLab 11Assasin KillerNo ratings yet
- PPĐG ReportDocument15 pagesPPĐG ReportHà ChiNo ratings yet
- Special StainingDocument11 pagesSpecial Stainingnoon noonNo ratings yet
- Assay of Ractopamine HCL 2Document7 pagesAssay of Ractopamine HCL 2Enpex LaboratoriesNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Protocol (Sop) : Subject: Determination of Flavonol Glycosides in GinkgoDocument6 pagesStandard Operating Protocol (Sop) : Subject: Determination of Flavonol Glycosides in GinkgopvrajivicasNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Caffeine From TeaDocument4 pagesExtraction of Caffeine From TeaAndrew GhobrialNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Protein (Manual)Document9 pagesAnalysis of Protein (Manual)actionNo ratings yet
- Estimation Protocol Antinutrional Factors in Oilseeds: M.Narayanan 2019508202 GPB513Document23 pagesEstimation Protocol Antinutrional Factors in Oilseeds: M.Narayanan 2019508202 GPB513narayananNo ratings yet
- 1 Scope:: C-7 Standardization of Fehling'S SolutionDocument8 pages1 Scope:: C-7 Standardization of Fehling'S SolutionYoni LoveNo ratings yet
- E LabDocument3 pagesE LabAlthea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Procedure: For Every Analysis, There Will Be 3 Trials A.2 Sulfate Analysis (Gravimetric Method With Ignition of Residue)Document4 pagesProcedure: For Every Analysis, There Will Be 3 Trials A.2 Sulfate Analysis (Gravimetric Method With Ignition of Residue)Rai CanNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 Topic 3 ESTIMATION OF STARCH FROM WHEAT FLOUR BY BENEDICT METHODDocument2 pagesUnit 16 Topic 3 ESTIMATION OF STARCH FROM WHEAT FLOUR BY BENEDICT METHODAhijit DeNo ratings yet
- Formal Report 1 Expt 7 Chem 26.1Document6 pagesFormal Report 1 Expt 7 Chem 26.1Franz Valencia100% (1)
- Lab NotebookDocument5 pagesLab NotebookGregbr62No ratings yet
- 2334-2335 Betahistine HydrochlorideDocument2 pages2334-2335 Betahistine HydrochlorideShady Ashraf LatifNo ratings yet
- Determina Metal in Soil Bby MehlishDocument3 pagesDetermina Metal in Soil Bby MehlishPurna PirdausNo ratings yet
- Experiment 32Document14 pagesExperiment 32Morgan Elizabeth Lepley100% (6)
- Detection of Beta LactamDocument18 pagesDetection of Beta LactamRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- ION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralDocument50 pagesION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralJinalNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1: ReagentsDocument15 pagesAppendix 1: ReagentsJoshua Zheng 郑建承No ratings yet
- I. Sample Preparation: Dilute To The Mark With Previously Boiled and Cooled Distilled WaterDocument3 pagesI. Sample Preparation: Dilute To The Mark With Previously Boiled and Cooled Distilled WaterCamille Lei100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocument3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Proteinstine314No ratings yet
- 1 08 Nitrogen Determination Semimicro Kjeldahl Method 47Document2 pages1 08 Nitrogen Determination Semimicro Kjeldahl Method 47Chiung wen YehNo ratings yet
- USP - Choline ChlorideDocument3 pagesUSP - Choline Chloridehh.8968No ratings yet
- Titration of Calcium and Magnesium in Milk and Milk Fractions With Ethylenediamine Tetra AcetateDocument3 pagesTitration of Calcium and Magnesium in Milk and Milk Fractions With Ethylenediamine Tetra AcetateThomas ChanNo ratings yet
- AOCS Ce6 - 86 (HPLC-Antioksidan Level) - 1Document6 pagesAOCS Ce6 - 86 (HPLC-Antioksidan Level) - 1Muhammad Nurul Masyhudi100% (1)
- Saliva and HCLDocument5 pagesSaliva and HCLAlex MakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4alphane2300No ratings yet
- Working With Hazardous Chemicals: A Publication of Reliable Methods For The Preparation of Organic CompoundsDocument5 pagesWorking With Hazardous Chemicals: A Publication of Reliable Methods For The Preparation of Organic CompoundsmghaffarzadehNo ratings yet
- CHM 2962 Report 4Document9 pagesCHM 2962 Report 4Yun KiatNo ratings yet
- Asta Analytical MethodsDocument4 pagesAsta Analytical Methodsravivarmahyd8173No ratings yet
- Biochemical Studies of FishDocument5 pagesBiochemical Studies of FishAdarsh LalitNo ratings yet
- Glycerine DeterminationDocument3 pagesGlycerine DeterminationorganodieselNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet