Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tute Sheet-4
Uploaded by
Krishnendu Nayek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
Tute_Sheet-4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTute Sheet-4
Uploaded by
Krishnendu NayekCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Applied Mechanics Department
Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad, India-211004
Tutorial Sheet-4 (Beams): Engineering Mechanics (AMN-12400)
B.Tech (2nd Semester), Session 2022-23
1. Derive relations between the Load Function/Load Intensity (w), Shear Force (V ) and the Bending Moment (M)
at an arbitrary position x along the length of a beam.
2. What do you understand by Shear Force Diagram (SFD) and Bending Moment Diagram (BMD) for a beam?
Obtain the SFD and the BMD for: (i) A simply supported beam of length l, subjected to an uniformly distributed
load (UDL) of intensity w (per unit length) and (ii) A cantilever beam of length l, subjected to an UDL of intensity
w.
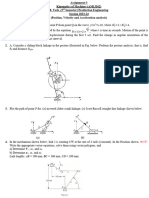
3. For the simply supported beams shown in Figs. (1-5) and the cantilever beams shown in Figs. (6-9), obtain the
relevant SFDs and the BMDs.
4. A cantilever beam of length L= 6 m carries an UDL q = 20 KN/m and a concentrated load P = 250 KN at the free end
(Fig - 10). Obtain the SFD and the BMD for the beam.
5. A rail- road-tie beam (or sleeper) is subjected to two concentrated loads of P = 500 kN, acting as shown in Fig-11.
The reaction q of the supporting ballast may be assumed to be uniformly distributed over the length of the tie beam.
Obtain the SFD and the BMD for the sleeper, assuming L =140 cm and a= 40 cm.
6. A beam ABC supports a concentrated load P at the end of the overhang, as shown in Fig-12. Obtain the SFD and the
BMD for the beam.
7. A continuously supported beam ABCD of length L = 6 m is applied with a concentrated load P = 50 kN and an
externally applied moment Mo = 180 kN-m, as shown in Fig-13. The beam is hinged at A and roller-supported at C
and D. An internal hinge is provided at B. Calculate the support reactions and obtain the SFD and BMD for the beam.
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Suspension Cable BridgesDocument29 pagesSuspension Cable Bridgesrameshbabu_197967% (3)
- 2011 The Interactive Vibration Behavior I PDFDocument14 pages2011 The Interactive Vibration Behavior I PDFCaroline Cole100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Shear and Moment in BeamsDocument42 pagesChapter 4 Shear and Moment in Beamssaleemm_2No ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Vibration TwoDocument20 pagesVibration TwoFeeling_so_flyNo ratings yet
- 3.strength of MaterialsDocument6 pages3.strength of MaterialsNandhini NallasamyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document47 pagesUnit 2Anbarasan Sivaraj100% (1)
- CHP 4 Beams PDFDocument14 pagesCHP 4 Beams PDFJeff AwNo ratings yet
- Anna University - 2007: B.E/B.Tech Model Examination (Aeronautical Engineering) Time-3Hour MARK-100 Answer All QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnna University - 2007: B.E/B.Tech Model Examination (Aeronautical Engineering) Time-3Hour MARK-100 Answer All QuestionsNagamani ArumugamNo ratings yet
- CV207Document63 pagesCV207dhiru03No ratings yet
- Ce2302 QBDocument17 pagesCe2302 QBRamesh Thangamani100% (1)
- Sa-I QP PDFDocument19 pagesSa-I QP PDFmythilispd_355305156No ratings yet
- Beam Analysis: Chapter - FOURDocument14 pagesBeam Analysis: Chapter - FOUR胡宇晟No ratings yet
- Ce2252 Strength of Materials - 2marksDocument21 pagesCe2252 Strength of Materials - 2marksrohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- CE8602 Structural Analysis II Dec 2021Document3 pagesCE8602 Structural Analysis II Dec 2021dhivyaNo ratings yet
- Strain Energy - Beams - Materials - Engineering Reference With Worked ExamplesDocument5 pagesStrain Energy - Beams - Materials - Engineering Reference With Worked ExamplesGarapati MurarjiNo ratings yet
- Ae2254 QBDocument13 pagesAe2254 QBMahesh J RaoNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Framed Bridge Structures: ScenarioDocument5 pagesThe Mathematics of Framed Bridge Structures: ScenarioDeborah NicdaoNo ratings yet
- CE2252 Strenth of Materials Question Bank-Xams9Document19 pagesCE2252 Strenth of Materials Question Bank-Xams9Hariharan ElangandhiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures - IiDocument4 pagesTheory of Structures - IiAjmal MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Som Cia 1Document3 pagesSom Cia 1Umar SabaNo ratings yet
- 3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsDocument14 pages3) Displacement Method of Analysis: Moment Distribution: General Principles and DefinitionsAyad SlabyNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: X: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code: X: Reg. No.Vijay MNo ratings yet
- Ae2254 Unit Test II QP ADocument1 pageAe2254 Unit Test II QP AAravindan SivanandanNo ratings yet
- Attachment PDFDocument19 pagesAttachment PDFjeroldscd0% (1)
- MoS AssignmentDocument3 pagesMoS AssignmentRathnavel PonnuswamiNo ratings yet
- Ce 1252 - Strength of Materials: Two Mark Question & AnswersDocument23 pagesCe 1252 - Strength of Materials: Two Mark Question & Answerslogeshboy007No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 AM1100Document2 pagesTutorial 3 AM1100Sanchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- KCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 4Document3 pagesKCG College of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Ce 6306-Strength of Materials (Sem: 3) Question Bank For Unit 4adamodaraNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Document6 pagesStructural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Michael BlairNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Beam MethodDocument5 pagesConjugate Beam MethodAnonymous KIUgOYNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionsDocument38 pagesEngineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionskganesanNo ratings yet
- Kings: Engineering MechanicsDocument16 pagesKings: Engineering Mechanicsgovind4ever5No ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions For Theory of Structures-I (Structural Analysis-I) in B.E. (Civil) - UIT-RGPV BHOPALDocument4 pagesShort Answer Questions For Theory of Structures-I (Structural Analysis-I) in B.E. (Civil) - UIT-RGPV BHOPALSantosh Kumar100% (1)
- SOM Unit-2 WriteUpDocument15 pagesSOM Unit-2 WriteUpAneesh KrNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bendind MomentDocument8 pagesShear Force and Bendind MomentAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Final Term Examination, CE 117, Summer 2020, CED (Main Campus)Document4 pagesFinal Term Examination, CE 117, Summer 2020, CED (Main Campus)Mohammad JavedNo ratings yet
- 1 Strengthofmaterials Interview QuestionsDocument21 pages1 Strengthofmaterials Interview QuestionsChanduReddyNo ratings yet
- Ce 2252 Strength of MaterialsDocument20 pagesCe 2252 Strength of MaterialsSivarajSivaNo ratings yet
- Alexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & Technology: 2020/2021 Sheet (2) Spring ElementsDocument6 pagesAlexandria Higher Institute of Engineering & Technology: 2020/2021 Sheet (2) Spring Elementskhaled mohamed0% (1)
- Strength of Materials 2 Mark QuestionsDocument21 pagesStrength of Materials 2 Mark Questionsrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- CUMBIA Theory and User GuideDocument43 pagesCUMBIA Theory and User GuideElias RojanoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesUNIT 2 AssignmentrameshNo ratings yet
- CE6402-Strength of Materials PDFDocument12 pagesCE6402-Strength of Materials PDFSathz FlynnNo ratings yet
- 9A21402 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IDocument4 pages9A21402 Aerospace Vehicle Structures IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Internal II Question Bank SOMDocument7 pagesInternal II Question Bank SOMsathyadallyNo ratings yet
- 1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsDocument4 pages1111-110010-Mech - of SolidsjaydeepNo ratings yet
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Document8 pagesE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101No ratings yet
- Karpagam UniversityDocument4 pagesKarpagam Universityவிஜய்ராஜ்No ratings yet
- Transverse Earthquake-Induced Forces in Continuous Bridges: Technical NoteDocument6 pagesTransverse Earthquake-Induced Forces in Continuous Bridges: Technical NotealanadadNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionFrom EverandHyperbolic Structures: Shukhov's Lattice Towers - Forerunners of Modern Lightweight ConstructionNo ratings yet
- EM Tutorial Sheet 1bDocument3 pagesEM Tutorial Sheet 1bAditya singhNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet-5Document2 pagesTute Sheet-5Krishnendu NayekNo ratings yet
- Tute Sheet-3Document3 pagesTute Sheet-3Krishnendu NayekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Krishnendu NayekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Krishnendu NayekNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3-A FinalDocument7 pagesLecture-3-A FinalKrishnendu NayekNo ratings yet
- PLMH Notes PDFDocument78 pagesPLMH Notes PDFRossi AghdaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii PPT (I.e)Document70 pagesUnit-Iii PPT (I.e)Krishnendu NayekNo ratings yet