Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Transfusion
Uploaded by
Jona Mae Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesncma 217
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentncma 217
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesBlood Transfusion
Uploaded by
Jona Mae Ramosncma 217
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
I.
BLOOD TRANSFUSION
- The introduction of whole blood or
components of the blood
(plasma, serum, erythrocytes or
platelets) into the venous circulation.
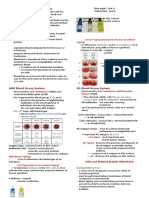
ABO BLOOD GROUP SYSTEM
- TYPE A
o Antigen (A)
o Antibodies (B)
- TYPE B
o Antigen (B)
o Antibodies (A)
- TYPE AB III. RH FACTOR
o Antigen (AB) - Another consideration when matching blood
o Antibodies (none) universal components
recipient - Refers to another antigen in RBC membranes
- TYPE O Rh (+) has an Rh antigen
o Antigen (none) Rh (+) does not produce antibody
o Antibodies (AB) universal donor Rh (-) has no Rh antigen
Rh (-) produces antibody
Who can give to whom?
o Rh (+) can donate to Rh (+) but can’t
donate to Rh (-)
o Rh (-) can donate both to Rh (-) and Rh
(+)
Who can receive from whom?
o Rh (+) can receive Rh (+) or Rh (-)
o Rh (-) can only get Rh (-)
IV. BLOOD TYPES
A+, A-
B+, B-
AB+, AB-
O+, O-
II. TERMINOLOGIES V. HEMATOLOGIC SYSTEM
FFP – fresh from plasma WBC (leukocytes) 4500-11000/cu mm
PRBC – packed red blood cell o Fights infection
ANTIGEN – agglutinogens NEUTROPHIL 45-73%
Rh – Rhesus o Prevents and limits bacterial infection
NEUTROPENIA – low neutrophil MONOCYTES 2-8%
NEUTROPHILIA – high neutrophil o As macrophage, highly phagocytic,
MONOCYTOPENIA – low fungus
EOSINOPHILIA – high EOSINOPHILS 0-4%
EOSINOPENIA – low o Allergic reactions
BASOPHILIA – high BASOPHILS
BASOPENIA – low o Contains histamine
LYMPHOCYTOSIS – high LYMPHOCYTES 20-40%
LYMPHOCYTOPENIA – low o Integral component of immune
system
T LYMPHOCYTES
o Cell-mediated immunity, recognizes
material as foreign body
(surveillance)
B LYMPHOCYTES
o Humoral immunity, form antibodies
RBC o 85% of people is Rh (+)
o Carries hemoglobin, average life span
120 days
PLATELET 150000-400000/mm3 IX. NURSING CARE
o Hemostasis, life span 10 days Assess history of allergy
Ensure that the IV catheter is 18 or 19g
Use .9 Nacl
VI. BLOOD PRODUCTS AND USE Verify the blood
Whole blood Take baseline vital signs
o Replaces blood volume and all blood Start transfusion slowly
products Stay with the client during the initial 15min
Red blood cell Maintain the transfusion rate
o Increase oxygen carrying capacity of o FWB – (3-4 HRS)
blood o PRBC – (2-4HRS)
Platelets o FFP, platelets, cryoprecipitate – fast
o Replaces platelets for clients with drip
bleeding disorders or platelet Monitor adverse reaction
deficiency Document the ff:
Fresh from plasma o Blood component and number
o Expands blood volume and provides o Infusion started and ended
clotting factors o Client reaction
Autologous red blood cell
o Use for blood replacement following
planned elective surgery
X. MATERIALS NEEDED
Clotting factors and cryoprecipitate
IV tray
o Used for clients with clotting factors
Compatible BT set
deficiencies
IV catheter /needle g 18/19
Albumin and plasma protein factor
Plaster
o Blood volume expanders provides
Tourniquet
plasma proteins
Blood product
Plain NSS
IV stand
VII. BLOOD TRANSFUSION PURPOSE
Gloves
- To increase O2 carrying capacity of blood as
in anemia
INITIATING BLOOD THERAPY
- To replace circulating blood volume or as
- Verified health care provider’s order for
volume expansion (WB) for cases of
specific blood of blood product and all
hemorrhage
pertinent information
- Provision of protein
- Provision of coagulation factors XI. HEMOLYTIC REACTION
(cryoprecipitate, FFP, FWB) - Blood donor is incompatible with the recipient
- To prevent bleeding if there’s platelet blood
deficiency - Most fatal, may present chills, diaphoresis and
- To combat infection if there’s decrease WBC back pains
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
o Headache
o Dizziness
o Dyspnea
o Palpation and tachycardia
o Lumbar/sterna/flank pain
o Hypotension
VIII. NURSING MGT & PRINCIPLES IN o Flushed skin’
BLOOD TRANSFUSION o (red) pot wine urine
- Proper refrigeration NURSING MGT.
- Proper typing & cross matching o Stop BT- remove and change the tubing
o TYPE O – universal donor o Notify doc
o AB – universal recipient o Flush with plain NSS
o Administer isotonic fluid solution to o Dyspnea
counteract shock o Orthopnea
o Send blood unit to blood bank for o Rales & crackles
reexamination o Tachycardia and hypertension
o Obtain urine & blood samples of pt &
send to lab for reexamination NURSING MGT.
o Monitor VS & allergic reaction o Stop BT and place the client upright with
feet dependent
XII. ALLERGIC REACTION o Notify doc, don’t flush due pt has
- Rashes and itchiness, dyspnea, bronchospasm circulatory overload
due to sensitivity in foreign proteins in plasma o Administer diuretics
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
o Fever/chills
o Urticaria/pruritus XV. SEPSIS
o Dyspnea - Contaminated blood administered
o Laryngospasm/bronchospasm
o Bronchial wheezing WATCH OUT FOR:
NURSING MGT. o High fever
o Stop BT o Chills
o Notify doc o Vomiting
o Flush with PNSS o Diarrhea
o Administer antihistamine – o Hypotension
diphenhydramine Hd (Benadryl)
o If (+) hypotension – anaphylactic shock. NURSING MGT.
administer – epinephrine o Stop
o Send blood unit to blood bank o KVO with NSS
o Obtain urine & blood samples – send to o Notify the MD
lab o Administer IVF and antibiotics as ordered
o Monitor VS & IO
o Administer antihistamine as ordered for PRIORITY CASES
allergic reaction o 1ST HEMOLYTIC REACTION -due to
o Administer antipyretic & antibiotic for hypotension- attend to destruction of Hgb
pyrogenic reaction & TSB -O2 brain damage
o 2nd CIRCULATORY OVERLOAD
o 3rd -ALLERGIC REACTION
XIII. PYROGENIC REACTION o 4TH - PYROGENIC
- Fever and chills due to sensitivity to leukocyte
or platelet antigen – most common
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
o Fever/chills
o Tachycardia
o Headache
o Palpations
o Dyspnea
o Diaphoresis
NURSING MGT.
o Stop BT
o Notify doc
o Flush with PNSS
o Administer antipyretics, antibiotics
o Send blood unit to blood bank
o Obtain urine & blood samples -send to lab
o Monitor VS & IO
XIV. CIRCULATORY OVERLOAD
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
You might also like
- Immunohema Transfusion MedDocument62 pagesImmunohema Transfusion MedyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Blood TX & Bone MarrowDocument12 pagesBlood TX & Bone Marrowqueen TinaNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology ASCPi Review Booklet (Part 2)Document21 pagesImmunohematology ASCPi Review Booklet (Part 2)Mark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- BLOOD GROUPS TYPING - PowerpointDocument38 pagesBLOOD GROUPS TYPING - PowerpointJoy SNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument74 pagesCirculatory Systemmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- MBBS - Blood Groups - 2020Document30 pagesMBBS - Blood Groups - 2020Abdullah AlthobaitiNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups and Blood TransfusionDocument18 pagesBlood Groups and Blood TransfusionAbdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument14 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationictmi45No ratings yet
- Blood TranfusionDocument4 pagesBlood TranfusionVia Kristel ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Forensic SerologyDocument13 pagesForensic Serologyempress venus bonillaNo ratings yet
- General Technique Agglutination Antigen + Antibody Red Cell Agglutination VisualisationDocument21 pagesGeneral Technique Agglutination Antigen + Antibody Red Cell Agglutination VisualisationKareem MubarakNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 1Document10 pagesLesson 2 1JASPER PENALBANo ratings yet
- How to Give a Safe Blood TransfusionDocument6 pagesHow to Give a Safe Blood TransfusionMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Blood: I) - Functions A) - Distribution B) - Regulation C) - ProtectionDocument17 pagesBlood: I) - Functions A) - Distribution B) - Regulation C) - ProtectionTarkan DemirNo ratings yet
- BBDocument6 pagesBBFrey Mary Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Blood Banking by BMTDocument126 pagesBlood Banking by BMTRachel Marie M. Gania100% (2)
- Physiology Chapter 3 BloodDocument31 pagesPhysiology Chapter 3 Bloodbitaniyanassir10No ratings yet
- Blood Case 6Document12 pagesBlood Case 6إنعام الحفيانNo ratings yet
- Blood Abo Group SystemDocument5 pagesBlood Abo Group Systemshapan biswaNo ratings yet
- 18BTC106J Lab ManualDocument49 pages18BTC106J Lab ManualpalrohangcptNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping and RH TypingDocument4 pagesBlood Grouping and RH TypingJeevs MusicNo ratings yet
- Immunhematologie Basic 2013Document87 pagesImmunhematologie Basic 2013Rusmin NoryadinNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood GroupDocument23 pagesABO Blood Groupboo.seungkwannieNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument28 pagesBlood Transfusionفيصل فهدNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupingDocument67 pagesBlood GroupingSandhra UsmanNo ratings yet
- Trans - Med (Chap. 109 Transfusion Biology and Therapy) PDFDocument8 pagesTrans - Med (Chap. 109 Transfusion Biology and Therapy) PDFMary Stephanie Parcon ChongNo ratings yet
- FORWARD AND REVERSE BLOOD TYPINGDocument10 pagesFORWARD AND REVERSE BLOOD TYPINGDanica AgojoNo ratings yet
- Blood Banking History and FundamentalsDocument60 pagesBlood Banking History and FundamentalsPerlie CNo ratings yet
- Notes-Body Fluids & CirculationDocument16 pagesNotes-Body Fluids & CirculationKisna guptaNo ratings yet
- 5 IhDocument61 pages5 IhGennelyn Ross Delos Reyes0% (1)
- Blood TypingDocument4 pagesBlood TypingMuhammad FurqanNo ratings yet
- Must Know To Identify Your Machine Depends On What SectionDocument32 pagesMust Know To Identify Your Machine Depends On What SectionAsxe CeeNo ratings yet
- Abobloodgroupsystem 170121130000Document31 pagesAbobloodgroupsystem 170121130000ashu pandeyNo ratings yet
- ABO Compatibilities For Transfusion Therapy: Donor RecipientDocument6 pagesABO Compatibilities For Transfusion Therapy: Donor RecipientDexie James Ventenilla DizonNo ratings yet
- 12 - Blood Groups and Blood Transfusion 2018Document27 pages12 - Blood Groups and Blood Transfusion 2018gimspath cme2022No ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion FinalDocument107 pagesBlood Transfusion Finalsanthiyasandy100% (11)
- Blood TransfusionDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusionrhenier_iladoNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group System RH Blood Group SystemDocument2 pagesABO Blood Group System RH Blood Group SystemDannie Desaca100% (1)
- The Cardiovascular System 3Document17 pagesThe Cardiovascular System 3aboody62621No ratings yet
- Abo Blood RH GroupingDocument22 pagesAbo Blood RH GroupingĐỗ Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument13 pagesBlood GroupsriantimuharromiNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group System NotesDocument45 pagesABO Blood Group System NotesAnne Carmel Verano100% (1)
- Transport & Excretion: StepsDocument5 pagesTransport & Excretion: StepsRahul EckaNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument53 pagesBlood GroupsSneh KevadiyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Group (استرداد) صيدله ثاني.2Document3 pagesBlood Group (استرداد) صيدله ثاني.2محمد أحمد علي العبشNo ratings yet
- DR - Jaisankar.P.: Blood Grouping and Transfusion TherapyDocument63 pagesDR - Jaisankar.P.: Blood Grouping and Transfusion TherapyDrSanjeev ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ABO and RH Blood Group SystemDocument31 pagesABO and RH Blood Group SystemKaab Ishaq100% (1)
- Blood Groups & CoagulationDocument12 pagesBlood Groups & CoagulationRAVI KANT PATELNo ratings yet
- Biology - Human Transport NotesDocument4 pagesBiology - Human Transport Notesacsbr4science133% (3)
- Blood Types & Transfusion CompatibilityDocument27 pagesBlood Types & Transfusion CompatibilityfamtaluNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Common Clinical Lab TestsDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Common Clinical Lab TestsPrincess EscandalloNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument14 pagesBlood GroupsIsaac MapulangaNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood GroupDocument12 pagesABO Blood GroupGhost AnkanNo ratings yet
- B F C C 18: ODY Luids AND IrculationDocument12 pagesB F C C 18: ODY Luids AND Irculation07 mathsNo ratings yet
- Blood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Document11 pagesBlood Typing Activity For Lab Practical 2Liliana PerezNo ratings yet
- Typing, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodDocument55 pagesTyping, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodAsad MirzaNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups: 1 PhysiologyDocument36 pagesBlood Groups: 1 PhysiologyAkash JaatNo ratings yet
- 7 - Blood and The Immune SystemDocument38 pages7 - Blood and The Immune SystemMinh Thiên VõNo ratings yet
- Blood Group Substances: Their Chemistry and ImmunochemistryFrom EverandBlood Group Substances: Their Chemistry and ImmunochemistryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)