Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gaseous Exchange
Gaseous Exchange
Uploaded by
VernonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gaseous Exchange
Gaseous Exchange
Uploaded by
VernonCopyright:
Available Formats
2. GASEOUS EXCHANGE- REVISION QUESTIONS.
Page 1 of 4
1. Define gaseous exchange. (1mk) b) Why was boiling tube A covered with aluminium foil?
2. Explain the significance of gaseous exchange. (2mks) (1mk)
3. Name two sites/structures used for gaseous exchange in c) Account for the observation made in boiling tube A and B.
higher plants. (2mks) (4mks)
4. Name two structures for gaseous exchange in aquatic 18. Giving a reason, name the gaseous exchange surface in
plants. (2mks) amoeba. (2mks)
5. Explain two ways in which the leaf is adapted for gaseous 19. Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in amoeba.
exchange. (2mks) (4mks)
6. Explain two ways in which floating leaves of aquatic plants 20. Explain why amoeba lacks elaborate gaseous exchange
are adapted to gaseous exchange. (2mks) system. (1mk)
7. How is the aerenchyma tissue adapted to its function? 21. a) Describe the adaptations of respiratory surfaces in
(2mks) animals. (10mks)
8. Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in the b) Explain why an adult grasshopper will not drown/ die
aerenchyma tissue. (4mks) when the head is immersed in water. (2mks)
9. Explain how the lenticels are adapted to their function? 22. Name the structure used for gaseous exchange in:
(2mks) a) Mosquito larvae. (1mk)
10. Explain the mechanism of gaseous exchange through the b) Mosquito pupae. (1mk)
lenticels. (4mks) c) Mayfly nymph. (1mk)
11. What are pneumatophores/ (1mk) d) Adult grasshopper. (1mk)
12. Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange through the 23. Describe the path taken by carbon (IV) oxide released from
pneumatophores. (4mks) the tissue of an insect to the atmosphere. (3mks)
13. What is the function of guard cells? (1mk) 24. The diagram below shows the gaseous exchange system of a
14. Explain the structural adaptations of guard cells to their locust.
function. (4mks)
15. Describe the mechanisms of opening and closing stomata.
(20mks)
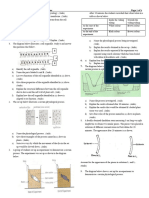
16. A group of students placed a fresh leaf in warm water. They
observed that air bubbles formed on the surface of the leaf.
a) What biological process were they investigating? P
b) Name the structures from which the air bubbles were
coming from. (1mk)
c) Explain the distribution of the structures named in (b)
above on the leaf surfaces of: a) Name the structure labeled P, Q, R and S. (4mks)
i) Aquatic plant. (2mks) b) How are the parts labeled P, Q, R and S adapted to their
ii) Land plant. (2mks) functions? (8mks)
iii) Xerophyte/ plant found on arid/ semi-arid areas. c) Describe the mechanism of gaseous exchange in structure
(2mks) labeled S. (4mks)
17. The form two students set up an experiment as shown 25. A rare disease was found to attack the respiratory system of
below. insects. Giving a reason, name the parts of the insect that
are likely to be affected by the disease. (2mks)
26. Name the respiratory surfaces in a frog. (3mks)
27. Explain the mechanism of gaseous exchange in a frog
through:
a) Mouth/ Buccal cavity. (4mks)
b) Skin. (4mks)
c) Alveolus. (4mks)
28. Describe the mechanism of breathing through the lungs in a
frog. (10mks)
29. Name the gaseous exchange surface in bony fish. (1mk)
a) State the aim of the set up. (1mk)
2. GASEOUS EXCHANGE- REVISION QUESTIONS. Page 2 of 4
30. The diagram below illustrates an organ used for gaseous 36. The diagram below represents part of gaseous exchange
exchange in bony fish. system in human
M P
a) Name the organ illustrated above. (1mk)
b) Name the parts labeled M, N and L. (3mks)
c) Explain how the parts labeled M, N and L are adapted K
to their function. (10mks)
d) Describe how oxygen dissolved in water reaches the a) Name the part labeled P, F, G, H, K and J. (6mks)
blood in capillary found in part L. (5mks)
b) State the function of epiglottis. (1mk)
31. Explain why the floor of the mouth is lowered during
c) How is the part labeled P adapted to its function? (3mks)
inhalation in a bony fish. (2mks)
d) State the function of the parts labeled G, H, J and K.
32. Explain why fish dies shortly after removal from water.
(4mks)
(3mks)
e) Give the function of pleural fluid. (1mk)
33. The diagram below illustrates flow of water and blood in
f) Name the process by which inhaled air moves from the
the gill filament.
structure labeled K into blood capillaries. (1mk)
37. The photograph below shows the inner surface of the upper
Direction of flow of blood
left side of the rib cage.
34.
Direction of flow of blood
a) What name is given to the flow illustrated above?
(1mk)
b) Explain the significance of the type of flow named in a) a) Name the bone covered by the fatty tissue labeled K. (1mk)
above. (2mks) b) Explain the role of the part labeled M in inhalation. (5mks)
35. The photograph below illustrates a procedure carried out 38. The diagram below represents a model used to
to study gaseous exchange in a certain animal. demonstrate breathing in mammals.
a) Identify two dissecting tools being used in the procedure
illustrated. (2mks)
b) Name the part of the organism labeled H and state its
a) Name the mammalian structure represented by the parts
function. (2mks) labeled:
c) i) Draw a well labeled gaseous exchange structure under i) D. (1mk)
study. (3mks) ii) F. (1mk)
ii) How is the part labeled in c) i) adapted to efficient iii) E. (1mk)
gaseous exchange? (3mks) iv) Balloon. (1mk)
2. GASEOUS EXCHANGE- REVISION QUESTIONS. Page 3 of 4
b) State the observation made when the string is pulled a) Name the parts labeled W, Y and Z. (3mks)
downwards. (1mk) b) How does the part labeled Z facilitates breathing in?
c) Explain the observation made in b) above. (2mks) (3mkss)
39. The diagram below illustrates a blood capillary surrounding
46. Explain two differences in mechanism of gaseous exchange
a structure for gaseous exchange in human beings.
between insects and mammals. (2mks)
47. Explain what happens when:
a) Diaphragm muscles contract. (3mks)
b) Diaphragm muscles relax. (3mks)
48. a) Explain how too much dust particles may affect the
respiratory system. (2mks)
b) Explain why allergies cause difficulty in breathing.
(2mks)
49. Name four diseases of the respiratory system. (4mks)
50. Name the causal agents of the following diseases:
a) Tuberculosis. (1mk)
b) Whooping cough. (1mk)
c) Pneumonia. (1mk)
51. A student divided a small airtight box into two chambers
with a wire mesh. In one chamber he kept a number of rats
a) Name the gaseous exchange structure. (1mk) and in the other a number of potted plants. What was likely
b) Identify the gases labeled Y and Z. (2mks) to happen if the box was placed in the dark for two hours?
c) How do the gases labeled Y and Z reach inside the blood Explain. (2mks)
capillary? (5mks) 52. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) is a disease
d) How does smoking cigarette lead to lung cancer? (2mks) transmitted through air and in china spread and killed
40. Describe the mechanism of breathing in mammals. (10mks) people in Europe.
41. State the difference in content of oxygen and carbon (IV) a) Name the parts of the body that are likely to be
Oxide in the air that enters and leaves the human lungs. infected. (3mks)
(2mks) b) State three ways of preventing the spread of the disease
42. Explain why it is advantageous to breathe through the from one person to another? (3mks)
nostrils. (2mks) 53. The form two students set up an experiment as shown
43. a) Name the part of brain which controls breathing. (1mk) below.
b) Explain four factors that control breathing in humans.
(4mks)
44. The diagram below shows gaseous exchange in tissues.
a) Name the gas that diffuses:
i) To the body cells (1mk)
ii) From the body cells (1mk)
b) Which compound dissociates to release the gas named in (a) a) What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
(i) above? (1mk)
45. The diagram below represents a part of the rib cage. b) Account for the observation made in test tubes A and B.
(4mks)
c) Explain why:
i) Clip A was closed during breathing out.
(1mk)
ii) Clip B was closed during breathing in.
(1mk)
2. GASEOUS EXCHANGE- REVISION QUESTIONS. Page 4 of 4
54. Below is a graphical representation of how basal metabolic 61. The table below shows the volume of gases contained in
rates compare in various animals. 100cm3 of a blood sample tapped at two points in the
mammalian circulatory system.
Gas Blood entering the Blood leaving lungs
lungs (cm3) (cm3)
Oxygen 8.65 20.25
Nitrogen 0.75 0.75
Carbon (IV) oxide 55.60 31.65
a) Account for the difference in gaseous composition of:
i) Blood entering the lungs. (2mks)
ii) blood leaving the lungs. (2mks)
b) Explain why most athletes prefer training from high
From the graph, explain why the mouse has a higher breathing altitude areas. (3mks)
rate than elephant. (3mks) 62. Explain how the presence of guard cells affect the opening
of stomata. (5mks)
55. a) Name the respiratory structure in the amoeba. (1mk)
b) Give a reason for your answer in a) above. (1mk)
56. Below is a photograph of Brassica oleracea, Sukuma wiki leaf.
a) Using observable features only explain how the leaf is
adapted the leaf to gaseous exchange. (2mks)
b) Explain the relationship between photosynthesis and
aerobic respiration within a leaf. (2mks)
57. State the role of each of the following in the mammalian
respiratory system:
a) Mucus. (2mks)
b) Cartilage rings. (1mk)
c) Epiglottis. (1mk)
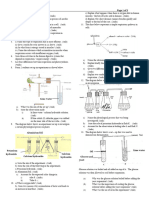
58. In an investigation, students set up the apparatus below in
the laboratory and made observations after 72 hours.
a) Explain how inclusion of the following components
would affect the mouse in the experiment:
i) Light. (2mks)
ii) Sodium hydroxide solution. (2mks)
b) State why the students preferred to use a bell jar and
not a tin box in the experiment. (1mk)
59. Describe how the gaseous exchange structures in plants are
adapted to their function. (20mks)
60. State the importance of a well-developed blood capillary
network in the alveoli. (1mk)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ergodic Theory Nonsingular TransformationsDocument61 pagesErgodic Theory Nonsingular TransformationsVernonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spacetime and Algebraic Quantum TheoryDocument49 pagesQuantum Spacetime and Algebraic Quantum TheoryVernonNo ratings yet
- Statutes Fields MedalDocument2 pagesStatutes Fields MedalVernonNo ratings yet
- Theano DocumentationDocument644 pagesTheano DocumentationVernonNo ratings yet
- Defects and Quantum Seiberg Witten GeometryDocument79 pagesDefects and Quantum Seiberg Witten GeometryVernonNo ratings yet
- PyperDocument19 pagesPyperVernonNo ratings yet
- Calibrated Brane Solutions of M TheoryDocument153 pagesCalibrated Brane Solutions of M TheoryVernonNo ratings yet
- PynputDocument30 pagesPynputVernonNo ratings yet
- PyrplDocument91 pagesPyrplVernonNo ratings yet
- Pylint DocsDocument183 pagesPylint DocsVernonNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Spin SystemsDocument55 pagesDynamical Spin SystemsVernonNo ratings yet
- Galaxy Mass Models MOND Versus Dark MatterDocument16 pagesGalaxy Mass Models MOND Versus Dark MatterVernonNo ratings yet
- Perturbative Superstring Theory RevisitedDocument304 pagesPerturbative Superstring Theory RevisitedVernonNo ratings yet
- Hodge Theory On Metric SpacesDocument50 pagesHodge Theory On Metric SpacesVernonNo ratings yet
- Complexified Dynamical SystemsDocument13 pagesComplexified Dynamical SystemsVernonNo ratings yet
- Entropic Gravity Derivation of MondDocument6 pagesEntropic Gravity Derivation of MondVernonNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ModellingDocument44 pagesMathematical ModellingVernonNo ratings yet
- Real Hamiltonian Forms of Hamiltonian SystemsDocument15 pagesReal Hamiltonian Forms of Hamiltonian SystemsVernonNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Hamiltonian SystemsDocument52 pagesGeometry of Hamiltonian SystemsVernonNo ratings yet
- C.R.E Form 2 - Question PaperDocument7 pagesC.R.E Form 2 - Question PaperVernonNo ratings yet
- Biology Form Two - Question PaperDocument12 pagesBiology Form Two - Question PaperVernonNo ratings yet
- Finite W Algebras For GLN 2018 Advances in MathematicsDocument52 pagesFinite W Algebras For GLN 2018 Advances in MathematicsVernonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 - Question PaperDocument10 pagesChemistry Paper 2 - Question PaperVernonNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper 2Document18 pagesMathematics Paper 2VernonNo ratings yet
- CRE Form 2 - Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesCRE Form 2 - Marking SchemeVernonNo ratings yet
- Business - Marking SchemeDocument10 pagesBusiness - Marking SchemeVernonNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument4 pagesCell PhysiologyVernon100% (1)
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationVernonNo ratings yet
- CRE Form 2 - Question PaperDocument9 pagesCRE Form 2 - Question PaperVernonNo ratings yet
- Geo p1Document4 pagesGeo p1VernonNo ratings yet