Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiopulmonary Dysfunction Poster - Case Smith
Uploaded by
dominiquejonker05Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiopulmonary Dysfunction Poster - Case Smith
Uploaded by
dominiquejonker05Copyright:
Available Formats
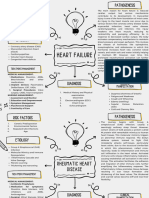
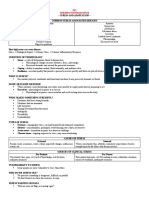
CARDIOPULMONARY
DYSFUNCTIONS
DEFINITION: CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
1. Patent ductus arteriousis:
Leads to heart failure and inadequate oxygenation to the brain
Conditions that affect 2. Atrial septal defects (ASD):
cardio (heart) and Opening in septum between the left and right atrial chambers
pulmonary (lungs) systems Poor exercise tolerance
Congenital and/or Small size for child’s age
acquired conditions that 3. Ventricular septal defects:
affect a child’s health and Opening in the muscular or membranous part of the
ventricular septum
ability to participate in
Feeding problems
occupations
Shortness of breath
Increased persperation
Fatigue during physical activity
CYSTIC FIBROSIS ASTHMA
Chronic inflammatory disorder
Highly prevelant inherited condition
May be an inherited trait from family
Leads to the production of thick and viscuous member
secretions accumilating in the lungs Exposure to certain materials may
Therapy requirements: trigger an attack
1. Pulmonary therapy Teach child to manage condition
2. Inhalation therapy Education on stress management on
3. Chest physical therapy slow controlled breathing exercises
4. Nutritional therapy
DYSRHYTMIAS NEONATAL RESPIRATORY
PROBLEMS
Irregular cardiac rhythms
Causes:
1. Bradydysrhythmia:
1. Prematurity
Abnormally slow heart rate
2. Aspiration
2. Tachydysrhythmia:
3. Malformation of respiratory system
Abnormally fast heart rate
4. CNS damage
3. Conduction disturbances
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS): Common at
birth
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Extracardiac Signs of Fluid Overload in The Critically IllDocument13 pagesExtracardiac Signs of Fluid Overload in The Critically IllBlanca Herrera MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - Dr. Allam 2021Document141 pagesCardiology - Dr. Allam 2021MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oral RevalidaDocument14 pagesOral RevalidaAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Total Health Chapter 1,2 Review GameDocument123 pagesTotal Health Chapter 1,2 Review GameAlicia HigdonNo ratings yet
- Biological BeginningsDocument24 pagesBiological BeginningsRabia DastiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDocument5 pagesTherapeutics - Gastrointestinal Tract: Heart FailureDarnell DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Kegawatan Napas Pada AnakDocument43 pagesKegawatan Napas Pada AnakRaelna SahaarNo ratings yet
- NCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIDocument46 pagesNCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Arrest and InsufficiencyDocument6 pagesRespiratory Arrest and InsufficiencyGetom Ngukir100% (1)
- Vol 19.1 - Sleep Disorders.2013Document252 pagesVol 19.1 - Sleep Disorders.2013Martoiu MariaNo ratings yet
- Veolia Water Tech AUS PharmaDocument7 pagesVeolia Water Tech AUS Pharmamanojdhamne5802No ratings yet
- Capstone ReportDocument39 pagesCapstone ReportSai MaheshNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Disease - SeminarDocument35 pagesCongenital Heart Disease - SeminarAsha jilu100% (2)
- (Atherosclerosis) - Accumulated PlaquesDocument7 pages(Atherosclerosis) - Accumulated PlaquesJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument17 pagesAddison's DiseaseMah Jezthy100% (1)
- NSG125 - Oxy Concept MapDocument6 pagesNSG125 - Oxy Concept Maplaurie.charlynjaneNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Handout 1Document3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Handout 1Alekxandra Erl ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Global Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNDocument14 pagesGlobal Nursing Pediatrics. Nclex - RNNANANo ratings yet
- Pediatric Basic Life SupportDocument3 pagesPediatric Basic Life Supportgail100% (1)
- PPW 3rd CasestudyDocument31 pagesPPW 3rd Casestudyfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- CHF NewDocument7 pagesCHF NewJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease NotesDocument4 pagesCardiac Disease NotesKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureJohn Vincent RiveraNo ratings yet
- IIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument14 pagesIIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular DisordersDocument43 pagesNeuromuscular DisordersReem 10No ratings yet
- ACCIDENTSDocument3 pagesACCIDENTSjohn_eisma_1No ratings yet
- Case 2Document41 pagesCase 2JUVIELY PREMACIONo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiology: Jocelyn C. BanataoDocument12 pagesPediatric Cardiology: Jocelyn C. BanataoCms CSUNo ratings yet
- Indanan - Individual RequirementsDocument36 pagesIndanan - Individual RequirementsMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- MusculardystropyDocument10 pagesMusculardystropy22118900011No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Vs SCDDocument1 pageCardiac Arrest Vs SCDNanda SaputraNo ratings yet
- OldDocument7 pagesOldROSE COLLINSNo ratings yet
- Disnea - Rosen - 230526 - 125351Document10 pagesDisnea - Rosen - 230526 - 125351Pablo BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataMoonNo ratings yet
- SPED REVIEWER by DHENdhen2Document9 pagesSPED REVIEWER by DHENdhen2Michael SomeraNo ratings yet
- SPED REVIEWER by DHENdhenDocument8 pagesSPED REVIEWER by DHENdhenMichael SomeraNo ratings yet
- Risk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesRisk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputMICHELLE FACTONo ratings yet
- Dyspnea - DR AllenDocument50 pagesDyspnea - DR AllenalmiraerickaiNo ratings yet
- Peros: General AssessmentDocument4 pagesPeros: General AssessmentKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Ngeles Niversity Oundation: Module #8Document8 pagesNgeles Niversity Oundation: Module #8hamisiNo ratings yet
- Stress and AdaptationDocument4 pagesStress and AdaptationAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Nurul Ilmi Hajar (PO.71.3.201.14.1.130) Nurul Khabliana (PO.71.3.201.14.1.131)Document27 pagesNurul Ilmi Hajar (PO.71.3.201.14.1.130) Nurul Khabliana (PO.71.3.201.14.1.131)Nurulilmi hajarNo ratings yet
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersDocument13 pages1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit On Myocardial Infarction: College of NursingDocument16 pagesResource Unit On Myocardial Infarction: College of NursingJoi Owen TevesNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Lec MidtermsDocument8 pagesNCM 109 Lec MidtermsAngel Kim MalabananNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DisorderDocument4 pagesCongenital Heart DisorderElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Health ModuleDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Health Modulenuera.christilahNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIDocument5 pagesCoronary Artherosclerosis - ACS and MIAila HinlogNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Breath Holding Spells in ChildrenDocument4 pagesReview Article: Breath Holding Spells in ChildrenMuh Ridho AkbarNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Myocardial InfarctionDocument7 pagesCare of Clients With Myocardial InfarctionaryshamyleeNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: San Lorenzo Ruiz College of Ormoc Brgy. San Pablo St. Ormoc City, LeyteDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: San Lorenzo Ruiz College of Ormoc Brgy. San Pablo St. Ormoc City, LeytePangalan ApelyidoNo ratings yet
- CasisDocument3 pagesCasisWilfredo PesanteNo ratings yet
- Acquired Cardiac DisordersDocument40 pagesAcquired Cardiac DisordersRajaNo ratings yet
- Geriatric SyndromeDocument49 pagesGeriatric Syndromewita prabawatiNo ratings yet
- Ijccm 23 s129Document7 pagesIjccm 23 s129Sonu AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke - 3B5Document77 pagesIschemic Stroke - 3B5Aireen Grace GilosNo ratings yet
- Types of Heart Failure DescriptionDocument28 pagesTypes of Heart Failure DescriptionDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Sick Sinus Syndrom PDFDocument8 pagesSick Sinus Syndrom PDFSigit PratamaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document2 pagesLesson 2Gwyneth Hezekiah PradoNo ratings yet
- Neurocardio NursingDocument101 pagesNeurocardio NursingMatt Lao DionelaNo ratings yet
- Drug Use DisorderDocument10 pagesDrug Use Disordergeng gengNo ratings yet
- Phctlec - Topic 3&4 - PrelimsDocument24 pagesPhctlec - Topic 3&4 - PrelimsasdfdjfeonaNo ratings yet
- Neuro Across - HandoutDocument10 pagesNeuro Across - HandoutLouie MartinezNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0749070421000956 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0749070421000956 MainEliseu AmaralNo ratings yet
- CHD SeminarDocument69 pagesCHD SeminarSayyed Ahmad KhursheedNo ratings yet
- Obcl - 2 - Cu - Week 4 CHFDocument8 pagesObcl - 2 - Cu - Week 4 CHFMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Lagermeister XXL-SDSDocument6 pagesLagermeister XXL-SDSPratik MoreNo ratings yet
- Ingles Compresion LectoraDocument6 pagesIngles Compresion LectoraAlvaro Josue HernandezNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper MULANAYDocument2 pagesReflection Paper MULANAYRob40% (5)
- Student Assessment Booklet: CHC33015 C III I SDocument23 pagesStudent Assessment Booklet: CHC33015 C III I SSibani Kar0% (1)
- Mindfulness and PTSDDocument19 pagesMindfulness and PTSDJosie VuckovichNo ratings yet
- Speaking Test (15-20)Document12 pagesSpeaking Test (15-20)Phạm Mai Hương100% (1)
- Communication and Nutrional EducationDocument11 pagesCommunication and Nutrional EducationSabrina PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Mcas Questions 1 2015Document3 pagesCarbohydrate Mcas Questions 1 2015api-263230840No ratings yet
- Angelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1Document5 pagesAngelina Hull Student - Heritagehs - Argumentative Essay - Student Name - Class Period - Spring 19 - H English 1api-461590822No ratings yet
- NZ Physiotherapy Code of Ethics Final 0Document6 pagesNZ Physiotherapy Code of Ethics Final 0Pintilie MihaelaNo ratings yet
- CID Cheese Mozzarella LiteDocument8 pagesCID Cheese Mozzarella LiteBayu SyurahmadNo ratings yet
- Neonatal MeningitisDocument24 pagesNeonatal MeningitisHelena Trinina Saragih100% (1)
- Purpose of Travel - SampleDocument3 pagesPurpose of Travel - SampleVirat GadhviNo ratings yet
- ANGIOSARCOMA pdf3 PDFDocument9 pagesANGIOSARCOMA pdf3 PDFعبدالعزيز عماد محمودNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Hazard PreventionDocument10 pagesOccupational Health and Hazard PreventionCarla Mae OlvenarioNo ratings yet
- 4217 - First Aid and Safety EducationDocument6 pages4217 - First Aid and Safety EducationSalahuddeen AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Contribution - 2019 - She Ji The Journal of Design Economics and InnovationDocument1 pageContribution - 2019 - She Ji The Journal of Design Economics and InnovationnitakuriNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever 2Document5 pagesDengue Fever 2Gayitiri MenonNo ratings yet
- Tips On NURSING LICENSURE EXAM PDFDocument4 pagesTips On NURSING LICENSURE EXAM PDFCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Superposition Principle, Repetitive IV, Drug Clearance (Sir Imran)Document21 pagesSuperposition Principle, Repetitive IV, Drug Clearance (Sir Imran)Rafay Sarwar MughalNo ratings yet
- Inclusivness AssignmentDocument17 pagesInclusivness AssignmentEphrem ChernetNo ratings yet
- Ralph E. Strobel: Professional SummaryDocument3 pagesRalph E. Strobel: Professional Summaryapi-354918865No ratings yet