Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adverse Events
Uploaded by
iceman1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesAdverse Events
Uploaded by
iceman123Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Adverse Events - Events with a negative consequence, such as system
crashes, network packet floods, unauthorized use of system privileges,
defacement of a web page or execution of malicious code that destroys
data.
Breach - The loss of control, compromise, unauthorized disclosure,
unauthorized acquisition or any similar occurrence where: a person other
than an authorized user accesses or potentially accesses personally
identifiable information; or an authorized user accesses personally
identifiable information for other than an authorized purpose. Source:
NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5
Business Continuity (BC) - Actions, processes and tools for ensuring an
organization can continue critical operations during a contingency.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP) - The documentation of a predetermined
set of instructions or procedures that describe how an organization’s
mission/business processes will be sustained during and after a
significant disruption.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) - An analysis of an information system’s
requirements, functions, and interdependencies used to characterize
system contingency requirements and priorities in the event of a
significant disruption. Reference:
https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/business-impact-analysis
Disaster Recovery (DR) - In information systems terms, the activities
necessary to restore IT and communications services to an organization
during and after an outage, disruption or disturbance of any kind or scale.
Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)- The processes, policies and procedures
related to preparing for recovery or continuation of an organization's
critical business functions, technology infrastructure, systems and
applications after the organization experiences a disaster. A disaster is
when an organization’s critical business function(s) cannot be performed
at an acceptable level within a predetermined period following a
disruption.
Event - Any observable occurrence in a network or system. Source: NIST
SP 800-61 Rev 2
Exploit - A particular attack. It is named this way because these attacks
exploit system vulnerabilities.
Incident - An event that actually or potentially jeopardizes the
confidentiality, integrity or availability of an information system or the
information the system processes, stores or transmits.
Incident Handling or Incident Response (IR) - The process of detecting
and analyzing incidents to limit the incident's effect.
Incident Response Plan (IRP) - The documentation of a predetermined
set of instructions or procedures to detect, respond to and limit
consequences of a malicious cyberattack against an organization’s
information systems(s). Source: NIST SP 800-34 Rev 1
Intrusion - A security event, or combination of security events, that
constitutes a security incident in which an intruder gains, or attempts to
gain, access to a system or system resource without authorization.
Source: IETF RFC 4949 Ver 2
Security Operations Center - A centralized organizational function
fulfilled by an information security team that monitors, detects and
analyzes events on the network or system to prevent and resolve issues
before they result in business disruptions.
Vulnerability - Weakness in an information system, system security
procedures, internal controls or implementation that could be exploited
or triggered by a threat source. Source: NIST SP 800-128.
Zero Day - A previously unknown system vulnerability with the potential
of exploitation without risk of detection or prevention because it does not,
in general, fit recognized patterns, signatures or methods.
You might also like
- Final Project - Penetration TestingDocument20 pagesFinal Project - Penetration TestingArif Zina90% (10)
- NT 2580Document2 pagesNT 2580LeeYoungNo ratings yet
- Operationalizing Information Security: Putting the Top 10 SIEM Best Practices to WorkFrom EverandOperationalizing Information Security: Putting the Top 10 SIEM Best Practices to WorkNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Plan PGS - QADocument36 pagesBusiness Continuity Plan PGS - QAGbenga Babatunde100% (1)
- Xtium DR Run Book Template IDC IntroDocument33 pagesXtium DR Run Book Template IDC IntrofluiduxNo ratings yet
- Audit Execution Plan (HFC & NBFC) - v1.2Document50 pagesAudit Execution Plan (HFC & NBFC) - v1.2surbhiNo ratings yet
- The ICT ProcessesDocument129 pagesThe ICT ProcessesCarol Nzui100% (2)
- Lecture 4 Cyber Security Plans and PoliciesDocument69 pagesLecture 4 Cyber Security Plans and Policies1221309443No ratings yet
- BS 25999Document3 pagesBS 25999Memet H BilgitekinNo ratings yet
- Official Glossary - ISC 2 CC PreparationDocument12 pagesOfficial Glossary - ISC 2 CC PreparationR NilNo ratings yet
- Session 6 Incident ResponseDocument6 pagesSession 6 Incident Responsedrelm7399No ratings yet
- 07-CC GlossaryDocument15 pages07-CC GlossaryManish JoshiNo ratings yet
- 17 Preventing and Responding To IncidentsDocument95 pages17 Preventing and Responding To Incidentsarlin aringoNo ratings yet
- Glossary of TermsDocument4 pagesGlossary of TermsBaltNo ratings yet
- Certified in Cybersecurity - Chapter 1 Terms & DefinitionsDocument4 pagesCertified in Cybersecurity - Chapter 1 Terms & DefinitionsProfgoonerNo ratings yet
- L2 Incident ResponseDocument9 pagesL2 Incident ResponseJayz JoeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1.3Document15 pagesPresentation 1.3KannanNo ratings yet
- Incident Management Policy DraftDocument4 pagesIncident Management Policy DraftDerick Burton (Ben Sisco)No ratings yet
- CC GlossaryDocument13 pagesCC Glossaryshahzaib.shk10No ratings yet
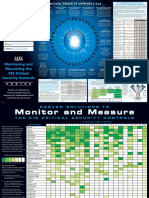
- Critical Controls Poster 2016Document2 pagesCritical Controls Poster 2016pepin1971No ratings yet
- Introduction To SecurityDocument37 pagesIntroduction To SecurityMukeshNo ratings yet
- Phases of The SDLCDocument5 pagesPhases of The SDLCAnnarathna ANo ratings yet
- 1.1. Incident Response: LessonDocument17 pages1.1. Incident Response: LessonDhruv ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CH01-IS PrinciplesDocument36 pagesCH01-IS PrinciplesblankyNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2020-21 CSE3501 ETH VL2020210105438 Reference Material I 05-Oct-2020 6 PDFDocument36 pagesFALLSEM2020-21 CSE3501 ETH VL2020210105438 Reference Material I 05-Oct-2020 6 PDFAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Cyber Incident Response: 1.0 Purpose and BenefitsDocument10 pagesCyber Incident Response: 1.0 Purpose and BenefitsLem Banez100% (1)
- Glossary Cybersecurity Terms (v.2.0)Document7 pagesGlossary Cybersecurity Terms (v.2.0)Chandan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Govt Resource Manual - Information Technology Section 23Document5 pagesGovt Resource Manual - Information Technology Section 23Eqbal GubranNo ratings yet
- Security ProcedureDocument8 pagesSecurity ProcedureBoobalan RNo ratings yet
- Comptia Security+ Notes: 1. Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesComptia Security+ Notes: 1. Risk ManagementCameronNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance and Security-ReviewerDocument11 pagesInformation Assurance and Security-ReviewerCristy VegaNo ratings yet
- Security Measures and Ineffective Monitoring SystemsDocument1 pageSecurity Measures and Ineffective Monitoring SystemsdrhassanmudeyNo ratings yet
- SADocument10 pagesSAAsna AbdulNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Improve Your NIST Assessment ScoreDocument11 pages7 Ways To Improve Your NIST Assessment ScoreK. K.No ratings yet
- Security PlanDocument4 pagesSecurity PlanDominique EijansantosNo ratings yet
- Security Assignment BriefDocument21 pagesSecurity Assignment BriefvishirushikaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security: Fifth Edition by William StallingsDocument54 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Fifth Edition by William StallingsSankar MangattuNo ratings yet
- W1-Module 001Document13 pagesW1-Module 001Dean LevyNo ratings yet
- Computer SecurityDocument37 pagesComputer SecurityEmmanuel RichardNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit TechnologyDocument7 pagesInternal Audit Technologyabhinav sinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1iceman123No ratings yet
- CEH Notes Cybrary PDFDocument34 pagesCEH Notes Cybrary PDFJashan Singh100% (1)
- FirsttestansDocument11 pagesFirsttestansramakrishnan drhvNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document3 pagesLab 6Jatin ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Tolerance Prevention System: TitleDocument6 pagesIntrusion Detection Tolerance Prevention System: Titleparul_purohitNo ratings yet
- Lab6 IAA202Document18 pagesLab6 IAA202Đào Mạnh CôngNo ratings yet
- Operations Security Operational Controls Are Not Concerned With Audit Trails!Document4 pagesOperations Security Operational Controls Are Not Concerned With Audit Trails!tellengaardNo ratings yet
- Bus Cont PlanDocument45 pagesBus Cont Planيُ يَNo ratings yet
- Isc2 CCDocument11 pagesIsc2 CCJoshua EbarleNo ratings yet
- Pentretion TestingDocument15 pagesPentretion TestingJimmykoNo ratings yet
- Mir 014Document12 pagesMir 014tksmpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 of Computer SecurityDocument44 pagesChapter 1 of Computer SecurityQasim BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Introduction To Information SecurityDocument22 pagesLecture 01 - Introduction To Information SecurityS t a r D u s tNo ratings yet
- Likelihood-Exposure Level, Ease of Breaking, Data Value Quantity $, Quality ScenarioDocument11 pagesLikelihood-Exposure Level, Ease of Breaking, Data Value Quantity $, Quality ScenariosibinsukumaranPsibi3No ratings yet
- Section 5: Incident Response: 1. Topic 1 Event Vs IncidentDocument7 pagesSection 5: Incident Response: 1. Topic 1 Event Vs IncidentfadhilNo ratings yet
- Ias101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Document3 pagesIas101 Sbit3l W8sum Vida, John Paul S.Vida, John PaulNo ratings yet
- It ControlsDocument10 pagesIt ControlsPines MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesementDocument28 pagesRisk AssesementADRIANNo ratings yet
- Isc Chapter 2Document19 pagesIsc Chapter 2Cristina Joy CruzNo ratings yet
- IAS ReviewerDocument26 pagesIAS ReviewerKevin Francis VeluzNo ratings yet
- Glossary - CompTIA CySA+Document9 pagesGlossary - CompTIA CySA+GF TeamNo ratings yet
- Security Policy 10 Security Incident ManagementDocument9 pagesSecurity Policy 10 Security Incident ManagementMarselsNo ratings yet
- Information Security Risk Assessment ChecklistDocument7 pagesInformation Security Risk Assessment ChecklistAdil Raza SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Computer Security Concepts (Inglés) (Artículo) Autor Zainab Abdullah JasimDocument7 pagesComputer Security Concepts (Inglés) (Artículo) Autor Zainab Abdullah JasimJavier David Afanador GüizaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Study NotesDocument6 pagesCyber Security: Study Notesshabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Computer Incident Response and Forensics Team Management: Conducting a Successful Incident ResponseFrom EverandComputer Incident Response and Forensics Team Management: Conducting a Successful Incident ResponseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Phoenix ResumeGiantsDocument1 pagePhoenix ResumeGiantsiceman123No ratings yet
- Phoenix ResumeGiantsDocument1 pagePhoenix ResumeGiantsiceman123No ratings yet
- Uche 15 Mins M0dule PlanDocument2 pagesUche 15 Mins M0dule Planiceman123No ratings yet
- 5min Presentation On LIFE VESTDocument12 pages5min Presentation On LIFE VESTiceman123No ratings yet
- Tic Module PlanDocument2 pagesTic Module Planiceman123No ratings yet
- Inem 15 Mins Module PlanDocument2 pagesInem 15 Mins Module Planiceman123No ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods TestDocument12 pagesDangerous Goods Testiceman123No ratings yet
- Definition of Terms DGRDocument6 pagesDefinition of Terms DGRiceman123No ratings yet
- ISO 17799 ChecklistDocument47 pagesISO 17799 ChecklistmicazziNo ratings yet
- RSA Archer Business Continuity Management 4 Overview GuideDocument21 pagesRSA Archer Business Continuity Management 4 Overview GuideShamir ShariefNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Plan Template For SME S FINALDocument18 pagesBusiness Continuity Plan Template For SME S FINALHSE LEARNERS SYED YOUSAFNo ratings yet
- ITSD104 IT Disaster Recovery Rev 1-0Document13 pagesITSD104 IT Disaster Recovery Rev 1-0Mustafa Rahman100% (1)
- Sample Disaster Recovery PlanDocument24 pagesSample Disaster Recovery PlantalhaniazNo ratings yet
- SDR Kirvan DR Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesSDR Kirvan DR Policy TemplateHumberto BellidoNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment Output On Crisis ManagementDocument8 pagesSummative Assessment Output On Crisis Managementjc segismundoNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Planning Final Internal Audit Report - Appendix 2 PDFDocument13 pagesBusiness Continuity Planning Final Internal Audit Report - Appendix 2 PDFkumarNo ratings yet
- Isaca CISMDocument371 pagesIsaca CISMvivek4ccs100% (1)
- BCP-DRP MaintenanceDocument3 pagesBCP-DRP MaintenanceadgclarkeNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Management A Practical Guide To Organizational Resilience and ISO 22301 (James CraDocument339 pagesBusiness Continuity Management A Practical Guide To Organizational Resilience and ISO 22301 (James CraalsbalvesfNo ratings yet
- IS3340 ProjectDocument393 pagesIS3340 ProjectBri DuqNo ratings yet
- Overview of BCDRPDocument55 pagesOverview of BCDRPKurnia SantosoNo ratings yet
- It's All About BCM InstituteDocument2 pagesIt's All About BCM InstituteBob GohNo ratings yet
- BCM Awareness M4 English Content For ArabicTranslation (Arabic) 20180113Document6 pagesBCM Awareness M4 English Content For ArabicTranslation (Arabic) 20180113Abhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- EITReportDocument50 pagesEITReportshah aliNo ratings yet
- CCISO v3 Courseware Table of Contents 1Document12 pagesCCISO v3 Courseware Table of Contents 1Ronald RamirezNo ratings yet
- Nayatel RPDocument20 pagesNayatel RPMansoor ShahabNo ratings yet
- AGN 232 1 Risk Assessment and Business Continuity Management 1Document4 pagesAGN 232 1 Risk Assessment and Business Continuity Management 1castluciNo ratings yet
- Terminology and Acronyms List: Critical Facilities Operations Framework (Ocp Cfops)Document22 pagesTerminology and Acronyms List: Critical Facilities Operations Framework (Ocp Cfops)LC100% (1)
- Kiểm Tra Quá Trình An Toàn Thông Tin Kế ToánDocument9 pagesKiểm Tra Quá Trình An Toàn Thông Tin Kế ToánMỹ QuyềnNo ratings yet
- CISA Job Practice 2019Document4 pagesCISA Job Practice 2019Arun Prakash Panjrath & AssociatesNo ratings yet
- BCI Resilience Report 2017Document27 pagesBCI Resilience Report 2017adolfoalavilaNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Scorecard Builder: GuideDocument15 pagesBusiness Continuity Scorecard Builder: GuideJMHRNo ratings yet