Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SC3a.4 Structure of An Atom - Extend - Worksheet
Uploaded by
arnavpatel138Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SC3a.4 Structure of An Atom - Extend - Worksheet
Uploaded by
arnavpatel138Copyright:
Available Formats
Structure of an atom
SC3a.4 Extend
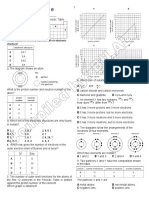
1 a Draw a diagram of the structure of an atom with 2 protons, 2 neutrons and 2 electrons.
Clearly label the nucleus and the electrons on your diagram.
b Why is this atom neutral?
c How was Dalton’s atomic model different from this model of an atom?
E1 Name each particle (a, b and c) on the diagram below. Explain your answer.
2 An experiment was carried out to investigate the properties of the three main subatomic particles –
protons, neutrons and electrons.
A beam of all three of these particles, all with the same energy (or speed), was passed through an electric
field produced by a pair of parallel steel plates – one positively charged and one negatively charged.
What happens to the beams as they pass through the electric field depends on their relative masses and
relative charges.
a Beam (c) is a beam of protons. Why is it deflected downwards when it passes through this electric
field?
b Identify the other two beams of particles and explain your choice in each case.
c Explain why the deflection of beam (a) in the electric field is much bigger than the deflection of
beam (c).
d Suppose that a beam of nuclei, each containing 2 protons and 2 neutrons, was passed through the
same electric field. In which direction would the beam be deflected?
e How would the deflection compare with that for the other particles?
3 Three atoms, A, B and C, contain the following subatomic particles.
Atom Neutrons Protons Electrons
A 18 17 17
B 18 16 16
C 16 17 17
Which two atoms are atoms of the same element? Explain your choice.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2016. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
4
You might also like
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument59 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test Bankkevinbeltranbztxrjdfsy100% (15)
- 9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFDocument11 pages9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFSeenu SNo ratings yet
- Atomic PropertiesDocument70 pagesAtomic PropertiesTichafara Paul ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Activities On Unit 2Document3 pagesActivities On Unit 2Switch JavidownNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - 1Document5 pagesAtomic Structure - 1Rosery BlevinNo ratings yet
- Chem12 C0402 SWBSDocument4 pagesChem12 C0402 SWBSWildboy 2008No ratings yet
- Which Statement About An Atom Is True?: 1 Compiled by S Z Bangash Saint Mary' Academy Lalazar RWPDocument13 pagesWhich Statement About An Atom Is True?: 1 Compiled by S Z Bangash Saint Mary' Academy Lalazar RWPHamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atomic Structure Notes Class 9 BDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Atomic Structure Notes Class 9 Bगोविंद माहेश्वरीNo ratings yet
- L2-Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesL2-Atomic StructureArbeiboy VarquezNo ratings yet
- And Lue ISBN Test BankDocument59 pagesAnd Lue ISBN Test Bankrobert100% (21)
- Reviewer in Science 1Document2 pagesReviewer in Science 1kim natividadNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure Worksheetswcaptain2008No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesAtomic StructureKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Explanation Notes 1.1 Tomic TR CT Re: Relative Charge and Relative Masses of These ParticlesDocument2 pagesExplanation Notes 1.1 Tomic TR CT Re: Relative Charge and Relative Masses of These ParticlesMaNosh KuMarNo ratings yet
- Book H.W CH 1Document21 pagesBook H.W CH 1Raiyad RezaNo ratings yet
- Test Topic 2Document4 pagesTest Topic 2Ashutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp ch4 3Document7 pages9 Science Imp ch4 3deepakNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Duy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- SCI9VIC Chapter 5 Differentiated Worksheets Consolidate QuestionsDocument33 pagesSCI9VIC Chapter 5 Differentiated Worksheets Consolidate Questionsloopedsauce22No ratings yet
- Section 2 Atomic Structure - EditedDocument83 pagesSection 2 Atomic Structure - EditedcpliamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Review Question For Grade 9 Unit 3Document5 pagesChemistry Review Question For Grade 9 Unit 3mtadesse158No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology How Life Works Second EditionDocument58 pagesTest Bank For Biology How Life Works Second Editionwilliamsamvucyn6No ratings yet
- G9 - NCERT - Structure of The Atom PDFDocument14 pagesG9 - NCERT - Structure of The Atom PDFSai AravapalliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding MenuDocument85 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding MenuSheryl Kalalo TumamacNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Earning UtcomesDocument25 pagesAtomic Structure: Earning Utcomessabrina_sarranNo ratings yet
- Atomicstructure 151006082251 Lva1 App6891Document45 pagesAtomicstructure 151006082251 Lva1 App6891Stephanie TeddNo ratings yet
- Atom ThryDocument6 pagesAtom ThrySumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Week22 G9 Chapter5.1-5.3Document5 pagesWeek22 G9 Chapter5.1-5.3kwokrenee827No ratings yet
- Atomic Models - TheoryDocument109 pagesAtomic Models - TheoryDr-Walid FemtosecondNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureDocument14 pages2.2. Electrons, Bonding and StructureAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- SME Chemistry Topic 2 NotesDocument32 pagesSME Chemistry Topic 2 NotesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondsDocument6 pagesCovalent BondsimunasingheNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TutorialDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure Tutorialchong56No ratings yet
- General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Denniston Test Bank PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Denniston Test Bank PDFa136596500No ratings yet
- Chem G10 First Term Exam20182019111Document12 pagesChem G10 First Term Exam20182019111Mona Against DampersNo ratings yet
- SLHL Atomic Structure ExamDocument4 pagesSLHL Atomic Structure ExamGlupiaSprawaNo ratings yet
- MS Paper 1A and BDocument10 pagesMS Paper 1A and Bamankothari2007No ratings yet
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument58 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test Bankamandablevinsqakymroeiw100% (52)
- (BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFDocument8 pages(BEST) Chem 16 LE1 Samplex + Answers PDFChris Andrew Mendoza100% (1)
- CHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Document10 pagesCHEM CLASS 9 NCERT Structure of The Atom Neha V1.3Gaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure StartDocument120 pagesAtomic Structure StartCedrick AltaresNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Solved QuestionsDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Solved QuestionsItu DeyNo ratings yet
- STD 8 Chapter 5Document6 pagesSTD 8 Chapter 5ROHIT KADAMNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument31 pagesAtomic StructureAnirbanNo ratings yet
- Bolleballi Naganivrithi (Greendaless) - 1ENA - Chapter 8 Atoms & Molecules (Notes)Document25 pagesBolleballi Naganivrithi (Greendaless) - 1ENA - Chapter 8 Atoms & Molecules (Notes)B.NiviNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS - Review The AtomDocument5 pagesANSWERS - Review The AtomDayana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam ScienceDocument8 pagesSecond Quarter Exam ScienceJovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument21 pagesAtomic Structurepoorv1235570No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Practice Sheet-1Document4 pagesAtomic Structure Practice Sheet-1bilalNo ratings yet
- Atom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineDocument10 pagesAtom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineGan Ee HengNo ratings yet
- Science 9 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesScience 9 2nd QuarterJocelyn Acog Bisas Mestizo100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Module 1 Lesson 3Document7 pagesQuarter 1 Module 1 Lesson 3Myka Ella VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetDeniz ParaNo ratings yet
- Main Postulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument24 pagesMain Postulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Slo Review Standard 3Document1 pageSlo Review Standard 3api-305204604No ratings yet
- All Chem RevisionDocument467 pagesAll Chem RevisionDoughy MargheritaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 2022Document7 pagesAtomic Structure 2022Evandra Ramadhan Azriel SanyotoNo ratings yet
- PQT Chapter 2 - Atomic Structure - Part 1Document12 pagesPQT Chapter 2 - Atomic Structure - Part 1Vũ Nguyễn QuangNo ratings yet