Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DENGUE
DENGUE
Uploaded by
aliciathalia290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesDengue is an acute febrile illness that presents with a range of symptoms from asymptomatic to severe. The most common symptoms include high fever over 38°C, headache, muscle and joint pain, and rash. For some patients, the fever subsides after 3-7 days but others progress to a critical phase with warning signs such as abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding and circulatory shock. Timely medical care is important to prevent deaths from severe dengue.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDengue is an acute febrile illness that presents with a range of symptoms from asymptomatic to severe. The most common symptoms include high fever over 38°C, headache, muscle and joint pain, and rash. For some patients, the fever subsides after 3-7 days but others progress to a critical phase with warning signs such as abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding and circulatory shock. Timely medical care is important to prevent deaths from severe dengue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesDENGUE
DENGUE
Uploaded by
aliciathalia29Dengue is an acute febrile illness that presents with a range of symptoms from asymptomatic to severe. The most common symptoms include high fever over 38°C, headache, muscle and joint pain, and rash. For some patients, the fever subsides after 3-7 days but others progress to a critical phase with warning signs such as abdominal pain, vomiting, bleeding and circulatory shock. Timely medical care is important to prevent deaths from severe dengue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
DENGUE
Symptoms and Signs
CID: A90
Dengue is an acute, systemic and dynamic febrile disease, ranging from
asymptomatic cases to serious conditions, including deaths. In symptomatic
cases, it may present three clinical phases: febrile, critical and recovery.
The first manifestation is fever, generally above 38ºC, with sudden onset and
lasting 2 to 7 days, associated with headache, tiredness, myalgia, arthralgia,
retro-orbital pain or rash. As the fever subsides (between the 3rd and 7th day
after the onset of symptoms), most patients gradually recover.
However, some may progress to the critical phase of the disease, starting with
warning signs.
.
Dengue fever can progress to remission of symptoms, or it can worsen,
requiring constant reassessment and observation, so that interventions are
timely and deaths do not occur.
.
What are the symptoms of dengue?
The main symptoms of dengue are
High fever > 38.5ºC.
Intense muscle pain.
Pain when moving the eyes.
Malaise.
Lack of appetite.
Headache.
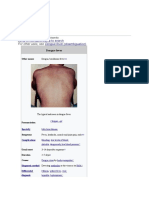
Red spots on the body.
However, dengue infection can be asymptomatic (without symptoms), mild or
severe. In the latter case it can lead to death. Normally, the first manifestation of
dengue fever is high fever (39° to 40°C), with an abrupt onset, which generally
lasts 2 to 7 days, accompanied by headache, body and joint pain, as well as
prostration, weakness , pain behind the eyes, rash and itchy skin. Weight loss,
nausea and vomiting are common. In some cases it also presents red spots on
the skin.
In the initial febrile phase of dengue fever, it can be difficult to differentiate. The
severe form of the disease includes intense and continuous abdominal pain,
persistent vomiting and mucosal bleeding. When experiencing symptoms, it is
important to seek a health service for adequate diagnosis and treatment, all
offered comprehensively and free of charge through the Unified Health System
(SUS).
Dengue warning signs:
Abdominal pain;
Persistent vomiting;
Fluid accumulation (ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion);
Postural hypotension and/or lipothymia;
Lethargy and/or irritability;
Hepatomegaly greater than 2cm below the costal margin;
Mucosal bleeding and;
Progressive increase in hematocrit.
You might also like
- Dengue FeverDocument10 pagesDengue Feversajeeb sarker100% (2)
- Lecture 07. Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument39 pagesLecture 07. Acute Rheumatic FeverImanuel Far-FarNo ratings yet
- Anti Inflammatory Diet Cookbook: Inflammation Be Gone! - Complete Clean Eating Meal Plans To Reduce Inflammation and Promote Gut Healing With Healthy Keto Air Fryer RecipesFrom EverandAnti Inflammatory Diet Cookbook: Inflammation Be Gone! - Complete Clean Eating Meal Plans To Reduce Inflammation and Promote Gut Healing With Healthy Keto Air Fryer RecipesNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Classic Dengue Fever Is Characterized by FeverDocument3 pagesSymptoms: Classic Dengue Fever Is Characterized by FevermackoypogiNo ratings yet
- Symptom Differences Between Zika, Chikungunya and Dengue FeverDocument4 pagesSymptom Differences Between Zika, Chikungunya and Dengue FeverHnia UsmanNo ratings yet
- Blood: Symptoms of Dengue FeverDocument7 pagesBlood: Symptoms of Dengue FeverPrincess Viluan PazNo ratings yet
- Dengue ReviewerDocument3 pagesDengue ReviewerSidney Bon LuceroNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument74 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverGERSON RYANTONo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Dian Refsi P00312017Document7 pagesDengue Fever: Dian Refsi P00312017RahmongNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument22 pagesDengueYumi MolinaNo ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIROSISDocument2 pagesLEPTOSPIROSISMarie JeanNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Considerations and Nursing Care ManagementDocument5 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Nursing Considerations and Nursing Care Managementjanns tumanengNo ratings yet
- Dengue Is The Fastest Spreading VectorDocument2 pagesDengue Is The Fastest Spreading VectorJudylyn SakitoNo ratings yet
- What Is Dengue FeverDocument6 pagesWhat Is Dengue Feveroctober_7No ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Is A Common MosquitoDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Is A Common MosquitoSri ParwatiNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever 03Document11 pagesDengue Fever 03Dr. GhauriNo ratings yet
- Recognizing Day To Day Signs and Symptoms of CoronavirusDocument1 pageRecognizing Day To Day Signs and Symptoms of CoronavirusMuhd AnasNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever - Docx SubaDocument6 pagesDengue Fever - Docx SubaZura ZahrinNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument3 pagesDengueManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation: It Is Studied Under 3 HeadingsDocument4 pagesClinical Manifestation: It Is Studied Under 3 HeadingsSahar JoshNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Facts: Headache Fever Joint Pain Swollen Glands Lymphadenopathy Rash Rash Headache Bleeding GumsDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Facts: Headache Fever Joint Pain Swollen Glands Lymphadenopathy Rash Rash Headache Bleeding GumsKeith Gulmatico FantinalgoNo ratings yet
- Pub HLT Ckik VDocument8 pagesPub HLT Ckik VKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations of Chikungunya Virus: Acute Disease 3-7 DaysDocument8 pagesClinical Manifestations of Chikungunya Virus: Acute Disease 3-7 DaysKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Dengue Prevention & Control ProgramDocument13 pagesDengue Prevention & Control ProgramJuliet Echo NovemberNo ratings yet
- What Is Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesWhat Is Dengue FeverMuhammad Saad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument5 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverRachma FadillahNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument7 pagesDengueHafsah MangarunNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument1 pageDengue Feverjchanti682No ratings yet
- Dengue: Cadawas, Daphne Gail S. BSN2-D5Document6 pagesDengue: Cadawas, Daphne Gail S. BSN2-D5Daphne Gail CadawasNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument13 pagesDengueHarshini ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument4 pagesDengueAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Dengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical ExaminationDocument3 pagesDengue Clinical Presentation - History, Physical ExaminationKeren Singam100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Feverdadah_09No ratings yet
- Background: What Are Dengue Fever Symptoms and Signs?Document12 pagesBackground: What Are Dengue Fever Symptoms and Signs?Hussain SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- DenguebsDocument7 pagesDenguebsAbdulwafi CamadNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument5 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverHarry SalinasNo ratings yet
- DHF SympDocument1 pageDHF SympArmenesNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Is A MosquitoDocument4 pagesDengue Fever Is A MosquitoPartha Permana PutraNo ratings yet
- Penegakan Diagnosis Dan Pengelolaan Pada Penderita Dengue Syok SyndromeDocument16 pagesPenegakan Diagnosis Dan Pengelolaan Pada Penderita Dengue Syok SyndromeArdityaNo ratings yet
- Zev - Dengue1Document1 pageZev - Dengue1zeverino castilloNo ratings yet
- Is It Dengue or Is It COVIDDocument5 pagesIs It Dengue or Is It COVIDKika PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever Case StudyDocument5 pagesDengue Fever Case StudyNadine PollescasNo ratings yet
- Flavivirus: Febrile Diseases Tropics Virus Serotypes FlaviviridaeDocument3 pagesFlavivirus: Febrile Diseases Tropics Virus Serotypes FlaviviridaeshezarNo ratings yet
- Dengue PresentationDocument12 pagesDengue Presentationmarjz20No ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument39 pagesAcute Rheumatic FeverUzma BanoNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument53 pagesDengue FeverAnnsha VeiNo ratings yet
- Alternative NamesDocument4 pagesAlternative NamesregineNo ratings yet
- Tugas Kelompok Ali & Nurrizky Fauzhi BAHASA INGGRISDocument4 pagesTugas Kelompok Ali & Nurrizky Fauzhi BAHASA INGGRISnurrizkyfauzhi66No ratings yet
- DengueDocument3 pagesDengueKASHYAPNo ratings yet
- DIREFDocument6 pagesDIREFRahmongNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Document7 pagesEtiologic Agent: Fatality As High As 40-50%Jolancr MarianoNo ratings yet
- What Is Dengue FeverDocument28 pagesWhat Is Dengue FeverNatalieNo ratings yet
- Early Symptoms of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesEarly Symptoms of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverAcohCChaoNo ratings yet
- Chemplast Cuddalore Vinyls Limited: Dengue Awareness ProgrammeDocument16 pagesChemplast Cuddalore Vinyls Limited: Dengue Awareness ProgrammeBala GaneshNo ratings yet
- Caused by The .: Dengue Dengue Fever Is ADocument2 pagesCaused by The .: Dengue Dengue Fever Is AEdrese AguirreNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument5 pagesDenguematin550% (2)
- JNWFBHJW Symptoms DFDocument5 pagesJNWFBHJW Symptoms DFwendyNo ratings yet
- Dengue OutlineDocument6 pagesDengue OutlineLouie George NeriNo ratings yet
- Still Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandStill Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet