Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective NCP
Ineffective NCP
Uploaded by
christian vincentOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective NCP
Ineffective NCP
Uploaded by
christian vincentCopyright:
Available Formats
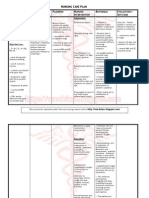
-P, K
-Ineffective airway clearance related to bronchial secretions secondary to upper respiratory tract
infection
-High
-Respiratory tract infection is defined as any infectious disease of the upper or lower respiratory
tract including coughing as a symptom.
-The patient will be relieved from coughing
S: The patient verbalized “ Mag sge rako og ubo tapos dli sya gakawala”
O: >Febrile
> Anxiety
> Inability to cough effectively
Short: After 2 hours of nursing intervention, the patient can cough phlegm effectively.
Long: After 3 days of nursing intervention the patient will have complete relief from cough and
maintain clear airways.
Independent: Encourage to increase fluid intake
- Fluids help to move secretions
Monitor VS
-To assess baseline data
Position the client in an upright position
-Promotes better lung expansion
Teach the patient the proper way of coughing
- The most convenient way to remove secretions is through coughing
Dependent: Give medication as prescribed by the physician
-Medication can relieve airway clearance and may help remove secretions
Refer to the physician if symptoms still occur and intervention doesn’t work.
-Referring to a physician will help to have better intervention and fast recovery
Coordinate with a respiratory therapist
-To evaluate and assess more to prevent further complications
S: Goal met, after 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient still coughs but with less phlegm by
increasing fluid intake
L: Goal met, After 3 days of nursing intervention the patient was able to relieve from cough and
maintain clear and open airways.
You might also like
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument79 pagesChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- A Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDocument7 pagesPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03Document6 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03AgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of CVA and NIDDMDocument12 pagesNursing Management of CVA and NIDDMKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Copd Case StudyDocument5 pagesCopd Case StudyJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- CVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesCVA NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceJoanne Kaye Taylor100% (1)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument88 pagesChest Physiotherapy私 シャーロットNo ratings yet
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceRosalie DelfinNo ratings yet
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GastroenteritisDocument8 pagesGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDocument9 pagesChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- NCP Baby DDocument3 pagesNCP Baby DYna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- SAMPLE NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Pneumoniakana_mercado100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan PediaYvonne Niña Aranton100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- NCP NminDocument5 pagesNCP NminkrizziajNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansjessamariesabioNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP Copd AirwaySugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- So A PieDocument3 pagesSo A PieHelena EliseNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNo ratings yet
- Ayu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing CareDocument4 pagesAyu Pratika Wati - Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Careson hyejooNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Copd Case StudyDocument6 pagesAhmed Copd Case StudyAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentEjoy Rayos AdawagNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- 5NCPDocument4 pages5NCPSara ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument17 pagesMechanical VentilationDorothy Joy CumigadNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care PlansBeng AlontoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument10 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHannah VueltaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabNo ratings yet
- Cap MRDocument3 pagesCap MRRhio Grulla RamboyongNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Short Term: Short Term: After 3-4Document2 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Short Term: Short Term: After 3-4esteffie21No ratings yet
- And Release of Pancreatic Enzyme: Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocument15 pagesAnd Release of Pancreatic Enzyme: Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- What Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsDocument11 pagesWhat Is COPD? Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Signs and SymptomsCecil Bhang-i Cacay - PabloNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Case Study Chapter 24Document10 pagesGroup 1 Case Study Chapter 24Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedDocument3 pagesNursing Management of Clients With COPD: - Initiate Infusion of Intravenous Antibiotic As PrescribedNiña AngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance: Assessment Diagnosis Outcome IdentificationDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance: Assessment Diagnosis Outcome IdentificationAngelokeizer GavinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Kochs2Document2 pagesNCP Kochs2Ava VierNo ratings yet
- THE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityFrom EverandTHE BUTEYKO METHOD (Translated): The secret of controlled breathing for health, well-being and vitalityNo ratings yet