Professional Documents
Culture Documents
111 - Notes Ratios
111 - Notes Ratios
Uploaded by
CharlotteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
111 - Notes Ratios
111 - Notes Ratios
Uploaded by
CharlotteCopyright:
Available Formats
GRADE 10 LESSON
111
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
WORKSHEET 1
It is important for a business to measure its performance
A business has to assess whether they have been successful or not and to determine the
areas in which they can approve.
A business has to answer the following questions:
How profitable is the business?
How well does the business control its expenses?
Should the owner be satisfied with the profit earned taking into account the amount
he invested in the business?
Can the business pay off all its debts?
Can the business pay off its debts without any problem in the short term?
Did the business handle its working capital effectively?
It is essential for the owner to analyse the financial statements.
The aim of analysis and interpreting the financial statements of a business is to
determine the following:
Profitability How profitable is the business?
How well does it control its expenses?
Return Does the owner earn a good return on the capital he has invested in
the business?
Solvency Can the business pay off all its debts?
Liquidity Can the business pay off its short-term debts (current liabilities)
without any problems in the short term?
These current liabilities can be paid only from current assets that can
be converted to cash.
111 Accounting Grade 10 1
WORKSHEET 2
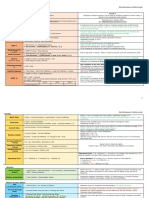
How do we calculate these ratios?
PROFIBILITY RATIO’S (from the Income Statement)
Percentage gross profit on sales Gross profit x 100
Turnover =%
Percentage gross profit on cost of sales Gross profit x 100
(also the mark-up percentage) Cost of sales 1 =%
Percentage net profit on sales Net profit x 100
Turnover 1 =%
Percentage operating expenses on Operating expenses x 100
sales Turnover 1 =%
Percentage operating profit on sales Operating profit x 100
Turnover 1 =%
LIQUIDITY RATIO’S (from the Balance sheet)
Current assets : Current liabilities
Current ratio
= x:1
Current assets - inventories : Current liabilities
Acid-test ratio
= x:1
SOLVENCY RATIO (from the Balance sheet)
Total assets : Total liabilities
Solvency ratio
=x:1
RETURN ON INVESTMENT (from Income statement and Balance sheet)
Return on owner’s equity net profit 100
owner’s equity x 1 =%
111 Accounting Grade 10 2
Where do we get our information from?
INCOME STATEMENT
Notes R
Sale 399 480 Grossprofit
Gross profiton
onsales
sales
profit profit
Gross x 100x 100
Cost of sales (200 000) sales
sales 11
Gross profit 199 480
Other operating income 341 988 Grossprofit
Gross profitononcost
costofofsales
sales
Rent income 332 260 Grossprofit
Gross profit x x 100
100
Costofofsales
Cost sales 11
Discount received 9 728
Gross operating income 541 468
NetNetprofit
profit
onon sales
sales
Operating expenses (165 140)
net profit x 100
net profit x 100
Stationery 6 860 salessales 1 1
Telephone 25 780
Water and electricity 22 100
Salaries 67 400
Operating expenses on
Depreciation 43 000 sales
Operating expenses x 100
Operating profit 376 328
sales 1
Interest income 100
Operating profit before interest expense 376 428
Operating profit on sales
Interest expense (52 200)
operating profit x 100
Net profit for the year 324 228
sales 1
BALANCE SHEET
ASSETS Returnon
Return oninvestment
investment
NON-CURRENT ASSETS 922 000 net
net profitprofit x x 100100
owner’s
owner’s equity equity 1 1
Tangible assets 3 912 000
Financial assets
Fixed deposit 10 000
CURRENT ASSETS 240 800
Inventories 4 200 200 CURRENT RATIO
CURRENT RATIO
Trade and other debtors 5 40 000
current assets
current assets :: current
current liabilities
liabilities
Cash and cash equivalents 6 600
TOTAL ASSETS 1 162 800
EQUITY AND LIABILITIES
Equity 7 904 300 SOLVENCYRATIO
SOLVENCY RATIO
NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES 200 000 totalassets
total assets: total
: totalliabilities
liabilities
Loan 200 000
CURRENT LIABILITIES 58 500
Trade and other creditors 8 40 500
Bank overdraft 18 000
TOTAL EQUITY AND LIABILITIES 1 162 800
111 Accounting Grade 10 3
CHALKBOARD SUMMARY / TRANSPARENCY
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Profitability Liquidity Solvency Return
Gross profit Current
on sales ratio
Gross profit
on Acid-test
cost of ratio
sales
Net profit
on sales
Operating
expenses
on sales
Operating
profit
on sales
111 Accounting Grade 10 4
You might also like
- Bold and Determided Vol 1Document167 pagesBold and Determided Vol 1Felipe Blanco100% (4)
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Income Statement Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesIncome Statement Practice Problemsmike0% (1)
- Petty Cash VoucherDocument4 pagesPetty Cash VoucherUgen SparkNo ratings yet
- 3 Statement of IncomeDocument16 pages3 Statement of IncomeMarlon LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Inancing Ecisions Everages: Learning OutcomesDocument35 pagesInancing Ecisions Everages: Learning OutcomesBhai LangurNo ratings yet
- The California State Budget and Revenue Volatility: Fiscal Health in A Deficit ContextDocument16 pagesThe California State Budget and Revenue Volatility: Fiscal Health in A Deficit ContextHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- MegaPower Project Memo VfinalDocument5 pagesMegaPower Project Memo VfinalSandra Sayarath AndersonNo ratings yet
- Financial Strategy in RetailDocument22 pagesFinancial Strategy in RetailGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument55 pagesRatio AnalysisShahruk AnwarNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument4 pagesProfitability RatiosAkansh NuwalNo ratings yet
- Inancing Ecisions Everages: Analysis of LeverageDocument8 pagesInancing Ecisions Everages: Analysis of LeverageParth BindalNo ratings yet
- Mio Booklet 2024Document22 pagesMio Booklet 2024Qurat Ul Ain NaqviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 1Document29 pagesChapter 24 1Nile NguyenNo ratings yet
- F3 - ACCA Chapter-24-1Document29 pagesF3 - ACCA Chapter-24-1Nile NguyenNo ratings yet
- Accounting RatiosDocument9 pagesAccounting RatiosRonnie Vond McRyttsson MudyiwaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document17 pagesUnit 2hassan19951996hNo ratings yet
- 05 BEP and LeverageDocument30 pages05 BEP and LeverageAyushNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 محاسبه اداريهDocument47 pagesUnit - 6 محاسبه اداريهsuperstreem.9No ratings yet
- Financial Statement - Nur HDocument22 pagesFinancial Statement - Nur Hshahjadpur BranchNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: Profitability RatiosDocument10 pagesRatio Analysis: Profitability RatiosREHANRAJ100% (1)
- 3.1 CVP & LeverageDocument16 pages3.1 CVP & LeveragePankaj BhardwajNo ratings yet
- S03 & S04 - External Financial StatementsDocument75 pagesS03 & S04 - External Financial StatementsYassin DyabNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Impact of Leverage: Operating Leverage Financial Leverage Combined LeverageDocument98 pagesAnalysis and Impact of Leverage: Operating Leverage Financial Leverage Combined Leveragethella deva prasadNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Financial StatementDocument5 pagesInterpretation of Financial StatementHuế ThùyNo ratings yet
- Operating and Financial LeverageDocument64 pagesOperating and Financial Leveragedanilyn uyNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatioDocument17 pagesProfitability Ratioaayushiji789No ratings yet
- AccountingDocument8 pagesAccountingHimanshu Upadhyay AIOA, NoidaNo ratings yet
- Final Cheat Sheet FA ML X MM UpdatedDocument8 pagesFinal Cheat Sheet FA ML X MM UpdatedIrina StrizhkovaNo ratings yet
- CH 27finacial Ratios Formulas Updated 20 May23Document23 pagesCH 27finacial Ratios Formulas Updated 20 May23kungadhondup12191No ratings yet
- Demo LeverageDocument18 pagesDemo LeverageIftikhar baigNo ratings yet
- Fm10 Op and Fin LeverageDocument63 pagesFm10 Op and Fin Leverageayu nailil kiromahNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument40 pagesProfitability Ratios401 KALAVALA SAI NAVEENNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: OST Ccounting Anagerial Mphasis Dition Rikant Eorge Adhav HristopherDocument17 pagesCost-Volume-Profit Analysis: OST Ccounting Anagerial Mphasis Dition Rikant Eorge Adhav HristopherFahim Ashab ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- I-CVP Analysis For Break-Even PlanningDocument10 pagesI-CVP Analysis For Break-Even PlanningNeshia May BariquitNo ratings yet
- Manajemen KeuanganDocument10 pagesManajemen KeuanganDetaNo ratings yet
- Operating and Financial LeverageDocument62 pagesOperating and Financial Leverageirshan amirNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument7 pagesABSTRACTZa DoelNo ratings yet
- TIFA CheatSheet MM X MLDocument10 pagesTIFA CheatSheet MM X MLCorina Ioana BurceaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis - RatioDocument7 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis - RatioJanelle De TorresNo ratings yet
- ACT2111 Fall 2019 Ch6 - Lecture 9&10 - StudentDocument62 pagesACT2111 Fall 2019 Ch6 - Lecture 9&10 - StudentKevinNo ratings yet
- Pof AFS SundayDocument32 pagesPof AFS SundayAsad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Impact of Leverages DR Pawan GuptaDocument53 pagesAnalysis and Impact of Leverages DR Pawan Guptamithunbanerjee2009No ratings yet
- Analisa Ratio Keuangan LatihansoalDocument4 pagesAnalisa Ratio Keuangan Latihansoalxiao yung12No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 For CUP Financial AccountingDocument15 pagesChapter 6 For CUP Financial Accountingratanak_kong1-9No ratings yet
- MODULE 3 CVP ANALYSIS - GROUP 2 AE6 Strategic Business AnalysisDocument5 pagesMODULE 3 CVP ANALYSIS - GROUP 2 AE6 Strategic Business AnalysisJaime PalizardoNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument22 pagesFinancial ManagementSapan AnandNo ratings yet
- Operating Financial LeverageDocument64 pagesOperating Financial LeverageArafatNo ratings yet
- Financial RatiosDocument20 pagesFinancial RatiosThiên TiênNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Evaluating Business PerformanceDocument3 pages3.5 Evaluating Business PerformanceredcutsaNo ratings yet
- LEVERAGEDocument46 pagesLEVERAGEFaza Rizky WijayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Analysis and Impact of LeverageDocument38 pagesChapter 15 - Analysis and Impact of LeveragepranavNo ratings yet
- LeverageDocument64 pagesLeveragePRECIOUSNo ratings yet
- Course Name Lecturer Name: Cost AccountingDocument21 pagesCourse Name Lecturer Name: Cost AccountingTurbo TechNo ratings yet
- ST DennisDocument8 pagesST DennisRovic NiemeNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis - RatiosDocument15 pagesFinancial Analysis - RatiosSiau Wen KiatNo ratings yet
- DMRM RM C6 RFSDocument14 pagesDMRM RM C6 RFSdinar aimcNo ratings yet
- Leverage Analysis: Vincent Joseph D. Disu, CPPS, MbaDocument17 pagesLeverage Analysis: Vincent Joseph D. Disu, CPPS, MbaMaria Maganda MalditaNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document63 pagesCH 16Labonno Reza AshaNo ratings yet
- Operating and Financial Leverage Operating and Financial LeverageDocument58 pagesOperating and Financial Leverage Operating and Financial LeverageFarzad TouhidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28Document34 pagesLecture 28Riaz Baloch NotezaiNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatioDocument29 pagesProfitability Ratiomushiechan888No ratings yet
- RATIO ANALYSIS by K K ChyDocument21 pagesRATIO ANALYSIS by K K Chydbgdemo6No ratings yet
- Accounting Slides Income StatmentDocument20 pagesAccounting Slides Income StatmentEdouard Rivet-BonjeanNo ratings yet
- Nternational Olitical Conomy: Ourse EscriptionDocument7 pagesNternational Olitical Conomy: Ourse EscriptionGuramiosNo ratings yet
- Cbjesspl 04Document9 pagesCbjesspl 04Drone MaxNo ratings yet
- Customers Perception On General Bamking Activities of Prime Bank Limited 3Document49 pagesCustomers Perception On General Bamking Activities of Prime Bank Limited 3Shuvo DeyNo ratings yet
- Vesta Property Holdings, Inc. v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, C.T.A. Case No. 9234, (November 28, 2017Document2 pagesVesta Property Holdings, Inc. v. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, C.T.A. Case No. 9234, (November 28, 2017JT GalNo ratings yet
- Mueller SyllabusDocument2 pagesMueller SyllabusAli SharifiNo ratings yet
- UGP Project-Report: Demonetization and Its Impact On Indian EconomyDocument9 pagesUGP Project-Report: Demonetization and Its Impact On Indian EconomyJyotika GuptaNo ratings yet
- FM 6 Financial Statements Analysis MBADocument50 pagesFM 6 Financial Statements Analysis MBAMisganaw GishenNo ratings yet
- Payment Receipt HDFCLIFEDocument2 pagesPayment Receipt HDFCLIFES. Kavya 8B 8214No ratings yet
- Retention Ratio ($248,000 - $160,000) /$248,000 .355Document2 pagesRetention Ratio ($248,000 - $160,000) /$248,000 .355mehdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Money MarketDocument30 pagesChapter 5 - Money MarketMai Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- FM Revision 3rd YearDocument39 pagesFM Revision 3rd YearBharat Satyajit100% (1)
- Core - 5 - Supply Chain and Trade FinanceDocument63 pagesCore - 5 - Supply Chain and Trade FinanceShailjaNo ratings yet
- Deposits: CA. Pramod JainDocument23 pagesDeposits: CA. Pramod JainNishant RajNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management: Complete The Crossword Puzzle BelowDocument2 pagesStrategic Financial Management: Complete The Crossword Puzzle BelowTarunvir KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Sanaul - CECM 4th - Assignment 1Document6 pagesSanaul - CECM 4th - Assignment 1Sanaul Faisal100% (1)
- Book Value Per Share & Basic Earning Per Share QuizDocument4 pagesBook Value Per Share & Basic Earning Per Share QuizMycah BolusanNo ratings yet
- Mku 7Document15 pagesMku 7Robin ListiantoNo ratings yet
- Eng BTCW SW Wisdomtree BitcoinDocument3 pagesEng BTCW SW Wisdomtree BitcoinChen LiangNo ratings yet
- APRIL 2019 International Finance Question PaperDocument9 pagesAPRIL 2019 International Finance Question PaperApruva BelapurkarNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions Markets and Money 12th Edition Kidwell Test BankDocument25 pagesFinancial Institutions Markets and Money 12th Edition Kidwell Test BankPatriciaSimonrdio100% (59)
- Vanuatu ImmigrationDocument4 pagesVanuatu ImmigrationKossNo ratings yet
- BFN1014 Assignment (T2, 201516) VDocument4 pagesBFN1014 Assignment (T2, 201516) VAlya IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Direct Taxation Paper-I - Course Outline - RahulDocument9 pagesDirect Taxation Paper-I - Course Outline - RahulABHIJEETNo ratings yet
- Asset Replacement DecisionsDocument6 pagesAsset Replacement DecisionsSam SamNo ratings yet
- University of Finance - Marketing Bachelor, Year 2: ECO102 Principles of Macroeconomics - Tutorial QuestionsDocument33 pagesUniversity of Finance - Marketing Bachelor, Year 2: ECO102 Principles of Macroeconomics - Tutorial QuestionsDanh PhanNo ratings yet
- 402 Assignment 1 - Austin OzierDocument2 pages402 Assignment 1 - Austin OzieraustinNo ratings yet