Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Differences
Uploaded by
boygarfan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page10 differences
Original Title
10 differences
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document10 differences
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 page10 Differences
Uploaded by
boygarfan10 differences
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Author: Abdulqader Ahmed. CPA, CIA, CMA, MPAcc.
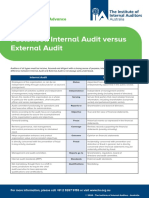
10 Differences Between Internal Audit Manager & Audit Committee Member
Aspect Internal Audit Manager Audit Committee Member
Serves on a committee responsible for
Manages the internal audit function within the oversight of the organization’s financial
organization, focusing on internal control systems, risk reporting, internal controls, and audit
Role management, and governance processes. functions.
Appointment Typically appointed by audit management. Appointed by the Board of Directors.
Reports functionally to the Audit Committee and
Reporting Line administratively to senior management. Reports to the Board of Directors.
Focuses on evaluating the effectiveness of internal Focuses on oversight of financial reporting,
controls, risk management, and governance processes compliance with laws and regulations,
Focus Area within the organization. internal audit, and external auditors.
Operational Directly involved in the day-to-day activities of Not involved in the day-to-day operations
Involvement auditing within the organization. but provides oversight and guidance.
Has authority to oversee the internal audit
function, select and appoint external
Operates with authority granted by senior management auditors, and review financial statements
Authority and the Audit Committee to conduct audits. and audit findings.
Responsible for reviewing the effectiveness
Responsible for planning and executing internal audits, of the internal audit function, the integrity
reporting findings, and making recommendations for of financial statements, and compliance
Responsibilities improvements. with legal requirements.
Requires a broad understanding of financial
Requires in-depth knowledge of auditing, accounting reporting, governance, and risk management
principles, and the specific operations of the principles, but not necessarily detailed
Expertise organization. auditing expertise.
Oversees the relationship with external
auditors and reviews their reports, but
Engagement with Directly manages and interacts with internal audit staff typically does not engage in direct auditing
Auditors and may coordinate with external auditors. activities.
Aims to add value and improve the organization’s Aims to ensure the integrity of financial
operations through systematic, disciplined approaches reporting, the effectiveness of the internal
to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk control environment, and compliance with
Objective management, control, and governance processes. legal and regulatory requirements.
Author: Abdulqader Ahmed. CPA, CIA, CMA, MPAcc.
You might also like
- Mastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachFrom EverandMastering Internal Audit Fundamentals A Step-by-Step ApproachRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Comprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeFrom EverandComprehensive Manual of Internal Audit Practice and Guide: The Most Practical Guide to Internal Auditing PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Corporate Governance and Internal AuditDocument10 pagesCorporate Governance and Internal AuditItdarareNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Overview of Internal Auditing FazDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 1 Overview of Internal Auditing FazHanis ZahiraNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit V External AuditDocument1 pageInternal Audit V External AuditlkhdasouNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Versus External AuditDocument1 pageInternal Audit Versus External AuditMahmoud ElbagouryNo ratings yet
- Risk Management and Internal AuditorDocument58 pagesRisk Management and Internal AuditorAnanda rizky syifa nabilahNo ratings yet
- Internal Control, Internal Auditor & Risk ManagementDocument58 pagesInternal Control, Internal Auditor & Risk ManagementWagimin SendjajaNo ratings yet
- 18AKJ - Sri Widya Ningsih-Audit InternalDocument5 pages18AKJ - Sri Widya Ningsih-Audit InternalTantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Internal Auditing Definition and Overview: Jovit G. Cain, CPADocument41 pagesChapter 1: Internal Auditing Definition and Overview: Jovit G. Cain, CPAJao FloresNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 (Part A)Document34 pagesTopic 6 (Part A)Amanda GuanNo ratings yet
- H001 - Intro To Internal AuditingDocument12 pagesH001 - Intro To Internal AuditingKevin James Sedurifa OledanNo ratings yet
- IA ReviewerDocument11 pagesIA ReviewerMaria Patrice MendozaNo ratings yet
- Internal and External AuditorsDocument19 pagesInternal and External AuditorsSHAMRAIZKHANNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditings Role in Corporate Governance (IIA)Document4 pagesInternal Auditings Role in Corporate Governance (IIA)Vidya IntaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document10 pagesTopic 2MussaNo ratings yet
- Auditing 1: Internal AuditDocument45 pagesAuditing 1: Internal AuditChrizt ChrisNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditings Role in Corporate GovernanceDocument4 pagesInternal Auditings Role in Corporate GovernanceJawadNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Internal Auditing PDFDocument113 pagesFundamentals of Internal Auditing PDFCarla Jean Cuyos100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Internal Control and Risk ManagementDocument50 pagesLesson 4 Internal Control and Risk ManagementAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit RoleDocument12 pagesInternal Audit RoleBobbyD.ResjaNo ratings yet
- Is The Freedom From Conditions That Threaten The Ability ofDocument14 pagesIs The Freedom From Conditions That Threaten The Ability ofangelica joyce caballesNo ratings yet
- Audit ProjectDocument14 pagesAudit ProjectDhara MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - GovernanceDocument18 pagesChapter 3 - GovernanceDeasy NoviyantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8Document10 pagesChapter 6-8DeyNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing:: Assurance, Insight, and ObjectivityDocument12 pagesInternal Auditing:: Assurance, Insight, and ObjectivityJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- 15 JournalDocument4 pages15 JournalJane DizonNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Entity'S InternalcontrolDocument44 pagesUnderstanding The Entity'S Internalcontrolgandara koNo ratings yet
- What Is Internal AuditDocument6 pagesWhat Is Internal AuditRaven GarciaNo ratings yet
- DASAR - Slide Fondasi Audit Internal - Hananto Widhiatmoko (PUBLISH)Document58 pagesDASAR - Slide Fondasi Audit Internal - Hananto Widhiatmoko (PUBLISH)Pingkan OmpiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Internal Auditing Assurance and Consulting Services 2nd Edition by RedingDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Internal Auditing Assurance and Consulting Services 2nd Edition by RedingBrianWelchxqdm100% (38)
- Slides - Chapter 9Document7 pagesSlides - Chapter 9Thu TrangNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Audit ComparisonDocument15 pagesInternal and External Audit ComparisonRegz TabachoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To IA STDTDocument21 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To IA STDTNor Syahra AjinimNo ratings yet
- Internal Control: Consideration ofDocument35 pagesInternal Control: Consideration ofMa. KristineNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Cost Control PDFDocument16 pagesInternal Audit Cost Control PDFNMA NMANo ratings yet
- All in A Day'S Work: A Look at The Varied Responsibilities of Internal AuditorsDocument12 pagesAll in A Day'S Work: A Look at The Varied Responsibilities of Internal AuditorsRhoda Marie R. CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Kirk Report Adtng 422Document21 pagesKirk Report Adtng 422Pritz Marc Bautista MorataNo ratings yet
- Udemy Course CIA Part 2 Focus MaterialsDocument77 pagesUdemy Course CIA Part 2 Focus MaterialsLayar KayarNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing.2022Document19 pagesInternal Auditing.2022One AshleyNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Internal and External AuditDocument3 pagesThe Difference Between Internal and External AuditRohit BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit CharterDocument6 pagesInternal Audit CharterManshu PoorviNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing Module 1Document21 pagesInternal Auditing Module 1kapaymichelleNo ratings yet
- L6 Internal ControlDocument15 pagesL6 Internal ControlMia FayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Internal ControlDocument60 pagesChapter 4 - Internal Controlyebegashet100% (1)
- CG - 4Document4 pagesCG - 4Pillows GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - Risk Governance & Control Environment v2 - Chris RazookDocument26 pagesSession 4 - Risk Governance & Control Environment v2 - Chris RazookEra HRNo ratings yet
- Managing The Internal Audit Function - CompDocument38 pagesManaging The Internal Audit Function - CompBea BajarNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Nature of WorkDocument43 pagesModule 4 - Nature of WorkMichaelNo ratings yet
- 13 Introduction To Internal AuditingDocument6 pages13 Introduction To Internal AuditingShailene DavidNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance TM6Document26 pagesCorporate Governance TM611210000015No ratings yet
- All in A Days Work BrochureDocument12 pagesAll in A Days Work BrochureRAÚL BARRADO MENDONo ratings yet
- Internal and External Audit ComparisonDocument15 pagesInternal and External Audit ComparisonRegz TabachoyNo ratings yet
- T@T November 2010 PDFDocument4 pagesT@T November 2010 PDFMauricio De La TorreNo ratings yet
- Chariza L. Colita Aud RPRDocument20 pagesChariza L. Colita Aud RPRPritz Marc Bautista MorataNo ratings yet
- OperationalDocument13 pagesOperationalAlona ColiaenNo ratings yet
- Govbusman Module 2 - Chapter 2Document7 pagesGovbusman Module 2 - Chapter 2Rohanne Garcia AbrigoNo ratings yet
- 2 Internal AuditDocument8 pages2 Internal AuditNurita A TyasNo ratings yet
- Internal Control System: Quarter 1 - Week 1Document17 pagesInternal Control System: Quarter 1 - Week 1KiermoralesNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument10 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlMAG MAGNo ratings yet
- IFRS 16: Lessor & Lessee Accounting Treatment in The Finance LeaseDocument2 pagesIFRS 16: Lessor & Lessee Accounting Treatment in The Finance LeaseboygarfanNo ratings yet
- GCC Ia Ia Rev.00.24Document3 pagesGCC Ia Ia Rev.00.24boygarfanNo ratings yet
- Data Integrity TemplateDocument4 pagesData Integrity TemplateboygarfanNo ratings yet
- 1122 482 2019-02-14 15-47-38 enDocument17 pages1122 482 2019-02-14 15-47-38 enboygarfanNo ratings yet
- Mss-Netherlands enDocument16 pagesMss-Netherlands enboygarfanNo ratings yet
- Retail Collection PolicyDocument39 pagesRetail Collection PolicyK Praveen RajNo ratings yet
- 1122 482 2019-02-14 15-47-38 enDocument16 pages1122 482 2019-02-14 15-47-38 enboygarfanNo ratings yet
- Telco Flowchart 2Document1 pageTelco Flowchart 2p01zawjNo ratings yet
- SAP Programming LanguageDocument76 pagesSAP Programming Languagejabbar1959No ratings yet
- 2750 514-23 en Rev BDocument4 pages2750 514-23 en Rev BGuitART TVNo ratings yet
- Prevent Leaks in Heat ExchangersDocument7 pagesPrevent Leaks in Heat ExchangersNirmal SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Samsung LE-40A866 - 20081009152533312 - BN68-01701B-00Eng-0910Document72 pagesSamsung LE-40A866 - 20081009152533312 - BN68-01701B-00Eng-0910a11615870No ratings yet
- (BS EN 932-5 - 2000) - Tests For General Properties of Aggregates. Common Equipment and CalibrationDocument18 pages(BS EN 932-5 - 2000) - Tests For General Properties of Aggregates. Common Equipment and CalibrationAdelNo ratings yet
- 2019 11 20 23 41 26Document227 pages2019 11 20 23 41 26Aqua Galon0% (1)
- Itu-T G.841Document98 pagesItu-T G.841Deolindo ZanuttiniNo ratings yet
- Pestle For ToyotaDocument2 pagesPestle For ToyotaAshvin Bageeruthee100% (3)
- As Cable Etp-394 Ysly-Jz - OzDocument2 pagesAs Cable Etp-394 Ysly-Jz - OzAlicia AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Expulsion Fuse Links For Use in High Voltage (Liston Fusible)Document36 pagesExpulsion Fuse Links For Use in High Voltage (Liston Fusible)Leon OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Calibration CertificatesDocument21 pagesCalibration Certificatesbhadresh2003cvlNo ratings yet
- ENG - Installation Manual For Sequential LPG-CNG (May 2005)Document77 pagesENG - Installation Manual For Sequential LPG-CNG (May 2005)Kar Gayee100% (1)
- SLP TX420Document2 pagesSLP TX420Estrellita BelénNo ratings yet
- Filtre TV EpcosDocument13 pagesFiltre TV Epcosparvalhao_No ratings yet
- Work Permit Systems - tcm17-13910Document16 pagesWork Permit Systems - tcm17-13910CJNo ratings yet
- Market Research Report Preparation and Presentation UpdateDocument28 pagesMarket Research Report Preparation and Presentation Updatecome2pratik33% (3)
- PIP INIH1000 SampleDocument6 pagesPIP INIH1000 SampleIvan Roco100% (1)
- Catálogo FlowserveDocument23 pagesCatálogo Flowserveanderson8657No ratings yet
- CSharp For Sharp Kids - Part 1 Getting StartedDocument10 pagesCSharp For Sharp Kids - Part 1 Getting StartedBrothyam Huaman CasafrancaNo ratings yet
- AS4324.1-1995 Standard For Design of Bulk Materials Handling MachinesDocument8 pagesAS4324.1-1995 Standard For Design of Bulk Materials Handling Machinesridzim4638100% (1)
- SQM Chapter6Document15 pagesSQM Chapter6azmastecNo ratings yet
- ELM323 OBD (ISO) To RS232 Interpreter: Description FeaturesDocument11 pagesELM323 OBD (ISO) To RS232 Interpreter: Description FeaturesAdauto Augusto Nunes FilhoNo ratings yet
- Basic Safety Plan: Aker Powergas PVT LTD Page NoDocument36 pagesBasic Safety Plan: Aker Powergas PVT LTD Page NoAbid AliNo ratings yet
- Common File Extensions PDFDocument8 pagesCommon File Extensions PDFRahul kumarNo ratings yet
- 8155 Is An Integrated RamDocument22 pages8155 Is An Integrated RamVipan SharmaNo ratings yet
- TR - Gas Appliances and Their Accessories - Version 1 - Amendment 2Document20 pagesTR - Gas Appliances and Their Accessories - Version 1 - Amendment 2陳端民No ratings yet
- TCP and UDP Ports Used by Apple Software ProductsDocument6 pagesTCP and UDP Ports Used by Apple Software ProductsEduardo CharllesNo ratings yet
- Optimized Clustering Algorithm For WBAN To WBAN CommunicationDocument13 pagesOptimized Clustering Algorithm For WBAN To WBAN CommunicationnadeemajeedchNo ratings yet
- Atm ProjectDocument18 pagesAtm Projectsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet