Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of R Contents
Uploaded by
Christopher OdyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of R Contents
Uploaded by
Christopher OdyCopyright:
Available Formats
The document discusses a recent change in the North Sea that is being studied by a
group of researchers from various institutions in the UK, Germany, USA, Canada, and
the Netherlands. They are investigating the impact of this change on the
oceanography and coastal research in the region.
Possible questions you can ask me about the document:
What specific changes are the researchers studying in the North Sea?
How are the researchers from different countries collaborating on this study?
What are the potential implications of the research findings for the North Sea
region?
Please feel free to ask me a question about the document!
06:44 PM
tell me about the water quality changes lastly according to the document
06:45 PM
The document discusses several water quality changes in the North Sea region,
including:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and pH changes influenced by circulation patterns, in-flow
from the Atlantic, local weather conditions, and properties of component water
masses.
Nutrient changes influenced by circulation patterns, in-flow from the Atlantic,
local weather conditions, and properties of component water masses.
Oxygen concentration changes, particularly near the sea bed, influenced by organic
matter respiration, breakdown of detrital organic matter in the sediment, lack of
oxygen supply, and temperature.
Suspended particulate matter and turbidity changes influenced by river inputs,
seasons, tidal resuspension and advection, waves, and stratification.
These changes are discussed in relation to their historical development, evidence
from measurements, process understanding, and models, as well as their impact on
the state and trends of the respective water quality variables in the North Sea.
SOURCES:
Page 2: Abstract
Page 18: ties and their effects on productivity in the North Sea have been
investigated using models (e.g. Lenhart et al. 2010; Lancelot et al. 2011)...
Page 24: affects ecosystem functioning and can lead to fish mortality. Air-sea
exchange and photosynthesis tend to keep upper waters oxygenated; oxygen
concentrations can be strongest in the thermocline associated with a sub-surface
chlorophyll maximum...
Page 42: the rates of global mean sea-level rise. Extreme sea levels have increased
over the past 100–150 years in the North Sea, mainly due to a rise in mean sea
level...
You might also like
- Enviromental ChemistryDocument216 pagesEnviromental ChemistryzockawNo ratings yet
- The Tragedy of the Commodity: Oceans, Fisheries, and AquacultureFrom EverandThe Tragedy of the Commodity: Oceans, Fisheries, and AquacultureNo ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument16 pagesOceanographyA S Verma100% (1)
- Biology Project HWDocument3 pagesBiology Project HWNoor ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Ocean Acidification PHD ThesisDocument13 pagesOcean Acidification PHD ThesisPayToDoPaperUK100% (2)
- Ocean Acidification ThesisDocument12 pagesOcean Acidification Thesisevkrjniig100% (1)
- Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesClimate ChangeJustisia KaunlaranNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Shriyash KarnikNo ratings yet
- Ocean Acidification Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesOcean Acidification Literature Reviewafmzodjhpxembt100% (1)
- Physical and Ecological Impacts of Climate Change Relevant To Marine and Inland Capture Fisheries and AquacultureDocument37 pagesPhysical and Ecological Impacts of Climate Change Relevant To Marine and Inland Capture Fisheries and AquacultureayanboyeNo ratings yet
- Ocean Deoxygenation: A Triple ThreatDocument3 pagesOcean Deoxygenation: A Triple ThreatАндрей КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- Poff2002PEW AquaticEcosysDocument57 pagesPoff2002PEW AquaticEcosyssiamo.z1801No ratings yet
- Warming Deep SeasDocument43 pagesWarming Deep SeasDickNo ratings yet
- Oceanography Research Paper TopicsDocument8 pagesOceanography Research Paper Topicsuwtsmecnd100% (1)
- Environmental ChemistryDocument39 pagesEnvironmental ChemistryErika EludoNo ratings yet
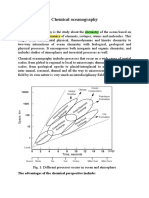
- CHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHYDocument8 pagesCHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHYHalima akterNo ratings yet
- Ashleigh 1Document23 pagesAshleigh 1api-253530068No ratings yet
- Ocean Acidification Case StudyDocument2 pagesOcean Acidification Case Studynicole yuNo ratings yet
- Water: Ecological Responses of Lakes To Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesWater: Ecological Responses of Lakes To Climate ChangeRicardo rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Global Environment: Water, Air, and Geochemical Cycles - Second EditionFrom EverandGlobal Environment: Water, Air, and Geochemical Cycles - Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Edmunds2009 ReviewDocument16 pagesEdmunds2009 ReviewYashashavi LadhaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesDocument7 pagesClimate Change: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesMajedaNo ratings yet
- Current Event Paper IDocument4 pagesCurrent Event Paper IOmbati StephenNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Ocean AcidificationDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Ocean Acidificationfdnmffvkg100% (1)
- Ocean AcidificationDocument9 pagesOcean AcidificationsivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- 8 PETM Abrupt-EventsDocument4 pages8 PETM Abrupt-EventsBrandel CoolenNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Climate ChangeDocument14 pagesImpacts of Climate ChangeDeborah LynchNo ratings yet
- SAI's Assignment METDocument9 pagesSAI's Assignment METSai Srimann SahNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text, Answer The Questions That Follows and Generate Your Own QuestionsDocument2 pagesRead The Following Text, Answer The Questions That Follows and Generate Your Own QuestionsDwi RetnoNo ratings yet
- Oceanography Term Paper TopicsDocument6 pagesOceanography Term Paper Topicsafdtzfutn100% (1)
- Fluid Systems: Fluids in The CrustDocument6 pagesFluid Systems: Fluids in The CrustAkoSiMambuconOtitNo ratings yet
- Open Letter ELA Final EnglishDocument2 pagesOpen Letter ELA Final EnglishjasonsaveelaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Marine Biodiversity and Ecosystems: An Indicator-Based AssessmentDocument35 pages5.4 Marine Biodiversity and Ecosystems: An Indicator-Based AssessmentVesnaBarbuliNo ratings yet
- The Climate of the Mediterranean Region: From the Past to the FutureFrom EverandThe Climate of the Mediterranean Region: From the Past to the FutureP. LionelloNo ratings yet
- Studies On The Planktonic Diversity From Different Islands of South Andaman and Little Andaman Island With Special Emphasis On PhytoplanktonDocument2 pagesStudies On The Planktonic Diversity From Different Islands of South Andaman and Little Andaman Island With Special Emphasis On Phytoplanktonarvind negiNo ratings yet
- Apes in The News Arctic Biodiversity Under Serious Threat From Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesApes in The News Arctic Biodiversity Under Serious Threat From Climate Changeapi-250807061No ratings yet
- Thirty Years of Unique Data Reveal What's Really Killing Coral ReefsDocument8 pagesThirty Years of Unique Data Reveal What's Really Killing Coral ReefsjenilenNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesSEMINAR-WPS OfficeOni FunmilayoNo ratings yet
- 2013-Smith - Deep Ocean Communities Impacted by Changing Climate Over 24 Years in The Abyssal Northeast Pacific OceanDocument4 pages2013-Smith - Deep Ocean Communities Impacted by Changing Climate Over 24 Years in The Abyssal Northeast Pacific OceanTroy LivingstonNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument52 pagesResearchhisyam_muhd8No ratings yet
- JHRS Os SiDocument1 pageJHRS Os SiRockstarNo ratings yet
- Groundwater Chemistry and Hydrological Processes Within A Quaternary Coastal Plain: Pimpama, Southeast QueenslandDocument304 pagesGroundwater Chemistry and Hydrological Processes Within A Quaternary Coastal Plain: Pimpama, Southeast QueenslandLizbeth MontenegroNo ratings yet
- G7 2015 Future of The OceansDocument2 pagesG7 2015 Future of The OceansAna CaixetaNo ratings yet
- Natsci 13Document9 pagesNatsci 13Yuji KojimaNo ratings yet
- Danovaro 2018Document17 pagesDanovaro 2018Dominique LefevreNo ratings yet
- Mitrie Sediment MarineDocument6 pagesMitrie Sediment MarineTati FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Global WarmingDocument37 pagesEffects of Global WarmingDaraFelisiaArdhityasariNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Groundwater Composition and ChemistryFrom EverandHydrogeochemistry Fundamentals and Advances, Groundwater Composition and ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Down in Arms - Marine Climate Stress Inhibits Growth and CalcificaDocument22 pagesDown in Arms - Marine Climate Stress Inhibits Growth and CalcificaAndrew AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- 07 - Biotic-Abiotic InteractionsDocument27 pages07 - Biotic-Abiotic InteractionsADWYTH GNAIRNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Is One of The Defining Issues of Our TimeDocument36 pagesClimate Change Is One of The Defining Issues of Our TimeM BILAL M BILALNo ratings yet
- Environment: Coral Reefs Climate ChangeDocument56 pagesEnvironment: Coral Reefs Climate ChangeFitra Wira HadinataNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the OceansFrom EverandDynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the OceansNo ratings yet
- Tsyban 1999Document6 pagesTsyban 1999Rahul AmbawataNo ratings yet
- FCIM L.17.2 - Aquatic Systems - I Do TEACHER FinalDocument24 pagesFCIM L.17.2 - Aquatic Systems - I Do TEACHER FinalAJ CootsNo ratings yet
- Oceanic Minerals: Their Origin, Nature of Their Environment, and SignificanceDocument8 pagesOceanic Minerals: Their Origin, Nature of Their Environment, and SignificancePoho LaharNo ratings yet
- OA20Facts NovDocument2 pagesOA20Facts NovDongsipoi HuynhNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics On OceanographyDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Topics On Oceanographywohekam1d0h3100% (1)
- Dok 2Document4 pagesDok 2michele nikeNo ratings yet