Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Eye and The Colourful World Previous Years Questions
Uploaded by
singhmrinalini1305Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Eye and The Colourful World Previous Years Questions
Uploaded by
singhmrinalini1305Copyright:
Available Formats
11- Human Eye and the Colourful World
1 Mark
1. Name the part of our eyes that helps us to focus near and distant objects in quick succession. [CBSE,2010]
2 Mark
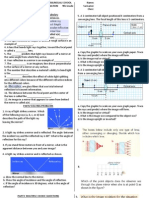
2. In a figure given below a narrow beam of white light is shown to pass through a triangular glass prism. After passing
through the prism it produces a spectrum 𝑋𝑌 on a screen. [CBSE,2010]
A. State the colour seen at 𝑋 and 𝑌.
B. Why do different colours of white light bend through different angles with respect to the incident beam of light?
3 Marks
3. What is meant by scattering of light? Use this phenomenon to explain why the clear sky appears blue or the sun appears
reddish at sunrise. [CBSE,2015]
4. Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light split by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light
by another identical glass prism. Also draw ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
[CBSE,2016]
5. State the cause of dispersion of white light by a glass prism. How did Newton, using two identical glass prisms, show
that white light is made of seven colours? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a narrow beam of white light, through
a combination of two identical prisms arranged together in inverted position with respect to each other, when it is
allowed to fall obliquely on one of the faces of the first prism of the combination. [CBSE,2017]
5 Marks
6. A. What is meant by dispersion of white light? Describe the formation of rainbow in the sky with the help of a diagram.
B. What is hypermetropia? Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation of an object by :
i. Hypermetropic eye
ii. Correction made with a suitable lens for hypermetropic eye.
OR
A. Give reasons for the following :
i. Colour of the clear sky is blue.
ii. The sun can be seen about two minutes before actual sunrise.
iii. We cannot see on object clearly if it is placed very close to the eyes.
B. What is Presbyopia? Write two causes of this defect. [CBSE,2008]
7. A. What is myopia? State the two causes of myopia. With the help of labelled ray diagrams show
i. the eye defect myopia.
ii. correction of myopia using a lens.
B. Why is the normal eye unable to focus on an object placed within 10 𝑐𝑚 from the eye?
OR
A. What is dispersion of white light? What is the cause of such dispersion? Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of
white light by a glass prism.
B. A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce
any spectrum. Explain why it is so. [CBSE,2009]
Avanti – 11- Human Eye and the Colourful World
8. Write the importance of ciliary muscles in the human eye. Name the defect of vision that arises due to gradual
weakening of the ciliary muscles in old age. What type of lenses are required by the persons suffering from this defect
to see the objects clearly? Akshay, sitting in the last row in his class, could not see clearly the words written on the
blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to
exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. He could now see the
words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it fit to send the message to Akshay’s parents advising
them to get his eyesight checked. In the context of the above event, answer the following questions :
A. Which defect of vision is Akshay suffering from? Which type of lens is used to correct this defect?
B. State the values displayed by the teacher and Salman.
C. In your opinion, in what way can Akshay express his gratitude towards the teacher and Salman? [CBSE,2015]
9. What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events. [CBSE,2016]
A. Twinkling of stars
B. Advanced sun-rise and delayed sun-set.
C. Draw diagram to illustrate your answers
10. A. A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 𝑚. List two possible
reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen. With the help of ray diagrams, explain
i. why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.
ii. the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this defect is corrected by the use of this
lens.
B. If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is 5 m, find the power of the lens as per
the new Cartesian sign convention. [CBSE,2017]
Practical Based Questions
1 Mark
11. A student traces the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism for different values of angle of incidence. On
analyzing the ray diagrams, which one of the following conclusions is he likely to draw? [CBSE,2015]
A) The emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.
B) The emergent ray bends at an angle to the direction of the incident ray.
C) The emergent ray and the refracted ray are at right angles to each other.
D) The emergent ray is perpendicular to the incident ray
12. In the following ray diagram the correctly marked angle are : [CBSE,2016]
A) ∠𝑖 and ∠𝑒 B) ∠𝐴 and ∠𝐷 C) ∠𝑖, ∠𝑒 and ∠𝐷 D) ∠𝑟, ∠𝐴 and ∠𝐷
13. Study the following ray diagram :
In this diagram, the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively have been
represented by [CBSE,2017]
A) 𝑦, 𝑝, 𝑧 B) 𝑥, 𝑞, 𝑧 C) 𝑝, 𝑦, 𝑧 D) 𝑝, 𝑧, 𝑦
Avanti – 11- Human Eye and the Colourful World
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument2 pagesAssignment - Human Eye and The Colourful Worldkrish.meenaaaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colourful World Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceDocument4 pagesHuman Eye and The Colourful World Previous Year Questiosn Class 10 ScienceZhugzhuang ZuryNo ratings yet
- Refraction Important Question Answers PDFDocument12 pagesRefraction Important Question Answers PDFprakashNo ratings yet
- Bifocal Lens Corrects Myopia and HypermetropiaDocument13 pagesBifocal Lens Corrects Myopia and HypermetropiaanandatulNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Avanti inDocument4 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Avanti inS Banerjee100% (1)
- Optics: 1 MarksDocument19 pagesOptics: 1 MarksTJSinghNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Physics - Revison Worksheet 2 - Human Eye and Colourful World - 2018-19Document3 pagesClass - X - Physics - Revison Worksheet 2 - Human Eye and Colourful World - 2018-19aayush619_com3918No ratings yet
- PYQs Mid Term CH 10 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument39 pagesPYQs Mid Term CH 10 Human Eye and The Colourful Worldeekshi0003No ratings yet
- Refraction Important Question AnswersDocument9 pagesRefraction Important Question AnswersprakashNo ratings yet
- 614202015946PM-Class 10 Physics Notes-Reflection and RefractionDocument10 pages614202015946PM-Class 10 Physics Notes-Reflection and RefractionMd ShariqueNo ratings yet
- HumanEye and Colourful World 7Document26 pagesHumanEye and Colourful World 7VinodKumarTummalurNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument11 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsAdarsh BhushanNo ratings yet
- 06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFDocument12 pages06 Human Eye and Colourful World Chapter Wise Important Questions PDFTannu KaurNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions - I (PYQ) : - F RespectivelyDocument18 pagesShort Answer Questions - I (PYQ) : - F Respectivelyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument12 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful Worldtrijal bhagatNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions, CBSE Sample Papers, Textbook SolutionsDocument27 pagesNCERT Solutions, CBSE Sample Papers, Textbook SolutionsSreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- ReflnDocument20 pagesReflnDaniel Boenfie100% (1)
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument2 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldpmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Human Eye (PYQs)Document11 pagesHuman Eye (PYQs)Sam BasNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions Light Reflection RefractionDocument37 pagesCBSE Class 10 Important Questions Light Reflection RefractiontummalaajaybabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldAdityaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Light Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark QuestionsDocument19 pagesLight Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark Questionsmayank007aggarwal100% (1)
- Cbse 7 LightDocument1 pageCbse 7 LightSagar NaikNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Colour Vision Defects Lenses PrismDocument2 pagesHuman Eye Colour Vision Defects Lenses PrismpmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Human Eye DhruvDocument6 pagesHuman Eye Dhruvswapnali bhutadaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper on Human Eye and VisionDocument5 pagesCBSE Test Paper on Human Eye and VisionTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- Human Eye AssignmentDocument6 pagesHuman Eye Assignmentrishabhsharma94163No ratings yet
- Answers - Worksheet - Homework - 10th - Science - 2023-06-26T11 - 30Document4 pagesAnswers - Worksheet - Homework - 10th - Science - 2023-06-26T11 - 30Aayush ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science Light Worksheets With Answers - Chapter 16Document3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Light Worksheets With Answers - Chapter 16Rayrc Pvt Ltd100% (1)
- Human Eye and The Colorful World: 1. One Mark QuestionsDocument11 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorful World: 1. One Mark Questionsrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- CBSE TEST PAPER-02 CLASS - X (Human Eye and the Colourful WorldDocument1 pageCBSE TEST PAPER-02 CLASS - X (Human Eye and the Colourful WorldSylvester GomesNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument33 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionshreyasbandi0904No ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd 18-19Document4 pagesScience 10 2nd 18-19Ryan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Science 10 2nd 18-19Document4 pagesScience 10 2nd 18-19Ryan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document9 pagesModule 6chef curryNo ratings yet
- 11-2 (1)Document5 pages11-2 (1)paparaoNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 Class - XII Physics (Ray Optics)Document1 pageCbse Test Paper-02 Class - XII Physics (Ray Optics)rahulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - 14 XII Physics Important Question SDocument24 pagesChapter 9 - 14 XII Physics Important Question SNirma SoniaNo ratings yet
- Class Test 10 (RRH)Document3 pagesClass Test 10 (RRH)Jeevanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsDocument10 pagesActivity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsMarley Chelsea LevantinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document8 pagesUnit 16 (Light) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Narsi KumarNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 LightDocument14 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 16 Lightanvu4848100% (1)
- Most Repeated PYQS Science - HUMAN EYEDocument7 pagesMost Repeated PYQS Science - HUMAN EYEpvkff1234No ratings yet
- 10 Science Exemplar Chapter 11 SQDocument4 pages10 Science Exemplar Chapter 11 SQPoojitha kamarajNo ratings yet
- Light Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark QuestionsDocument19 pagesLight Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark Questionsrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- Chung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Document16 pagesChung Cheng High School (Main) Sec 1 Physics Chapter E3Ken TanNo ratings yet
- Optics TestDocument2 pagesOptics TestiskenderbeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADocument9 pagesChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNo ratings yet
- BAL BHAVAN PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT RAY OPTICSDocument9 pagesBAL BHAVAN PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT RAY OPTICSKaran RanaNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023Document7 pagesHuman Eye Adhyasa Deepika 2022-2023prakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - QWADocument23 pagesChapter 11 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Type QuestionsDocument2 pagesMCQ Type QuestionsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument13 pagesReflectionRajesh kuamrNo ratings yet
- MirrorsandLensesQuiz 1Document3 pagesMirrorsandLensesQuiz 1eenamorataNo ratings yet
- LightDocument6 pagesLightVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15Document7 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15deepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Geoteknik - Analisis Stabilitas Lereng Dengan Metode GrafisDocument24 pagesGeoteknik - Analisis Stabilitas Lereng Dengan Metode Grafisrandi saimonaNo ratings yet
- B-14-03925 KMT Technical Engineering Guide DensalloyDocument46 pagesB-14-03925 KMT Technical Engineering Guide DensalloyElMacheteDelHuesoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDocument16 pagesChapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDimple Sharma100% (1)
- 10th Intro To TrigoDocument11 pages10th Intro To TrigoDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Science 8Document2 pagesLong Quiz Science 8Diamond CrsktNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 ConvectionDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 ConvectionFikri RahimNo ratings yet
- Indian Night Vision TechDocument10 pagesIndian Night Vision Techshashank_shrNo ratings yet
- Nepal Aviation Authority 8Document5 pagesNepal Aviation Authority 8Janup PokharelNo ratings yet
- Physics Report Snell S Law RefractionDocument4 pagesPhysics Report Snell S Law RefractionAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Internal AssessmentDocument11 pagesChemistry Internal AssessmentTinesh GovindarajooNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2 de Op IIIDocument26 pagesTarea 2 de Op IIIbrendaNo ratings yet
- Cooper Bussmann Safety Basics Electrical HazardsDocument46 pagesCooper Bussmann Safety Basics Electrical HazardsAtika Rahma HadianaNo ratings yet
- Steel Tabsteel Table - AiscDocument45 pagesSteel Tabsteel Table - Aiscabhinav73730% (2)
- Euchner Esm Ba 301 - Bfb0471cca PDFDocument39 pagesEuchner Esm Ba 301 - Bfb0471cca PDFJorge SilvaNo ratings yet
- NLC23 - Grade 7 Enhancement Mathematics Student Workbook - FinalDocument58 pagesNLC23 - Grade 7 Enhancement Mathematics Student Workbook - FinalJohn Christopher Romero100% (1)
- 11 WG1 Fire-Demaged WangDocument19 pages11 WG1 Fire-Demaged WangJustin MusopoleNo ratings yet
- Oem ManualDocument38 pagesOem ManualMohamed Rashed100% (4)
- Mechanical Measurements Lab ManualDocument26 pagesMechanical Measurements Lab ManualseminarprojectNo ratings yet
- Compresibility of Clay Determined From In-Situ TestsDocument158 pagesCompresibility of Clay Determined From In-Situ TestsHüseyin EkiciNo ratings yet
- Study On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesDocument12 pagesStudy On Mechanical Properties of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Short Columns Under Different Curing TemperaturesTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- ISOELECTRIC Insulators CatalogueDocument62 pagesISOELECTRIC Insulators CatalogueJoel Palomares100% (1)
- Dry-Out and Heat-Up Procedures - 2015 WorkshopDocument30 pagesDry-Out and Heat-Up Procedures - 2015 WorkshopyuriNo ratings yet
- Electronic Concepts First EditionDocument34 pagesElectronic Concepts First EditionAnkit100% (9)
- CEN-622 Advanced Foundation Engineering: By: Anumita MishraDocument31 pagesCEN-622 Advanced Foundation Engineering: By: Anumita Mishraabcd efghNo ratings yet
- SDS Screw CapacityDocument5 pagesSDS Screw CapacityJose L MexiaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesShivam GaunsNo ratings yet
- Random Matrix Theories in Quantum PhysicsDocument178 pagesRandom Matrix Theories in Quantum PhysicsThongkool CtpNo ratings yet
- Classification: Silicate Phyllosilicate Minerals Basal Cleavage Monoclinic CrystalsDocument4 pagesClassification: Silicate Phyllosilicate Minerals Basal Cleavage Monoclinic CrystalsArthur DumanschiNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 2Document22 pagesProblem Set No. 2Yessel PogiNo ratings yet
- Capture a wide range of tones with proper exposure and developmentDocument8 pagesCapture a wide range of tones with proper exposure and developmentTunisha SharmaNo ratings yet