Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2 - 08-01-2024 - AK
Uploaded by
yashlm10170 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 2_08-01-2024_AK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesLecture 2 - 08-01-2024 - AK
Uploaded by
yashlm1017Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Biochemical engineering/ Bioprocess
engineering
Biochemical Engineering also known as Bioprocess Engineering is a
branch of Chemical Engineering or Biological Engineering. It is a
branch of engineering that deals with the design and construction of
unit processes that involve biological organisms or molecules.
The efficient utilization of physical, chemical and biological
processes to convert raw materials into useful products, at
minimal cost, with minimal energy consumption, and with
minimal impact on the environment.
Bioprocess/Biochemical
Engineering
• Process for developing useful products by taking
advantage of natural biological activities.
• Classical example include making alcoholic
beverages – the yeast cells and nutrients (cereal
grains) formed a fermentation system in which the
organisms consumed the nutrients for the growth
and produce by-products (alcohol).
• Today's modern bioprocess technology is based on
the same principle: combining living matter (whole
organisms or enzymes) with nutrients under the
conditions necessary to make the desired end
product.
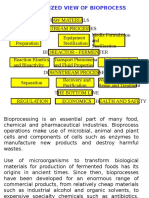
Bioprocessing
• Many potential uses of biotechnology are
developed through laboratory procedures
that generally produce only small amounts of
useful substances.
• As advances in bioprocess technology,
particularly, fermentation, separation and
purification techniques, are made-
commercial firms are able to economically
produce these substances in large amounts
Bioprocessing
• Because bioprocesses use living
material, they offer several
advantages over conventional
chemical methods of production:
➢ They usually require lower temperature,
pressure, and pH.
➢ They can use renewable resources as raw
materials; and greater quantities can be
produced with less energy consumption.
Bioprocessing
• In bioprocesses, enzymes are used to catalyze the
biochemical reactions by whole microorganisms or
their cellular components.
• The biological catalyst causes the reactions to
occur, but is not itself changed.
• After a series of such reactions (which take place in
large vessels called fermentors or fermentation
tanks), the initial raw materials are chemically
changed to form the desired end product.
Bioprocessing
• Bioprocesses have become widely used in fields, such as
production of enzymes and proteins that are used in:
➢ food processing
➢ waste management
➢ medical research
➢ agriculture
➢ pharmaceutical development
➢ numerous other fields of science and industry.
Microorganisms as production factory
• Microorganisms in the process of self
replication, produce numerous complex
macromolecules from about 100 different
monomer units.
• To achieve this a bacterial cell uses well
over 1000 different enzymes and a
eukaryotic cell may employ twice as many.
Products of Bioprocess Technology
You might also like
- Fungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassFrom EverandFungi and Lignocellulosic BiomassChristian P KubicekNo ratings yet
- What Is Bioprocess?Document28 pagesWhat Is Bioprocess?sanyukta sinhaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Power Point Chapter OneDocument22 pagesBiochemical Power Point Chapter OneEstifa negashNo ratings yet
- Untitled 2 2Document6 pagesUntitled 2 2nicksscribd7No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Fermentation ProcessesDocument18 pagesAn Introduction To Fermentation ProcessesPhú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument57 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYBenzDave AgsoyNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 1Document28 pagesBio Chapter 1Areej AlissaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Bioprocess Engineering: Lecturer Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout Assistant Prof. of BiotechnologyDocument54 pagesAdvanced Bioprocess Engineering: Lecturer Dr. Kamal E. M. Elkahlout Assistant Prof. of Biotechnologybelete fentayeNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Applied and Industril MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesCH 28 Applied and Industril Microbiologyramonlennon1980No ratings yet
- Chapter One Biotechnology and Biochemical EngineeringDocument22 pagesChapter One Biotechnology and Biochemical EngineeringYonas MegersaNo ratings yet
- Lecture IntroductionDocument9 pagesLecture IntroductionTejasv RajputNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Microorganisms Used in Industrial MicrobiologyDocument62 pagesCharacteristics of Microorganisms Used in Industrial Microbiologyjaveriazia97No ratings yet
- Fermentation TechnologyDocument24 pagesFermentation TechnologySamiul Alam Rajib100% (2)
- Generalized View of BioprocessDocument20 pagesGeneralized View of BioprocessTamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- Colors of BiotechnologyDocument66 pagesColors of Biotechnologyasdfgh0% (1)
- Mbio313 Assignment 2Document8 pagesMbio313 Assignment 2Razia UrmiNo ratings yet
- 1 Bioprocess Engineering CH 1Document22 pages1 Bioprocess Engineering CH 1Fasil ManNo ratings yet
- App Chem AsigDocument9 pagesApp Chem Asighafiz_qamarNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess 1 SBT 2132Document13 pagesBioprocess 1 SBT 2132Biotechnology IIUM Kuantan100% (2)
- Slide Intro BioprocessDocument10 pagesSlide Intro BioprocessNaufal AdityasNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction of BioprocessDocument8 pagesBasic Introduction of BioprocessRavenSkullNo ratings yet
- Basic Introduction of BioprocessDocument8 pagesBasic Introduction of BioprocessRavenSkullNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To Biotechnology Ramadan YahiaDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To Biotechnology Ramadan YahiaRamez JasonNo ratings yet
- Scope of Industrial MicrobiologyDocument21 pagesScope of Industrial MicrobiologyMelvin JoeNo ratings yet
- Che 511 Lecture Note 2023Document5 pagesChe 511 Lecture Note 2023Bright ChimezieNo ratings yet
- Production of Metabolites, Industrial Enzymes, AminoDocument50 pagesProduction of Metabolites, Industrial Enzymes, AminoInuyashayahooNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biochemical Engineering (Biot. 4132) Course ECTS: 3Document61 pagesFundamentals of Biochemical Engineering (Biot. 4132) Course ECTS: 3Andebet HabtamNo ratings yet
- Recycling 3Document29 pagesRecycling 3adhamelthnNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Biotechnology by Salman SaeedDocument100 pagesFermentation Biotechnology by Salman SaeedSalman SaeedNo ratings yet
- Biochem, Chapter 1 SlideDocument8 pagesBiochem, Chapter 1 SlideGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- CHE323-Biochemical Engineering 1 - PresentationDocument119 pagesCHE323-Biochemical Engineering 1 - PresentationPreciousNo ratings yet
- Génie Biochimique Et Enzymatique 2010-2011 MDocument37 pagesGénie Biochimique Et Enzymatique 2010-2011 Mbruno bietekeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1eire_dankeNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Engineering (BT 508) : Credits-4 Units - 6 Total Marks - 150Document26 pagesBioprocess Engineering (BT 508) : Credits-4 Units - 6 Total Marks - 150Savita100% (1)
- Biofuel and Plant Tissue CultureDocument6 pagesBiofuel and Plant Tissue CultureRUSHIKESH SINDKHEDKARNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bioprocessing and PharmabiotechDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Bioprocessing and PharmabiotechPeyman SazandehchiNo ratings yet
- Industrial MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesIndustrial MicrobiologyNoor Ul Naeem100% (1)
- Enzyme Biotech.Document42 pagesEnzyme Biotech.Samarth TalatiNo ratings yet
- CHE323-Biochemical Engineering 1 - PresentationDocument30 pagesCHE323-Biochemical Engineering 1 - PresentationPreciousNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and IndustryDocument7 pagesBiotechnology and IndustryDionne Carel Paliwanan-RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Yellow Blue Colorful Illustrated Education Presentation 169Document14 pagesYellow Blue Colorful Illustrated Education Presentation 169Mike Clinton BilogNo ratings yet
- White Biotechnology Final PDFDocument4 pagesWhite Biotechnology Final PDFMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manfaat Dan Aplikasi Bio IndustriDocument24 pagesManfaat Dan Aplikasi Bio IndustriAlexizz AizenNo ratings yet
- TK 4009 Bioproses Industrial 3 Maret 2015Document30 pagesTK 4009 Bioproses Industrial 3 Maret 2015Ryan Fitrian Sofwan FauzanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Biotechnology (231257)Document8 pagesIndustrial Biotechnology (231257)hitu0972No ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Industrial MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 12: Industrial MicrobiologyMayucious MayuNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor Types (Industrial Notes)Document23 pagesBioreactor Types (Industrial Notes)anjaliNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4Document24 pagesUnit - 4Shivam GNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Technology 2022Document47 pagesBioprocess Technology 2022Sowjanya NekuriNo ratings yet
- 1243 - Industrial Micro OverviewDocument18 pages1243 - Industrial Micro OverviewGounder KirthikaNo ratings yet
- Biotech Note - MODULE 3Document11 pagesBiotech Note - MODULE 3ainomugisha arnoldNo ratings yet
- Bioreactors LatestDocument34 pagesBioreactors LatestSyeda KazmiNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess TechnologyDocument33 pagesBioprocess TechnologyAMALAY RAFFLI ARNOLDYNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Processes (Section 2) : What Is Biochemical Process?Document8 pagesBiochemical Processes (Section 2) : What Is Biochemical Process?Ren H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument26 pagesBiotechnologyJ. DiroshikaNo ratings yet
- Week 9Document15 pagesWeek 9Fernanda QuelNo ratings yet
- Industrial MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesIndustrial MicrobiologyRajini hc100% (2)
- Environmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenEarfanNo ratings yet
- Study On The Quality of Compressed Baker's Yeast in Hasahissa Factory A ... (Pdfdrive)Document144 pagesStudy On The Quality of Compressed Baker's Yeast in Hasahissa Factory A ... (Pdfdrive)Florin MureseanuNo ratings yet
- LUBKEN - 2015 - Parameter Estimation and Long-Term Process Simulation of A BiogasDocument9 pagesLUBKEN - 2015 - Parameter Estimation and Long-Term Process Simulation of A BiogasThobiasNo ratings yet
- 3 Glikolisis 9Document17 pages3 Glikolisis 9Rafi Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Senior 12 Biology 1 Q2 - M7Document18 pagesSenior 12 Biology 1 Q2 - M7Grandpa ZhongliNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument24 pagesBiology Projectprince gupta50% (2)
- Anaerobic Thermophilic Fermentation For Acetic Acid Production From Milk PermeateDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Thermophilic Fermentation For Acetic Acid Production From Milk PermeateViet_Len_Troi_XanhNo ratings yet
- Wine - MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesWine - MicrobiologyVirendra JoshiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Chapter 2 RRLDocument37 pagesLesson 4 Chapter 2 RRLPallas AthenaNo ratings yet
- Production of Pyruvate and AcetaldehdeDocument6 pagesProduction of Pyruvate and AcetaldehdeVictor Nyarugwe67% (3)
- Chapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesChapter 2: Physical and Chemical ChangesNaqvi play'sNo ratings yet
- A Squash Players Training Handbook FINALDocument176 pagesA Squash Players Training Handbook FINALbarbumihai50% (2)
- Fermented in AfricaDocument26 pagesFermented in AfricaPaul Tetteh AsareNo ratings yet
- All IBD ArticlesDocument110 pagesAll IBD ArticlesJavier Salas100% (5)
- Beer Spoilage Bacteria and Hop Resistance PDFDocument20 pagesBeer Spoilage Bacteria and Hop Resistance PDFkelamahimNo ratings yet
- Biorefineries - Industrial Processes and Products PDFDocument948 pagesBiorefineries - Industrial Processes and Products PDFSachikanta Pradhan100% (1)
- 22 CH106 Metabolic Paths For Carbohydrates Timberlake 2ndDocument70 pages22 CH106 Metabolic Paths For Carbohydrates Timberlake 2ndEnrique LiKeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Wine Prepared From Sugarcane and Watermelon JuiceDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Wine Prepared From Sugarcane and Watermelon Juiceayam Victor SinghNo ratings yet
- Scritp Gen BioDocument5 pagesScritp Gen BioHannah Gwyneth NovicioNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration: General BiologyDocument12 pagesAerobic Respiration: General BiologyV KimNo ratings yet
- 2023genomic Sequencing in Colombian Coffee Fermentation Reveals New Records of Yeast SpeciesDocument10 pages2023genomic Sequencing in Colombian Coffee Fermentation Reveals New Records of Yeast SpeciesAngels ValenciaNo ratings yet
- SterelizationDocument16 pagesSterelizationtarannumNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Bioresource TechnologyDocument50 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Bioresource TechnologyJosué Rafael García RamónNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationmaria genio100% (2)
- 7 Microbial Bio ProductsDocument29 pages7 Microbial Bio Productsdetras de ti imbecilNo ratings yet
- EB3225 Chapter 1 - Overview of Industrial MicrobiologyDocument43 pagesEB3225 Chapter 1 - Overview of Industrial MicrobiologyPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNo ratings yet
- Concoctions and FertilizersDocument99 pagesConcoctions and Fertilizersjames lacanilao100% (1)
- Bio-Butanol Separation by AdsorptionDocument12 pagesBio-Butanol Separation by AdsorptionDiah MuslimawatiNo ratings yet
- Biomanufacturing History and PerspectiveDocument12 pagesBiomanufacturing History and PerspectiveYedhaGuerrero100% (1)
- Pns-Bfad 20-2009Document21 pagesPns-Bfad 20-2009dekth LibunaoNo ratings yet
- MCB 407 Lecture OneDocument4 pagesMCB 407 Lecture OnePopoola OlakunleNo ratings yet