Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impact of Interest Rate 2
Uploaded by
nedexed4040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
Impact of interest rate 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageImpact of Interest Rate 2
Uploaded by
nedexed404Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1.
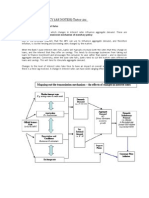
Consumer Borrowing and Spending: One of the most noticeable impacts of
interest rates is on consumer borrowing and spending. Lower interest rates
make borrowing cheaper, encouraging individuals to take out loans for
purchases such as homes, cars, and consumer goods. This increased
borrowing and spending stimulate economic activity and can lead to higher
consumer confidence.
2. Mortgage and Real Estate Market: Interest rates significantly influence the
mortgage and real estate markets. Lower interest rates make homeownership
more affordable, leading to increased demand for housing. This demand can
drive up home prices, benefiting existing homeowners and real estate
investors. Conversely, higher interest rates can decrease demand, potentially
leading to a slowdown in the real estate market.
3. Business Investment and Expansion: Interest rates also impact business
investment decisions. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing for
businesses, making it more attractive to invest in expansion projects,
equipment upgrades, and new ventures. Increased business investment can
lead to job creation, economic growth, and improved productivity.
4. Bond Market and Investment Returns: Interest rates have a significant impact
on the bond market. When interest rates rise, the yields on newly issued
bonds also increase, making existing bonds with lower yields less attractive.
Consequently, bond prices tend to fall in a rising interest rate environment.
Conversely, falling interest rates can lead to higher bond prices and lower
yields. This relationship affects the returns on fixed-income investments and
the overall performance of bond portfolios.
5. Currency and Exchange Rates: Interest rate differentials between countries can
influence currency exchange rates. Higher interest rates in one country relative
to another can attract foreign investors seeking higher returns. This increased
demand for the currency can appreciate its value. Conversely, lower interest
rates may result in capital outflows and depreciation of the currency. Exchange
rate fluctuations impact international trade, export competitiveness, and
import costs.
You might also like
- Summary of Anthony Crescenzi's The Strategic Bond Investor, Third EditionFrom EverandSummary of Anthony Crescenzi's The Strategic Bond Investor, Third EditionNo ratings yet
- Factors in Stock MarketDocument14 pagesFactors in Stock MarketAnirudhAditya100% (1)
- International Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesDocument5 pagesInternational Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesUtkarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange Ratesanish-kc-8151No ratings yet
- Contemporary Economic Issues Facing The Filipino EntrepreneurDocument32 pagesContemporary Economic Issues Facing The Filipino EntrepreneurJuvelle Cudal83% (93)
- 3.2 Real Estate FinanceDocument14 pages3.2 Real Estate Financegore.solivenNo ratings yet
- San Jose Mod3HWDocument2 pagesSan Jose Mod3HWloganramenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41-Economic InfluencesDocument12 pagesChapter 41-Economic InfluencesRanceNo ratings yet
- Roncal, Andrei G - Engaging Activity 1 - Valuation Equity ShareDocument4 pagesRoncal, Andrei G - Engaging Activity 1 - Valuation Equity ShareDrei Galanta RoncalNo ratings yet
- Answers To End of Ch.1 MOFIMDocument2 pagesAnswers To End of Ch.1 MOFIMSamia MemonNo ratings yet
- c10.pdf InvestmentDocument6 pagesc10.pdf InvestmentevanaannNo ratings yet
- 53 03Document1 page53 03Numaer SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadmanirajpoot45No ratings yet
- Higher Interest Rates Tend To Moderate Economic GrowthDocument2 pagesHigher Interest Rates Tend To Moderate Economic GrowthNestor Liwagon BalansagNo ratings yet
- 6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument9 pages6 Key Factors That Influence Exchange RatesRizwan BashirNo ratings yet
- Four Factors That Impact a Company's Cost of CapitalDocument4 pagesFour Factors That Impact a Company's Cost of Capitalsanjana sethNo ratings yet
- Differentials in Inflation: Cost-Push Inflation Versus Demand-Pull InflationDocument2 pagesDifferentials in Inflation: Cost-Push Inflation Versus Demand-Pull InflationKirat GillNo ratings yet
- Devaluation of Currency Refers Specifically To A Deliberate and Official DownwardDocument19 pagesDevaluation of Currency Refers Specifically To A Deliberate and Official DownwardNgọc Minh VũNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors That Influence Exchange RatesJoelene ChewNo ratings yet
- Singapore Property Weekly Issue 208Document17 pagesSingapore Property Weekly Issue 208Propwise.sgNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Interest RatesDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Interest RatesTanvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Implications of The Federal ReserveDocument3 pagesImplications of The Federal ReserveP Singh KarkiNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document4 pagesHW 3Marino NhokNo ratings yet
- Why study financial markets and institutionsDocument2 pagesWhy study financial markets and institutionsAsdasd AsdadsNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Good Things or Bad Things?Document8 pagesInterest Rate Good Things or Bad Things?noraNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy (As Notes) Tutor 2U:: Effects of Changes in Interest RatesDocument3 pagesMonetary Policy (As Notes) Tutor 2U:: Effects of Changes in Interest Ratesch_1890No ratings yet
- Exchange Rates Foreign-Exchange Rate, Forex Rate or FX Rate)Document5 pagesExchange Rates Foreign-Exchange Rate, Forex Rate or FX Rate)SaadRasheedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Home Work QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 2-Home Work QuestionsSarah MoonNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy PDFDocument7 pagesMonetary Policy PDFDaniel SozonovNo ratings yet
- FIM AssignmentDocument5 pagesFIM AssignmentNoor AliNo ratings yet
- Finance Pytania 1Document3 pagesFinance Pytania 1Marta SzczerskaNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Particulars Pg. No.: IndexDocument25 pagesSr. No. Particulars Pg. No.: IndexjansimumNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Level and Structure of Interest RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Level and Structure of Interest RatesSuryansh GargNo ratings yet
- Interest RateDocument19 pagesInterest RatenzlNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Interest Rates ExplainedDocument4 pagesDeterminants of Interest Rates ExplainedJunvy AbordoNo ratings yet
- câu-4 adjustedDocument2 pagescâu-4 adjustedNguyễn Tấn ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Related Notes On Financial ForcesDocument3 pagesRelated Notes On Financial ForcesJesilin ManjulaNo ratings yet
- Why Monetary Policy MattersDocument2 pagesWhy Monetary Policy MattersKatieYoungNo ratings yet
- 1explain The RiDocument5 pages1explain The RiWilliam MuhomiNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesFinancial MarketsRudella LizardoNo ratings yet
- Discussion QuestionsDocument19 pagesDiscussion QuestionsrahimNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument12 pagesHandoutAmira NajjarNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument7 pagesEnglisharibahamjad8129No ratings yet
- 6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pages6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesfredsvNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Exchange RateDocument2 pagesDeterminants of Exchange RateSajid Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- FIN 422 (Chapter 2)Document9 pagesFIN 422 (Chapter 2)Sumaiya AfrinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Javeria LeghariNo ratings yet
- A Vicious Currency TrendDocument2 pagesA Vicious Currency Trendmlaz2406No ratings yet
- 380 Exam NotesDocument37 pages380 Exam NotesshlokNo ratings yet
- Main Factors That Influence Exchange Rate.: 1. InflationDocument9 pagesMain Factors That Influence Exchange Rate.: 1. InflationHiren GanganiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EconomicsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 EconomicsParthChhedaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. Charu BangaDocument52 pagesBy Dr. Charu BangaChintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Assignment Day 3Document12 pagesAssignment Day 3Qazi MobeenNo ratings yet
- MACC 224 Narrative ReportDocument3 pagesMACC 224 Narrative ReportaceNo ratings yet
- THE BOND and FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKETSDocument11 pagesTHE BOND and FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKETSmonster_newinNo ratings yet
- Deflation DefinitionDocument5 pagesDeflation DefinitionVarshitha K.S.BNo ratings yet
- Reading Lesson 4Document7 pagesReading Lesson 4AnshumanNo ratings yet
- Interest RatesDocument8 pagesInterest RatesMuhammad Sanawar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introduction and Research MethodologyDocument40 pagesChapter - 1 Introduction and Research Methodologypoojagopwani3413No ratings yet