Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bahamas Primary Maths Workbook 3 Answers
Bahamas Primary Maths Workbook 3 Answers
Uploaded by
Teacher Maedel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views80 pagesOriginal Title
Bahamas Primary Maths Workbook 3 Answers (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views80 pagesBahamas Primary Maths Workbook 3 Answers
Bahamas Primary Maths Workbook 3 Answers
Uploaded by
Teacher MaedelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 80
_ BAHAMAS PRIMARY
Mathematics Workbook So
The authors and publishers would like to thank the following members of the Teachers’ Panel,
who have assisted in the planning, content and development of the books, led by Dr Joan Rolle,
Senior Education Officer, Primary School Mathematics, Department of Education:
Deidre Cooper, Catholic Board of Education
Vernita Davis, Ministry of Education Examinations and Assessment Division
LeAnna T. Deveaux-Miller, T.G. Glover Professional Development and Research School
Joelynn Stubbs, C.W. Sawyer Primary School
Dyontalee Turnquest Rolle, Eva Hilton Primary School
Karen
Morrison
curl
Daphne
Paizee 4
6 SORE
AN HACHETTE UK COMPANY
Contents
Topic 1
Topic 2
Topic 3
Topic 4
Topic 5
Topic 6
Topic 7
Topic 8
Topic 9
Topic 10
Topic 11
Topic 12
Topic 13
Topic 14
Topic 15
Topic 16
Topic 17
Topic 18
Topic 19
Topic 20
Topic 21
Topic 22
Topic 23
Topic 24
Topic 25
Getting Ready
Numbers in Our World
Exploring Patterns
Counting and Place Value
Temperature
Talking About Time
Number Facts
Classifying Shapes
Rounding and Estimating
Number Patterns and Relationships
Money
Addition Strategies
Subtraction Strategies
Graphs
Problem Solving Strategies
Measuring Length
Multiplying and Dividing
Fractions
Working with Time
Decimal Fractions
Capacity and Mass
Exploring Shapes
Perimeter and Area
Probability
Mixed Measures
10
13
15
19
22
26
29
33
34
37
40
44
47
51
54
58
62
64
66
69
2B
7s
Topic 1 Getting Ready
Number Work
1 Fill in the missing numbers on each number line.
a
IS5]] t4o]} taS}}/1 So}}iss
20 femal 2 open o0) : -
b
300 || 350 |} 460}! u50
100 150 200 250
200 || 300 |} 4.00 || Soa || G00
700 800 900
d
LOO
300
500
2 Circle the largest number in each set. Underline the smallest number.
a 234 456 245 b112 G0) 102 210
3 Look at this number line.
400 uwio 4SO
4IO uso 490 500
Write these numbers in the correct
position on the number line. pe i ast ZO | a
—e—eGCi+-71''_—“———~ @G
A Mixed Bag
1 Sandra counted the shapes in a pattern.
Circles Squares Triangles Rectangles
12 7 1 16
Show this information on the graph.
Number of Shapes in a potten
ie
it
o
5
:
i!
ave
Type of Shape
Cirles,
12 SRS OC TBF ON ISIS
Numer of Shapes.
2 Draw a line to divide each shape into halves. Colour one half.
Draw another line to show fourths. Colour one fourth. Use a different
colour.
Topic 2 Numbers in Our World
Ordinal Numbers
1 Label the runners in this race with these ordinal numbers:
Ast, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, Sth.
toes = Oy) 2-4] Suk
es “fs ~ kth]
2 Write the following numbers as ordinal numbers.
24, 33, 6, 30, 12, 45
Zu Bde 6th, 30th, 12th 4 Sth
3 There are five boys standing in a line. Their names are Sean,
Mario, Jesse, Micah and Brad. Fill in the names under the
pictures. Here are some clues:
Sean is not second. Mario is not first. Jesse is third in line. Brad
is not Sth. Jesse is behind Micah. Brad arrived before Sean.
Bead Mican Jesse Mewio Sean
Sean Mano
4 Mrs Adderley has a very busy month. Read the calendar and answer
the questions.
[Men]
meeting
ee
Seroo ne
free
1 [tenes fie [a7 re |i
& Tennis
zo far ie
a7 282g a0.
a Write the dates of the first and last days of January.
Lo January + 31 January
b Write the dates of the Wednesdays that fall on odd numbers.
4 1S 29
c Write the dates on which Mrs Adderley will play tennis.
Band 49 Senicng
d What will Mrs Adderley do on the 12th?
Se will have a _plenic
e On which date is Mrs Adderley’s birthday?
14 JSenuars
f Mrs Adderley visits her mother on the 2nd and 4th Saturdays of
every month. Circle these dates on the calendar.
g Mrs Adderley is going camping for three days from the Wednesday
in the 4th week of the month. Colour these days on the calendar.
o----~-~~~
Roman Numerals
1 Complete the numbers on this clock.
AN
2 Write down the ordinal numbers that xe x! eae
match these Roman numerals.
a XIN ust? sb xT)
¢ XIV d X_toe
exxm_22“' of va
3 Write these numbers in Roman numerals.
a 4_iN b9_ix c¢ 13_X2iE
d18_xXVvia e 21_X%Xxt f 25_xxv
4 Create a logo for your sports club. The logo should include a Roman
number; for example, if your club is 5 years old, you could include
that number.
Numbers We Use Every Day
1 Add up the cost of the items on this grocery list. How much money will
you have left over from $20.00 if you buy these items?
Apples $2.30
Ice cream $2.35
Toothpaste $1.65
Shampoo $1.50
Soap $1.00
Total cost:|$3 .3O]
Change: | $ \1.20
2 Make up licence plates with digits that add up to these
numbers. The licence plates can have 4 or 5 digits.
a 17 b 15
° NASSAU ° ° NASSAU °
7235 32712
*BAHAMAS = *BAHAMAS =
¢ 21 d19
- NASSAU = ° NASSAU °
34423 8145!
-BAHAMAS < 2=BAHAMAS -
@~~-~-~~T---T--’-
Topic 3 Exploring Patterns
Repeating and Growing Patterns
1 Complete these repeating shape patterns. Use a ruler to draw straight
lines. Colour the completed patterns.
3 Draw the element that comes next in each growing pattern.
io IE
d
(
¢
( 2)
OOOO Xk
4 Use the first and third letters in your name and the digit 8 to make
your own growing pattern.
Patterns and Number Lines
1 Use the rule and fill in the missing numbers on the number lines.
a Count forwards by 5s.
45
50 te)o) eo 65 10
b Add 100 each time.
120 320
20 220 429 || S20
¢ Count back by 10s.
60
830 10 50 LO 30
d Subtract 4 each time.
ii 26 = 30
\O Vy 12 eee
e Add 6 each time.
ie 36
2 || 30 42 |] LB
f Add the two previous numbers to get the next number.
1 3
4 7 NW 18
——eerrrrrrrrrr-_~ @
Topic 4 Counting and Place Value
Place Value
1 Colour the shapes to match the number, its name and its expanded
notation form. Use the same colour for each set.
2 Read the information about the number.
Write the digits in the correct places to make a four-digit number
that fits the information.
a Iam between 1000 and1500. b Iam greater than 3000 and I
4, 7, 8,1 have 4 tens.
8, 7,3,4
Th} H| T|O Th} H|T/|O
on
) uy) a}s [o8 3/4 BZ) S347
ae al 7343) 13u3
3143) 8347
c Tam between 4370 and 4390. d Iam between 2000 and 2500.
3, 84,1 3, 9, 8, 2
Th} H|T|O Th} H|}T/O
| 3/341 2/32)3 1/9 eee
e Iam greater than 2780 but f [have 6 hundreds and I am
smaller than 2850. greater than 3000.
8,7, 4,2 1, 4, 3,6
Th) H| T/} 90 Th} H/|T/|O
ot
2{7]a | a foo Zleluly | acai
S614
Sly
g Ihave notensand morethan —_h Iam between 7000 and 7060.
five hundreds. On 79
0, 2, 4, 6
Th} H| T|O Th) H}T/O
Z/6/O]}]4 Jor Tloli fq
yeor
eee ~~ - @
Comparing Numbers
1 Start on 4000. Move across the rocks in ascending order. You must
jump to the next highest number each time. Draw arrows as you move.
Colour the item you get to.
S
& oe,
6 ef
“5
ree
em
2 Write the 1st, 3rd, 8th and 10th numbers you landed on.
OOO 5000 1050 3OSO
3 Fill in the boxes with < or > to make each statement correct.
a 8616 | > | 8166 b 2467 | < | 4267
c 3142} ¢ | 3412 d 2655] ) | 2650
e 5099 | ¢ | 9055 f 4009 | > | 4000
e-----T---- ---~
Topic 5 Temperature
Reading Temperatures
1 Circle the cooler item in each pair.
10°C = 50°F 15°C = 59°F 30°C = 86°F 80°C = 176 °F
—_——eeraereerrrr~-r-w - @
Recording and Interpreting Ternperatures
Use this chart to record your estimates and measurements.
Place: Place: Place: Place:
Time: Time: Time: Time:
Estimate
Measurement
Difference
What did you find out?
Topic 6 Talking About Time
How Long Does It Take?
1 Think about these activities and events. How much time do they take?
taking a shower getting dressed eating a meal
playing a game of football getting to school
a Underline the activities that take about the same amount of time.
b Write the activities in the chart. Add another activity to complete it.
Short Time Long Time
taking a snewser | ployng a gore of
Footie all
getticg essed geting t© scincol
taking a lus to
the mext town
ecteg a meal
2 Think of two activities that you do quite often. Estimate how long each
activity takes. Then time yourself to see how long they really take.
Work out the difference. Record your answers on the chart.
Activity Estimated Time | Measured Time Difference
WA
A.M. or P.M.?
Draw up a plan to show what you are going to do on your birthday.
e Think about what you will need to do to prepare: for example, blow
up some balloons.
e Think about what activities you will do: for example, play a game.
Fill in the times and the activities. Use a.m. and p.m. for the times.
My birthday ison 1 Mag
Times Activities
4209 am. Bloow up the Walloons
A+SO oem. Put the feed om the table
lO: SOa.rm-~ Play 3S gore
1OtuUS a.m.- Seg hepry lov day
Wt00 am. Play a gare
bt BO am. Eat
12% 30 p.m. Open) Presents
——_—_—_———
Using a Calendar
1 Use this information to fill in the calendar.
This is the month of August. August has 31 days.
This year, the first day of August is a Tuesday.
Month: A, gust.
Mon | Tues | Wed |Thurs| Fri | Sat | Sun
\ 2 3 i" Ss 6
a SB a is} Hu 12 3
Up is Jel m1 1g 19 20
2 22) 2S 26 27
28 23] 30 \
2 Complete these sentences about the calendar.
@ The last day of the month is a_Thuwsctoy
b The date of the third Friday in the month is the 188
¢ Emancipation Day is ona_1_August
d There are___4 _ Mondays in August.
eee - - FG
3 Your class is December
planning a
class party on Mon | Tues | Wed |Thurs| Fri | Sat | Sun
16 December.
You have to do i Z 3 4
several tasks 5) 6 7 8 9 10 | 11
before the party
to prepare. Other 12) 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18
tasks need to be 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25
done on the day
of the party and 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |} 31
some tasks need
to be done after the party.
a Read the tasks and decide in which order you should do them.
Number the tasks.
b Use the calendar and fill in the dates on which you will do each task.
Order Task Date
y Bake some cakes, make sandwiches. 1S Oecermoer
3 Collect plates, forks and cupstouseatthe |, 6 pee
party.
5 Decorate the classroom. 16 Decantcer
Clean up the classroom and throw away
6 all the litter. v1 Occenioer
2 Buy cold drinks. 12 Decermloer
\ Write a letter to invite the teachers. iDecenioe
o~----------~--_-
Topic 7 Number Facts
Addition and Subtraction Facts to 10
1 Marcie has these pieces of ribbon. Colour pairs to make lengths of
10 cm. Use a different colour for each pair.
2 Fillin the missing numbers in these flow diagrams.
Addition and Subtraction Facts to 20
1 Pair the sets of crayons to make groups of 20. Colour each group of 20
a different colour.
‘NNN
NN !
i
ng
|
2 Use your coloured sets to complete these subtraction sentences.
a 20-5=/)5 b 20-18=| 2
¢ 20-0=/20 d 20-4=) 16
e20-| & |=14 f 20-| 1 |=9
o7---~~~-~~
More Adding and Subtracting
1 How quickly can you complete this set of facts?
The answer is 20.
G& [+14 | 114) 9 10+| 10 9+}
12+ g A [16 | 6+) 14 0+| 20
25-1 5 20-| o 19+) | S415
2 The number of people who get on and off a bus at different stops is
given. Work out how many people are on the bus as it leaves each stop.
Write the number on the bus.
Topic 8 Classifying Shapes
Plane Shapes
1 Draw the shapes. Measure and label the sides.
Triangle Square
Zen
2 Zan
2em 2em
Zorn
zens
Rectangle Pentagon
——bsan
1 tern
Zon Zo
\ Venn
neon Tea
2 Measure from the centre of this circle to points A, B, C, D, E and F.
Write down your measurements.
A
Solid Shapes
1 Complete this table.
Name Drawing Number of Faces | Number of Edges
a | cube
6 (2
b
lcyliccier C1 2 2
c
|O]° |e
d
cone A 2 \
2 Circle the shape that does not belong in each set.
aw &F 6H
3 Colour in these pictures. Colour each type of shape a different colour
(for example, colour the cubes yellow).
4 Make solid shapes. You can use any materials (for example,
paper, clay, sticks, polystyrene). H
Draw a picture of each shape you make.
Name of shape: Name of shape:
What did you use to make the shape? |What did you use to make the shape?
Describe what the shape looks like. Describe what the shape looks like.
Bap mace cerca
Lines, Points and Line Segments
1 Draw line segments between the points.
Measure the line segments.
4, Son
4, Sone
2 Add a3 cm section and a 4 cm section to each path.
‘To
c
Topic 9 Rounding and Estimating
Rounding Numbers
1 For each set of numbers, round each number to the nearest ten.
Write the numbers in the correct columns in the tables.
*) Rounds to 10 | Rounds to 20
4 4 23
8g \o
ie IS
13 Ca
im
was
5! Rounds to 70 | Rounds to 80
6B 149
alice 1S
tS Bi
m=) 16
Su
Rounds to 100 | Rounds to 110
111
qe Lo qe 109
lol dul 104
tan Wiz 105 49, 112
103 Vide 103
aa 10S aq 114
2 One number in each set was rounded to the nearest hundred shown
above. Colour that number.
400 200 300
[8 452 | 349| | 147 | 258 [is 193 | 247 268]
600 400 100
713 650| | 491 Ba se 407 | 170| 201
200 900 1000
127 | 175 | 250 [270] °22 950 ‘| 909 | 948
700 500
850 649 751| | 662| 559 520 |
3 The number of pieces of litter left on a beach each day for week is
recorded in the table.
Mon Tues Wed Thurs Fri Sat Sun
oo | ws | mo | se | ae | oe |
Round each number to the nearest hundred and estimate how much
litter was left on the beach in that week.
Bios) pieces of litter.
—_——ew~aserre~nr-wn FB
Estimating Answers
Round the numbers to the nearest ten or hundred. Estimate the answers.
Calculation |Rounding and Estimated Answer
a 56+49 604+S50 =110
b 42+81 LO+tBO #120
Cc 48+33 50 +20 =30
d 55+28 60 +30 = 90
e 64439 60 +40 =1C0
fF 39+28 uO +30 = 710
66-19 19 - 20 = 50
59-22 6O -20 =u40
i 92-56 qo -6o =30
j 93-55 dO - 6O = 30
k 97-79 1O0 —ZO =20
| 153+198 {5G + 200 = 350
m 207 +448 2O0 + 4505650
n 1314499 | 130 + Soo =630
© 688-420 ASOD — USO = 300
p 891-175 | qao- 200= 7190
q 550-320 eco — 300 =300
e~-------T--T--”- --_-
Topic 10 Number Patterns and
Relationships
Odd and Even Numbers
1 Find and colour a path over the river, hopping only on even numbers.
2 Circle the odd numbers. Underline the even numbers. Use the Venn
diagram to organize them. Label each circle in the diagram.
qs) 200
68) 6
@3) 22,
1o @
@) 144
404 90
wn
S
S
S88 |
&@
Skip-counting
1 Count by 3s. Draw a D over each number you count.
2 Count by 4s. Draw a O over each number you count.
3 Count by 5s. Draw a © over each number you count.
aa
1}/2/a|]@
7 | Ble
ma | 22 | 23 | em
(al | 34
«|Bal|«/@
33 | AM
ei | 62 | 6 | @
n | Awl 74
wl | 82 a |
91 | @ | BI | 94
Al7/@®/|qa
@|v | a
26 | 2 | @ | 29
®
37 38 Ba
a | | «
31
BA | 58 | 59
a
Aas | or | @ | 0
iN
Ads
©
el
77 79
2 | @ | 389
SS O1S SO) S/o] &
97 98 (99)
®| ©) | 2 |B S| O/B @|e
4 Choose one more skip-counting pattern. Use a triangle to mark the
numbers you count. 6s
o~~~~~-~-~~
[ 101 | Oe 193 1o6 108 des
wae fe Wy ~ nadie 3
12) Les 124 126 }120 129
136 138] 139
V4T) 1s ¥
156/'(ST7 159 |NGO)
(GG IGB } 169
117 | 178 130)
1e7 Sq fg
19S IGB liga
a Count by 3s from 101. Colour each number you count yellow.
Underline the odd numbers you count.
b Count by 5s from 105. Circle the numbers you count in blue.
Underline the even numbers you count.
¢ Count by 50s from 100. Draw a star on each number you count.
d Count backwards by 10s from 200. Draw a red square round each
number you count.
e Choose one more skip-counting pattern. Use green to show it on the
grid. Describe it in words.
Count by 1s from 102.
oor |. @
6 Write the next three numbers in each pattern.
(lp 5 pene aeeemmnen amen] emo eres eee
b 17,20, 23,_2G , 29 , 232
¢ 130,120,110, 1c@ ,__SO__,__8O
d 175,170,165, 1GO , 195 ,_ 150 _
7 Follow the instructions. Write the numbers you would count.
a Count by 50s. 450} 500 || 5&0 |} 600 || GSO || 400
b Subtract 10. 128) 11% 108% |] qg 38 43
¢ Count back 140} 1 3G 132 |} 128 12h. |] 120
by 4s,
d Subtract 2. 800) 193 || ISG |} 794 [1792 || 790
e Subtract 50. 800) 150 || 100 || 650 || 6Co || SSO
8 A packet of chips has a mass of 50 grams. Work out the
mass of:
a 5packets_25° 9 — b 10 packets SOO g
o~~~~~------~
page
Topic 11 Money
Working with Money
What would you have to pay for each group of items? Work out the total
cost and the change.
Total Cost__| You Pay With} — Change
$2.30 $5.00 $2.40
4 4.12 $5.00 $0.28
2%
$5.50 $10.00 $ 4-50
$ iy -70 $15.00 40.30
30c
$ 14.20 $20.00 $ 2-40
Topic 12 Addition Strategies
Methods of Adding
Each number in the number pyramid is the sum of the two numbers in
the blocks below it.
The first pyramid has been completed as an example.
Work out the missing numbers in the other pyramids. Use the space
below each one for working out if you need it.
1 2
476 1033
250 | 226 351] 636
200 | 50 | 176 180 | 217 | 419
3 4
165 i4el
4349126 1224/1397
122 | 317 | 409 812 | 412 | 325
More Adding
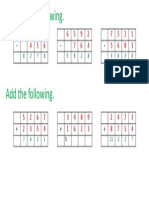
1 Some digits are missing from these sums. Work out what they
are and write them in the correct places.
a b
3 3/4 C9)
+ 6] 8 +) 3 1 8
9 5 5 8 0 5
c d
VT) aia 5 1/4
+ 6 3 4 +1914 7
t | 6 3 3 3)}5 1/8
2 Find two pairs of numbers in the box that will each give a total of
6 555 when added together. Write them in the spaces provided.
4234 2411 4 23y + 2321
2855 4550
3500 3550 3550 + 3005
3005 2321
—eeeerer rr - @
3 Micah has found a different method of working out sums.
using place value.
He makes dots on the place value table to represent the
numbers and then uses those to get the answer.
Th) H|T|O
eee ee ice
#3125 [eo] ° [rca
6249 6 2 4 49
= |< 1st number
= 2nd number
= Totals
He has already drawn dots for the top number in each sum.
Draw dots for the second number and find the answers.
G 1 2
+301
7 8
2 2
Th| H
Topic 13 Subtraction Strategies
Methods of Subtracting
Complete these number pyramids using subtraction. Remember, each
number is the sum of the two numbers below it.
1
377
160 | 2174
BZ 78 | 139
24 Ww) 4 26 | 710
699
3043 | 390
iuy | 165 | 225
271 13) 14 2\ 32 | 41
More Subtracting
1 The total distance and the distance already flown by each plane is shown
on the diagrams. Work out how much further each plane has to fly.
a s
528 Ze~ 1342 km
2 i
a =
1872 km
2Z6OIZ {km
517 km
Jr TOeererorr"0—099
4324 km
@~-~-~-~---T-T-----
482 km
yy
ws
1310
fee
oro
2039 km
2 Check Tennielle’s homework. If her answer is correct, tick it. If her
answer is wrong, work out the correct answer and write it below the
calculation.
(OEesE
-182
— 1
ma(enOw/sS
-308
117
km
Topic 14 Graphs
Collecting and Recording Data
1 Work in pairs. Throw a die 20 times and record the numbers you throw
on this frequency table.
Numbers Tally Total
1
2
3
4
5
6
N
Record the data on a pictograph. Choose a symbol to represent the
animals.
8 rabbits 3 goats 2 ponies 10 ducks S hens 2 dogs
1O2SOGQ0Ce
©2Ce
a
fim| © ©
SOOCSCSCOCOOCGCO
ISRCKOROAC)
© @
o---~~~-----~
Drawing Graphs
Use this page to draw your own bar graph.
Title:
Use this page to draw your own bar graph.
Title:
1 Ernest asked everyone in his class what they liked to put in their
sandwiches. He recorded the results on this tally table.
a Complete the totals.
Sandwich Filling Tally Total
Cheese HATII 7
Egg LAT 5
Chicken Ut! Se
Meat u 2
Jam JT HT II 12
b Complete the bar graph.
12
1
10+
Number of Students
o
|
ie
Cheese |
Egg "Chicken!
T
Meat
Favourite Sandwich Fillings
oor ~~ - F@
Topic 15 Problem Solving Strategies
Choosing a Strategy
1 Zorgs have 4 eyes and yabs have 2 eyes.
Draw zorgs, yabs or a combination of zorgs and yabs in each box so
that there is a total of 16 eyes in every box.
©
es
zorgs yabs
OB
me
:
on
2 Put the numbers in ascending order to crack the code and work out
the message.
300 |} 689 || 1202]) 218
®© | © | ©] ®
1300]} 127 || 1200|| 1020
©_@© | ©] ©
999 || 237 |) 742 || 345
® | @LO]©
301}) 208 || 1282} 273
©] © | ©]©
3 The picture shows the shapes you can make by joining three squares.
The rule is that squares have to touch each other and when they
touch, the whole side of one has to touch the whole side of the other.
| the shapes yot
Topic 16 Measuring Length
Measuring in Metres
1 Draw pictures of two items that you would measure in metres. Explain
why you would measure in metres and not in centimetres.
would measure this
—dee _in metres
because
tS a lowe piece
wane! ley using
Ametves Net
ect 42 worn ct
big muImicer ,
I would measure this
Odnletcs track in metres
because
it is 284 long
Measuring in Millimetres, Centimetres
and Decimetres
1 Look at these objects.
a Estimate how long the objects are in centimetres. Write your
estimates in the table.
b Now measure each object in the picture using centimetres. Write
down your answers in the table.
Object Estimate Measurement (in
(in centimetres) centimetres)
sessors 20 enn oem
Eraser tem 5am
Glue stick, Vor Cra
Paint joen 25am Vinie ern
Pape clip 3am Stone
Srorperer 2am Zon
2 Measure the objects in the picture below in millimetres and
centimetres. Record your results in the table.
Object Centimetres Millimetres
Pencil Bon Borers
Coins Lom 1OmMm
aeeeeeeeeeeeeeer-S GB
3 Measure these paths in centimetres or in millimetres. Write down the
measurements of each section, then add them.
oN > SY
1S [+] 1B |=] Berg IS [t+] 12 JF] 2 Tapes
1S |*] 20 [FP 2 [Fly dep
Topic 17 Multiplying and Dividing
Multiplication and Division Facts
1 Use your class fact city posters to complete each table.
2timestable |3timestable | 4timestable | 5 times table
Ox2=| 0 Ox3=| oO Ox4=| o Ox5=| 0
1x2=| 2 1x3=| 3 Teas] y 1x5=| 5
2x2=] 4 2x3=| 6 Qxhel g 2x52] 10
3x2=1 G6 3x3=| q 3x42] 12. 3x5=| 15
4x2=| 3% 4x3=] 12 4x4=| 16 4x5=| 20
5x2=| 1c Sx3=] 15 Sx4=| 20 5x5S=| 25
6x2=| 12 6x3=| 18 6x4=! ay 6x5=| 20
7x22] iy 7x3=| 2) 7x4=!| 23 7x5=| 35
8Bx2=| lo 8x3=] 24 8x4=| 32 8x5=| 4o
9x2=| 18 9x3=| 27 9x42] 26 9x5=| 45
10x2=| 20 10x3=| 30 10*x4=| yo 10x5=| SO
6timestable | 7timestable | 8timestable | 9 times table
Ox6=| o Ox7=| 0 Ox8=| 0 Ox9=) O
1x6=| 6 4x72] 4 1x8=] 3 1x92] q
2x62] 12 27] Wy 2x8=| Io 2x92] 18
3x6=| 13 3x7=| 2) 3Bx8=/ 24 3*9=1 29
4x6=] 24 4x7=| 29 4x8=| 32 4x9=| 26
5x6=| 20 Sx7=| 35 5x8=| Lo 5x9=| 4S
6x6=| 26 6x72] 42 6x8-] ns 6x9=| Sy
7x6=| 42 7*7=| 49 7*8=| So 7x9=| 63
8x6=| us 8x7=| 56 8x8=| Gy 8x9=|) TZ
9x6=| St 9x7=| 63 9x8=| 72 9x9=1 81
10«6=| g6 | |10«7=| Fo | | 10*8=| go | | 10«9=| 90
2 Complete the flow diagrams using the facts you have learned.
a
12
8
4
20
14
50
30
45
20
615
49
70
42
21
35
6
4
Topic 18 Fractions
Understanding Fractions
1 Shade each shape to show the fraction given. Write the fraction that is
unshaded in the boxes.
z
Shade = == Shade 3 ==
2 Colour items in the group to show the fraction given. Write a fraction
to represent the unshaded items.
al O00 b®@@@OO0O | kc AAAA
@®@@000
OyoIe79 @@0000 || AAAAA
Shade 2 Shade 3 Shade 3
\ 5 3g
Unshaded: == Unshaded: ==! Unshaded: ==
a q q
Fe@ @ O
@®@O0
5 @@o0o
Shade 2 Shade §
' 3
Unshaded: = Unshaded: ==
S 6 q
9A A A h pan ie $e
A A A Aa ©@ oe
A A @ °
AA NIM ee oO
Shade 3 Shade ; Shade 4
1 2 3
Unshaded: == Unshaded: == Unshaded: ==
i Ss 7
—ewererarer_'"1—""'"'['"-—~ @
Equivalent Fractions
1 Colour 3 of each shape. Complete the equations.
‘HE
1s ° freee)
2 2
1o 12
More Equivalent Fractions
1 Draw lines between pairs of equivalent fractions. Colour any fractions
that are in simplest form.
3
4
44
33
14
28 16
20
14
q 21
10
A
10
3
iy
A
5
1
2
18
27 24
30
q
15 1
3
2
5
2
3
Topic 19 Working with Time
Talking Time
Sort these activities into a.m. and p.m. activities. List the activities in the
correct column.
a a birthday party which starts at 10:00
b asun which sets at 8:30
¢ atrip to the shop at 11:15
d eating breakfast
e having a shower before school
f playing with friends after school
g doing homework after school
h eating supper
a.m. Activities p.m. Activities
SUA which sets
a Birtrcy poregy which | o
ot S:80
stores at 00
a trio tt tre Sice playing with feds
ot uns afte: Sscreo!
3 loin horresork
ich lor
eating cokast 7 8 SS
having a Shower .
ave sorcol eoerg Suprer
o~~~~~~~-~~~~~
How Long Does It Take?
1 Complete all the columns in the table.
Activity | Start End How Long Did
It Take?
Making a 15 minutes
sandwich
Walking to
the beach
IO minutes
30 minutes
Werth.
“3
a TN
Pregramn
Grocery ate
sreprrg,
Making a
cake
2 Fours,
2 Sam takes 10 minutes to walk to the beach, 30 minutes to play cricket
with his friends, 10 minutes to look for shells and 5 minutes to buy a cold
drink. He then walks home again. How long has he been out altogether?
19 +30 +O +5410 = 65 minutes
= 1 hour
Somosees
—e—eGWrr rrr -
3 Fill in the calendar. The month is September. The month starts on a
Wednesday.
September
Mon | tues | Wed | urs | Fi Sat. Sun
1 2 3 Ly 5
e 7 3 q is my ZW
is toy 1S Io aay 1S WG
20 2) res 23 Zu 25 26
27 23 24 30
4 Use your calendar to answer these questions.
a How many Saturdays are there in September? 4
b You have music lessons twice a week, on Tuesdays and Thursdays.
How many music lessons do you have in September?
q__ lessons
¢ There is a carnival on the 3rd weekend in the month. What are the
dates of the carnival?
IS-\9 Septem toer
d Sean’s birthday is on the fourth Wednesday of September. What is
the date?
22 Septem cer
e Your father is going on a trip from the 6th to the 14th of September.
How many days will he be away?
J stays
o~~~-~~-~-~~-~
Equivalent Times
1 Match the times. Write the pairs below.
24 hours 3 3 days 730 days 3 weeks
36 months 300 minutes 6 weeks.
3 years 120 seconds 21 days
84 hours
24 months 5 hours
1 day 2 minutes
42 days 49 days 7 weeks
a 3 hours = 180 minutes
b 2b hours = i soy
¢ 3% doys e
d 1390 cays _=
By hours
Zu mentins
e _1ZO secorcls = 2 minutes
f 36 mentees = __3 yeors
g —3 weeks = 2) Sous
h _ 300 mines = 5 hours
j G6 weers =u 2cdoys
j 4a ays = TW voeeks
Topic 20 Decimal Fractions
Tenths and Hundredths in Decimal Form
1 Shade the given fractions. Write each one as a decimal.
i b Ty cM
7.
79 7
2 Shade 3 of the first grid and i of the second grid.
Write the shaded section of each as a decimal fraction.
b
0, S_ shaded 0, 18 shaded
o~~~~~~~~-~-~~
3 Colour part of each hundred square to match the given decimal
fraction. Complete the number sentence.
a
0.09 0.90 0.55
0.09+0.4' =1 0.90+0.49 =1 055+0,49 =1
0.75 0.99 0.8
0.75+0.25 =1 0,99+0,o1 =1 08+0,.2 =1
4 Fillin the boxes with >, = or < to make each statement correct.
3
*5L= 0.3 b 0.26] y |0.22 c 1} > {0.99
d 0.32) > |0.3 e 0.45) ¢ |0.5 f 0.5] > |0.1
errr ~~ - GB
Topic 21 Capacity and Mass
Measuring Capacity
1 Which unit would you use to measure the capacity of each object?
Circle the correct answer.
b
"iS litres
millilitres
d
litres
Measuring Mass
1 Estimate the mass of each object. Circle the mass that is closer.
c
2 Use this chart to record measurements of mass.
Object Estimate of Mass Actual Mass Difference
:
Textook 3 S09 Seg 100 5
2)
Workloco kk, Zoos (Beg 205
3
Rex oF 600g Boag 100g
4
Re — loos S009 Loog
5.
Tse 5
es Say 2459 18Sg
——eerrrerrrrr''i~rren @
Topic 22 Exploring Shapes
Lines of Symmetry
1 Circle the objects that are symmetrical.
2 Draw lines of symmetry through these shapes. Both sides must be
exactly the same.
3 Complete these shapes to make them symmetrical.
a b
Moving Shapes
1 a Draw four small, simple shapes on coloured paper. The shapes
should have straight and curved lines. Cut out your shapes.
b Trace each shape in the first column of the table.
c Move the shapes. Slide them, flip them and turn them. Complete
the table by drawing the shapes to show their positions when you
move them.
Shape Slide the Shape | Flip the Shape | Turn the Shape
Topic 23 Perimeter and Area
Perimeter
1 Measure and write down the perimeter of each shape.
c
A B
6am (Oom 1Ocmn
‘ » C)
t2Zam 19 -Bem A. Sern
2 Which shape has the greatest perimeter? Write them down in order
from the greatest to the least.
Shape oD |e | Be Ccy]eEILA
Perimeter 12 '9-B] 190 19 A516
om eres aa om am um
3 Draw two different shapes, A and B, each with a perimeter of 15 cm.
Measure and label the sides of your shapes.
Area
1 Find the area of each shape.
= one square centimetre
|
| |
] | ina |
| fof pt
[tT La
| | en
| | | | |
| oT |
LI] ILET TTI
A=__12 __ square cm B= __2\ _ square cm
— PTT
| | | ] ] ~
| L
1 | | |
| | | |
Lt L 1 | a
=___4 _ square cm D=___5 _ square cm
square cm
Fe__4 square cm
——eereer ~~ @
2 Draw the following figures on this squared grid.
a ashape with an area of 12 square cm
b ashape with an area of 18 square cm
¢ asmall animal with an area of 20-26 square cm
Topic 24 Probability
Certain, Possible and Impossible Events
1 Colour the counters in each bag so that the statements are true.
| A | ZA
It is possible to get red, but It is possible to get two
impossible to get yellow. red or two yellow.
>
a
You are certain to get It is possible to pull out
red or yellow. four different colours, but
impossible to get yellow.
a
eX
You are certain to get It is impossible to get
green or blue. red or yellow.
2 Read the information, then colour
the crayons.
@ Itis possible to choose a red,
blue or yellow crayon.
e Itis impossible to choose a
white or green crayon.
e You are certain to choose a
colour with an ‘e’ in its name.
3 Use the calendar for this month. Write three events in each column of
the chart.
This month, these events are:
impossible certain
possible
Topic 25 Mixed Measures
Working with Different Units
1 Draw lines to join the equivalent measurements. The first one has been
done for you.
100 cm 100 mm 50cm 2cm 2m
4m am 20mm 200 cm 10cm
2 Fill in the missing measurements.
atcm=| io mm bim=| iGo |em=|\o00 |mm
ce1ft =| iz in d} 3 ft=1 yard
3 Write each of these measurements in centimetres.
a4m =! poo fem b 12m =}1200 |cm
c 140mm = Vy jem didmand3cm =] 193 |cm
e 85mm = 3.5 |em f 9mand25cm = q25 |cm
RAR ARRAS
Equivalent Measurements
1 Complete the number sentences using equivalent measurements.
a 200cm=| 2 |m b 380cm =| 3 |m|go j|cm
c 201cm=| 2 |m} \ [cm d525cm =| S |m| 25 }|cm
e 1000cm=} 1G |m f 300 mm =| 3G |cm
g 2450cm =| 24. |m} SO {cm h San= Ss }mm
2 Karen walked 20 metres to Clare’s house, then turned around and
walked 50 metres in the other direction to John’s house.
a How many centimetres did she walk altogether?
NOOSE ceo Gor50 = jor)
b How many centimetres was she from her original starting point?
900 enn (5000 em — 2000= 3000 244)
w
Some units are missing from these equivalent measures.
Fill in the missing units.
a 316] cnn |= 3mand 16cm b 316] a. = 31 cmand 6 mm
c 316] ens]=3160mm d 316) day |= 3160cm
eo~------ --~-_-_--
Find the Mistakes!
There is a mistake in each of these calculations. Find the mistakes and
write the correct answers below each calculation.
(3)_ 3m 35cm __
—_ +4m 80cm _
— 7m5cm
—2m50cm X -7m 40cm xX
Hachette UK's policy is to use papers that are natural, renewable and recyclable products and made
from wood grown in sustainable forests. The logging and manufacturing processes are expected to
‘conform to the environmental regulations ofthe country of origin
(Orders: please contact Bookpoint Ltd, 130 Park Drive, Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxon OX14 ASE.
“Telephone: (44) 01235 827720. Fax: (44) 01235 400454. Email education@bookpoint.co.uk
Lines are open from 9 a.m. to 5 ppm. Monday to Saturday, with a 24-hour message answering
service. You can also order through our website: wivwhoddereducation.com
ISBN: 978 14718 6462.9
© Cloud Publishing Services 2016
First published in 2016 by
Hodder Education,
‘An Hachette UK Company
Carmelite House
50 Victoria Embankment
London ECAY oDZ.
swonwhoddereducation.com
Impression mumber 10987654321
Year 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016
All rights reserved, Apart from any use permitted under UK copyright law, no part of this
publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
‘mechanical, including photocopying and recording, or held within any information storage
and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher or under licence from
the Copyright Licensing Agency Limited. Further details of such licences (for reprographic
‘eproduction) may be obtained from the Copyright Licensing Agency Limited, Saffron House,
6-10 Kitby Street, London ECIN STS,
Cover photo © Giovanni Costa/123REcom
lustrations by Oxford Illustrators
‘Typesetin India by Aptara Inc.
Printed and bound by CPI Group (UK) Ltd, Croydon, CROAYY
‘A catalogue record for this ttl is available from the British Library
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- LANGAUGEDocument54 pagesLANGAUGETeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- AP-UN-CErt 2022Document117 pagesAP-UN-CErt 2022Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Sched 23 24Document4 pagesSched 23 24Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- MSCS 6 - Criteria For Distributive Justice 2Document20 pagesMSCS 6 - Criteria For Distributive Justice 2Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Tuition Fee BreakdownDocument1 pageTuition Fee BreakdownTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- PATIENCE GIVES pOSITIVE rESULTSDocument2 pagesPATIENCE GIVES pOSITIVE rESULTSTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Blue newCertificate-Participation-RedDocument2 pagesBlue newCertificate-Participation-RedTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Toddler Illustrated Preschool Report Card 1Document1 pageToddler Illustrated Preschool Report Card 1Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Special AwardDocument7 pagesSpecial AwardTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- United Nations Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument1 pageUnited Nations Reading Comprehension WorksheetTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- 6 Chroniclesand 5 KingsDocument20 pages6 Chroniclesand 5 KingsTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- AP First Quarterly ExamDocument5 pagesAP First Quarterly ExamTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Biprisa VocalDocument8 pagesBiprisa VocalTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Bryce Tuesday Sept 27Document10 pagesBryce Tuesday Sept 27Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Daphne Oct 16 SeatworkDocument1 pageDaphne Oct 16 SeatworkTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument11 pagesArtsTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Values 6Document3 pagesValues 6Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- MUSIC and HealthDocument13 pagesMUSIC and HealthTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- English - Many, Much, Few, and LittleDocument7 pagesEnglish - Many, Much, Few, and LittleTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Purple Modern Recording Microphone Instagram PostDocument3 pagesPurple Modern Recording Microphone Instagram PostTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 6 P. E 2 (Autosaved)Document10 pagesMapeh 6 P. E 2 (Autosaved)Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Values QuarterlyDocument6 pagesValues QuarterlyTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- MAPEH PTTDocument10 pagesMAPEH PTTTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Math 2ND Monthly Examination 12 14Document14 pagesMath 2ND Monthly Examination 12 14Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- MAPEH4 Second Quarterly Monthly 11 29Document2 pagesMAPEH4 Second Quarterly Monthly 11 29Teacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- G6 MapehDocument2 pagesG6 MapehTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- p7 Maths Mon 8th JuneDocument24 pagesp7 Maths Mon 8th JuneTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- Division of IntegersDocument19 pagesDivision of IntegersTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- G4 1ST MonthlyDocument3 pagesG4 1ST MonthlyTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- WEEK11 - Maths 6 - Percentage-Base-and-RateDocument24 pagesWEEK11 - Maths 6 - Percentage-Base-and-RateTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet