Professional Documents
Culture Documents
## The Universe Unveiled - Space, Its Limits, and Formation
Uploaded by
yashusaumil13Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
## The Universe Unveiled - Space, Its Limits, and Formation
Uploaded by
yashusaumil13Copyright:
Available Formats
## The Universe Unveiled: Space, Its Limits, and Formation
The concept of space has captivated humanity since the dawn of civilization. From gazing at
the stars to launching probes into the unknown, our quest to understand the vastness and
potential of space continues to this day. This document delves into the nature of space, its
theoretical limits, and the prevailing theories about its formation.
**Defining Space:**
Space, in its simplest form, can be defined as the three-dimensional expanse in which
everything exists. It provides the stage for the grand cosmic drama, from subatomic particles
to galaxies spanning billions of light-years. However, space is more than just an empty void.
It's interwoven with the concept of time, forming the fabric of what we call spacetime. This
intricate relationship dictates the laws of physics and shapes the evolution of the universe.
**Limits of Space:**
The question of whether space has limits is a complex one. There are two main
interpretations:
1. **Observable Universe:** This refers to the portion of the universe we can potentially see
or influence. Limited by the speed of light, our observations are restricted to a sphere with a
radius of roughly 46.5 billion light-years. Beyond this lies the unknowable, forever out of
reach.
2. **Total Universe:** This encompasses the entirety of space, regardless of our ability to
observe it. Current cosmological models suggest an infinitely expanding universe, meaning
there could be regions infinitely far away, forever beyond our grasp.
However, the concept of infinity in physics is still under debate, and alternative models
propose a finite but unimaginably vast universe.
**Formation of Space:**
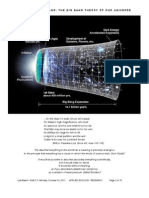
Our understanding of the universe's origins remains an active area of research. The
prevailing theory is the Big Bang model, which suggests that the universe began
approximately 13.8 billion years ago from an incredibly hot, dense state. Through a process
of inflation, space itself rapidly expanded, setting the stage for the formation of matter and
energy.
Within the Big Bang framework, several hypotheses attempt to explain the initial singularity
and the mechanisms of inflation. Some prominent theories include:
* **Quantum Fluctuations:** Random fluctuations in the quantum vacuum could have
triggered the initial expansion.
* **String Theory:** This theory proposes that fundamental particles are tiny, vibrating
strings, and the Big Bang could be a transition between different string vacua.
It's important to note that these theories are still under development and lack definitive proof.
Future observations and advancements in physics might reveal different or entirely new
explanations for the formation of space.
**The Human Perspective:**
Understanding space broadens our perspective on our place in the universe. It forces us to
confront our inherent limitations and challenges our understanding of reality. Studying space
not only satisfies our curiosity but also holds the potential for technological advancements
and resource discovery. As we continue to explore, the mysteries of space will undoubtedly
push the boundaries of human knowledge and inspire generations to come.
**Further Exploration:**
This document provides a brief overview of a vast and complex topic. For further exploration,
consider delving into the following resources:
* **Books:** "A Brief History of Time" by Stephen Hawking, "Cosmos" by Carl Sagan
* **Websites:** NASA (.gov), Space.com, National Geographic
* **Documentaries:** "Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey" by Neil deGrasse Tyson, "The Fabric
of the Cosmos" by Brian Greene
Remember, the journey to understand space is ongoing, and exciting discoveries await
those who dare to explore!
You might also like
- From the Beginning of Space and Time: Modern Science and the Mystic UniverseFrom EverandFrom the Beginning of Space and Time: Modern Science and the Mystic UniverseNo ratings yet
- The Moment of Creation: Big Bang Physics from Before the First Millisecond to the Present UniverseFrom EverandThe Moment of Creation: Big Bang Physics from Before the First Millisecond to the Present UniverseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Astronomy: Cosmology, Photometry, and Spectroscopy Explained (3 in 1)From EverandAstronomy: Cosmology, Photometry, and Spectroscopy Explained (3 in 1)No ratings yet
- The Unknown Universe: A New Exploration of Time, Space, and Modern CosmologyFrom EverandThe Unknown Universe: A New Exploration of Time, Space, and Modern CosmologyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Whole Shebang: The Big Bang Theory of The UniverseDocument10 pagesThe Whole Shebang: The Big Bang Theory of The UniverselbrechtNo ratings yet
- Constructive Interference: Developing the brain's telepathic potentialFrom EverandConstructive Interference: Developing the brain's telepathic potentialNo ratings yet
- Summary of A Brief History of Time: by Stephen Hawking | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of A Brief History of Time: by Stephen Hawking | Includes AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics for People In A Hurry - Summarized for Busy People: Based on the Book by Neil deGrasse TysonFrom EverandAstrophysics for People In A Hurry - Summarized for Busy People: Based on the Book by Neil deGrasse TysonNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesWeek 1 Day 1 Module Physical ScienceEunice Acuna100% (1)
- The Cosmic Microwave Background: How It Changed Our Understanding of the UniverseFrom EverandThe Cosmic Microwave Background: How It Changed Our Understanding of the UniverseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- After the Big Bang Could Come the Big Crunch: Primordial Black Holes and the Big CrunchFrom EverandAfter the Big Bang Could Come the Big Crunch: Primordial Black Holes and the Big CrunchNo ratings yet
- How Big Is The Universe? Astronomy Book for 6 Year Olds | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandHow Big Is The Universe? Astronomy Book for 6 Year Olds | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet
- The Universe: Leading Scientists Explore the Origin, Mysteries, and Future of the CosmosFrom EverandThe Universe: Leading Scientists Explore the Origin, Mysteries, and Future of the CosmosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- OrigenuniversoagunegroDocument3 pagesOrigenuniversoagunegroNicole Muñoz VerdeNo ratings yet
- Steady State TheoryDocument7 pagesSteady State TheoryLenz BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Beginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseFrom EverandThe Beginning and the End of Everything: From the Big Bang to the End of the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- A Joosr Guide to... A Brief History of Time by Stephen Hawking: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Joosr Guide to... A Brief History of Time by Stephen Hawking: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSEDocument2 pagesUNIVERSEikkinenganioNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chris Ferrie & Geraint F. Lewis's Where Did the Universe Come From? And Other Cosmic QuestionsFrom EverandSummary of Chris Ferrie & Geraint F. Lewis's Where Did the Universe Come From? And Other Cosmic QuestionsNo ratings yet
- Sto-ology: A Metaphysical Exploration of the Human ConditionFrom EverandSto-ology: A Metaphysical Exploration of the Human ConditionNo ratings yet
- Debunking Dark Energy: A New Model for the Structure of the UniverseFrom EverandDebunking Dark Energy: A New Model for the Structure of the UniverseNo ratings yet
- Summary of Astrophysics for People in a Hurry by Neil deGrasse TysonFrom EverandSummary of Astrophysics for People in a Hurry by Neil deGrasse TysonNo ratings yet
- A Degree in a Book: Cosmology: Everything You Need to Know to Master the Subject - in One Book!From EverandA Degree in a Book: Cosmology: Everything You Need to Know to Master the Subject - in One Book!No ratings yet
- What Is The Big Bang TheoryDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Big Bang Theorystealth solutionsNo ratings yet
- Creativity and Modern TheoriesDocument3 pagesCreativity and Modern Theoriesroxana149No ratings yet
- Comparing Steady State Theory and Inflation TheoryDocument4 pagesComparing Steady State Theory and Inflation TheoryAnime AddictNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang TheoryDocument13 pagesThe Big Bang TheoryHilary YvonneNo ratings yet
- Gravity ManipulationDocument3 pagesGravity ManipulationSunčica NisamNo ratings yet
- Science Islam and CosmologyDocument69 pagesScience Islam and CosmologyArafat FaniNo ratings yet
- Exam PaperDocument4 pagesExam PaperSaad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- 6th Imam and BIG BANGDocument1 page6th Imam and BIG BANGSyed Haidar Ali ZaidiNo ratings yet
- JULIANDA - STS Michael Francis Ian G. Vega LL, PHDDocument2 pagesJULIANDA - STS Michael Francis Ian G. Vega LL, PHDMicah Joy JuliandaNo ratings yet
- Isolated DSPH Galaxy Kks3 in The Local Hubble Flow: I.D. Karachentsev, A.Yu. Kniazev, and M.E. SharinaDocument12 pagesIsolated DSPH Galaxy Kks3 in The Local Hubble Flow: I.D. Karachentsev, A.Yu. Kniazev, and M.E. SharinaNguyên TuânNo ratings yet
- Neil Barnaby - Cosmological InstabilitiesDocument332 pagesNeil Barnaby - Cosmological InstabilitiesTurmav12345No ratings yet
- Clinton High School 2 Ve JD: NYSSO Regional Student Answer Sheet C2021Document4 pagesClinton High School 2 Ve JD: NYSSO Regional Student Answer Sheet C2021JohnNo ratings yet
- Kerr Metric Ellipsoid Coordinate Transformation RevisedDocument15 pagesKerr Metric Ellipsoid Coordinate Transformation RevisedRefugio Rigel Mora LunaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Galaxies in SpaceDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Galaxies in SpaceSusilo Edy Purnomo100% (1)
- TheoryDocument2 pagesTheoryAngelyne PotencianoNo ratings yet
- Universe EssayDocument3 pagesUniverse EssayAndrijana J.No ratings yet
- Arrows of Time and The Beginning of The UniverseDocument24 pagesArrows of Time and The Beginning of The UniverseJulian BermudezNo ratings yet
- Expanding UniverseDocument35 pagesExpanding UniverseBarbie GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Physics 100 Chapt 5Document32 pagesPhysics 100 Chapt 5Kuludip Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ ĐỀ XUẤT 11Document31 pagesĐỀ ĐỀ XUẤT 11abc abc100% (1)
- Wormholes, Warp Drives and Energy Conditions by Francisco S. N. LoboDocument306 pagesWormholes, Warp Drives and Energy Conditions by Francisco S. N. LoboMiguel Santos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Tut3 OLET1640 Student NotesDocument4 pagesTut3 OLET1640 Student Notesdesheng wangNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Module 1 EditedDocument15 pagesEarth Science Module 1 EditedSangcad Ambolo Jr.No ratings yet
- The Warp Drive and AntigravityDocument6 pagesThe Warp Drive and AntigravityPeter Morris-HindNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics For PhysicistsDocument17 pagesAstrophysics For PhysicistsRoman AsukaNo ratings yet
- A Fundamental Relation Between Mass, SFRDocument1 pageA Fundamental Relation Between Mass, SFRScrobblerNo ratings yet
- Allah Known Through Reason BurmeseDocument184 pagesAllah Known Through Reason Burmeseမ်ိဳးမင္းသက္100% (2)
- Formation of The Universe Student SheetDocument2 pagesFormation of The Universe Student SheetDubu Dubu DahyunieeNo ratings yet
- A Model of The Expanding Universe - Group 4-ICT 2Document1 pageA Model of The Expanding Universe - Group 4-ICT 2Zyrah Mae M. DotolloNo ratings yet
- Black Hole Research PaperDocument4 pagesBlack Hole Research Papergz91rnat100% (1)
- !!!destiny MatrixDocument107 pages!!!destiny Matrixjuancorraliza0% (1)
- Chicago Undergraduate Physics BibliographyDocument12 pagesChicago Undergraduate Physics Bibliographyyouth4everNo ratings yet
- Reheating of The Universe As Holographic ThermalizationDocument5 pagesReheating of The Universe As Holographic ThermalizationR DaniNo ratings yet