0% found this document useful (0 votes)
431 views15 pagesRisk-Based Maintenance Overview
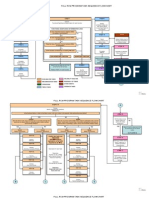
Risk-based maintenance (RBM) is a strategy that focuses on managing maintenance based on assessing risks and their potential impacts. It uses tools like a risk matrix and failure mode and effects criticality analysis (FMECA) to determine critical equipment, potential failures, and appropriate preventive maintenance strategies. This provides a customized maintenance plan for each machine based on its usage and importance. The benefits include improved overall equipment effectiveness, a known maintenance budget, and continuous optimization of the maintenance program over time.
Uploaded by
gizaikoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
431 views15 pagesRisk-Based Maintenance Overview
Risk-based maintenance (RBM) is a strategy that focuses on managing maintenance based on assessing risks and their potential impacts. It uses tools like a risk matrix and failure mode and effects criticality analysis (FMECA) to determine critical equipment, potential failures, and appropriate preventive maintenance strategies. This provides a customized maintenance plan for each machine based on its usage and importance. The benefits include improved overall equipment effectiveness, a known maintenance budget, and continuous optimization of the maintenance program over time.
Uploaded by
gizaikoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- What is Risk-Based Maintenance?
- What is the advantage of applying RBM?
- Complete maintenance strategy
- Example case
- Conclusion
- How can we help you?