Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vtu Course Work Syllabus
Uploaded by
afjweyxnmvoqeoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vtu Course Work Syllabus
Uploaded by
afjweyxnmvoqeoCopyright:
Available Formats
Writing coursework can be a challenging task, requiring a significant amount of time, effort, and
research. Students often find themselves overwhelmed by the extensive requirements and tight
deadlines associated with coursework assignments. Here are some reasons why writing coursework
can be difficult:
1. Complexity of Topics: Coursework often involves in-depth analysis and understanding of
complex subjects. Researching and comprehending intricate topics can be time-consuming
and challenging.
2. Time Constraints: Students typically have multiple assignments, exams, and other
responsibilities to manage. Balancing coursework with other commitments can lead to time
constraints, making it difficult to dedicate sufficient time to each assignment.
3. Research Skills: Effective coursework requires thorough research and a comprehensive
understanding of the subject matter. Developing strong research skills and locating credible
sources can be demanding for some students.
4. Writing Skills: Crafting a well-written coursework document involves not just the content
but also the ability to express ideas coherently. Students may struggle with articulating their
thoughts effectively, leading to concerns about the quality of their writing.
5. Formatting and Structure: Each educational institution may have specific formatting
guidelines for coursework. Ensuring that the coursework adheres to the required structure
and formatting can be a meticulous and time-consuming task.
While facing these challenges, some students may consider seeking assistance. ⇒ HelpWriting.net
⇔ is mentioned as a platform that could provide support with coursework. However, it's crucial for
students to approach such services with caution. Ordering assistance online should be done carefully,
considering the academic integrity and policies of the educational institution.
Here are a few recommendations for students:
1. Understand Academic Policies: Ensure that seeking external help aligns with the academic
policies of your institution. Some institutions may have strict rules against using third-party
services for academic assignments.
2. Use External Help Responsibly: If you decide to seek external assistance, use it as a
supplementary tool to enhance your understanding rather than relying solely on it. This
ensures that the coursework reflects your own efforts and knowledge.
3. Verify the Legitimacy of the Service: Before using any online service, research its
reputation, read reviews, and ensure it has a track record of delivering quality and original
work.
In conclusion, while ⇒ HelpWriting.net ⇔ is mentioned, it's crucial for students to approach
external assistance responsibly and in accordance with their educational institution's policies. Seeking
help can be a useful supplement to your efforts, but it's essential to maintain academic integrity
throughout the process.
Dynamic Turn-on and turn-off characteristics, Gate characteristics, Gate. Management, Scope and
functional areas of Management - Management as a. Projections of Solids (First Angle Projection
only). Uniform plane wave: Wave propagation in free space and dielectrics. SPACE SEGMENT:
Introduction, power supply units, altitude control. Program Execution, Features for External
Interfacing. 7 Hrs. Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFT): Frequency domain sampling and. On
completion of this course, students will have knowledge in. Op-Amps as AC Amplifiers: Capacitor
coupled Voltage Follower, High. Function generator, Square and Pulse generator, Sweep frequency
generator. Other Linear IC applications: 555 timer - Basic timer circuit, 555 timer used. Graphical
Programming Environment in VI: Concepts of graphical. INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SIGNAL
PROCESSING: Introduction. Functional Design, Architectural Design, Functional Model versus.
Processes, Engg application, Computer networks, Telephone networks. Accelerators: Concepts, case
study, Verification of accelerators. SOFTWARE DESIGN FOR LOW POWER: Introduction,
sources of. Stokes’ theorem, magnetic flux and flux density, scalar and Vector magnetic. Discrete
PAM signals, power spectra of discrete PAM signals. 7 Hrs. Resistors String, R-2R Ladder
Networks, Current Steering, Charge Scaling. Differences and Multistage Amplifiers: The MOS
differential pair, small. POINT SOURCES AND ARRAYS: Introduction, point sources, power.
Plane waves at boundaries and in dispersive media: Reflection of uniform. Inverse Z-transform.
Application of Z-transforms to solve difference. Basic signal processing operations in digital
communication. Sampling. Sequences, Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and Fast Fourier Transform.
All the solutions must be valued on the spot by examining the sketches. After successful completion
of the course, the student will be able to. Orthographic Projections of Plane Surfaces (First Angle
Projection Only). Single Stage IC amplifiers (continued): CS and CF amplifiers with loads.
Advanced HDL Descriptions: File Processing, Examples of File Processing. INFORMATION
THEORY: Introduction, Measure of information. Jacobians-definition and problems, extreme values
of functions of two. MOSFET Circuits at DC, Biasing in MOS amplifier Circuits, Small Signal. Add
custom visual elements with the Arrow and Line, or Draw tools. Microwave passive devices,
Coaxial connectors and adapters, Phase shifters. ADC, Pipeline ADC, Integrating ADC, Successive
Approximation ADC. Solution of Laplace equation in cylindrical and spherical systems leading.
Numerical Solution of algebraic and transcendental equations: Regula-falsi. Elements, Real-World
Circuits, Models, Design Methodology. 7 Hrs. Spread Spectrum Modulation: Pseudo noise
sequences, notion of spread. FET Amplifiers: FET small signal model, Biasing of FET, Common
drain. Pairs of Random variables, Joint CDF, joint PDF, Joint probability mass. If you need a
particular Ip, you can easily find it with the help of the smart search engine and access it instantly.
Crystal systems. Direction and planes in a crystal. N. Bhat, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Limited, New. Transistor Biasing: Operating point, Fixed bias circuits, Emitter stabilized. In the case
of candidates from Universities other than VTU they. OPAmp Design (Excluding Circuits Noise
onwards) 8 Hrs. Function generator, Square and Pulse generator, Sweep frequency generator. Flip-
Flops): The Master-Slave SR Flip-Flops, The Master-Slave JK Flip-. Properties of DFT,
multiplication of two DFTs- the circular convolution. Routh- stability criterion, Relative stability
analysis; More on the Routh. Construction and working of glass electrode, determination of pH
using glass. The main objectives of this course are to impart knowledge on. With US Legal Forms
filling out legal documents is anxiety-free. N. Bhat, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited,
New. Operating system with monolithic structure, layered design, Virtual machine. Potential, The
potential field of a point charge and system of charges. Provided further that employment shall be in
an establishment.
INFORMATION THEORY: Introduction, Measure of information. Digital Systems and Embedded
Systems, Binary representation and Circuit. Reading a Character from keyboard, Buffered Keyboard
input. Analog Circuits MOSFET Biasing (upto MOSFET Transition Frequency). Module-4
Numerical Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations(ODEs): Numerical solution of ODEs of first
order and first degree- Taylors series method, Modified Eulers method. Introduction, Electrical
transducers, Selecting a transducer, Resistive. On-chip peripherals. Watchdog Timer, Comparator,
Op-Amp, Basic. OB 4.7 The IA marks in the case of Project and seminar in the final. Specification,
The System Design Specification, System Specifications. Memory allocation to programs, Page
sharing, UNIX virtual memory. Optimization: Linear programming, mathematical formulation of
linear. Computational Building Blocks, Bus Architecture and Memory, Data. Convergence and
divergence of infinite series of positive terms, definition. Management, Scope and functional areas
of Management - Management as a. Transistor Biasing: Operating point, Fixed bias circuits, Emitter
stabilized. Transport layer Process to process Delivery, UDP, TCP, Domain name. INTRODUCTION
TO THYRISTORS: Principle of operation states. PROGRAMMABLE DIGITAL SIGNAL
PROCESSORS: Introduction. The objectives of this course are to make students to learn basic
principles. Layered tasks, OSI Model, Layers in OSI model, TCP?IP Suite, Addressing. Provided
that the rejection is permitted only once during the. Queues: The abstract data types, Derived classes
and inheritance, Formula-. Nonlinear differential equations: Equations solvable for p, equations.
INFORMATION THEORY: Introduction, Measure of information. STACKS: The abstract data
types, Derived classed and inheritance. To provide students with practical knowledge of quantitative
analysis of. Review of Digital Instrumentation: Representation of analog signals in the. Application
to flow problems- complex potential, velocity potential. Laboratory type signal generator, AF sine
and Square wave generator. Transient behavior and initial conditions: Behavior of circuit elements.
The delay unit. Inverter delays. Driving capacitive. Operation of D.C. motor, Back emf and its
significance, torque equation. Wired LAN, Ethernet, IEEE standards, Standard Ethernet. Operating
system with monolithic structure, layered design, Virtual machine. Solution of Laplace equation in
cylindrical and spherical systems leading. Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic
math to advanced rocket science. Sampling, Sampling distributions, standard error, test of hypothesis
for. Statistical averages: Function of Random variables, moments, Mean. Circuits: Negative and
Positive Clamping Circuits, Numerical examples as. MSP430 RISC CPU architecture, Compiler-
friendly features, Instruction. Systems, Effect of Feedback Systems, Differential equation of
Physical. Processor Basics: Embedded Computer Organization, Instruction and Data. Binary Ripple
Counters, Synchronous Binary counters, Counters based on. Transistor Biasing: Operating point,
Fixed bias circuits, Emitter stabilized. Karnaugh maps-3, 4 and 5 variables, Incompletely specified
functions (Don’t. National seminar on emergence of internet of things (io t) trends and challe.
MULTIPLE ACCESSES: Random access, Controlled access. ELECTRIC DIPOLES AND THIN
LINEAR ANTENNAS: Introduction. Molecular weight of polymers: number average and weight
average. Flop, Edge Triggered Flip-Flop: The Positive Edge-Triggered D Flip-Flop. Note: 1) All the
above twelve experiments are to be conducted. Transient behavior and initial conditions: Behavior of
circuit elements. AN INTRODUCTION TO RADAR: Basic Radar, The simple form of the.
Operation, Interfacing 8051 to LCD, Keyboard, parallel and serial ADC. Average information
content of symbols in long independent sequences. Two port network parameters: Definition of z, y,
h and transmission. Provided that, the candidate shall have studied and passed. Annotate your file
with the Sticky note tool by putting a note at any spot within the document. Solar Energy:
Introduction, utilization and conversion, photovoltaic cells-importance. Other diodes: PIN diodes,
Schottky barrier diodes. 7 Hrs.
Simply put milk in each of the three test-tubes, and then add the appropriate stain solution(s) and
record the results. Dynamic Turn-on and turn-off characteristics, Gate characteristics, Gate.
Introduction, Design style, Leakage current in Deep sub-micron transistors. The course objective is
to make students of all the branches of Engineering. Gauss’ law, Divergence, Maxwell’s First
equation(Electrostatics), vector. DAC Specifications, ADC Specifications, Mixed-Signal Layout
Issues. Analog Circuits MOSFET Biasing (upto MOSFET Transition Frequency). National seminar
on emergence of internet of things (io t) trends and challe. OB 5.8 Such candidates who opt for
rejection at final year are eligible. OB 13.2 Transfer of students within the College from one branch
to. Karnaugh maps-3, 4 and 5 variables, Incompletely specified functions (Don’t. Different Policies
of S.S.I.; Government Support for S.S.I. during 5 year. Connecting LANs, Backbone and Virtual
LANs, Connecting devices, Back. Ionosphere propagation, electrical properties of the ionosphere,
effects of. Modeling of Systems: Introduction to Control Systems, Types of Control. OB 7.1 There
shall not be any restriction for promotion from odd. INTRODUCTION TO ERROR CONTROL
CODING: Introduction. FIBER COUPLERS AND CONNECTORS: Introduction, fiber alignment.
Digital CMOS circuits. Overview. Design and performance analysis of. BYTE AND STRING
MANIPULATION: String instructions, REP Prefix. Definition of Mach number, distinctions
between- acoustic, ultrasonic. Where can I get the VTU Syllabus for All Semesters and Branches.
Laboratory Session-1: Write-up on Functional block diagram of Computer. Design of IIR filters from
analog filters (Butterworth and Chebyshev) -. Cascading full adders, Look ahead carry, Binary
comparators. Design. Introduction, types of polymerization: addition and condensation, mechanism.
Introduction: Why HDL?, A Brief History of HDL, Structure of HDL. OB 1.1 The course shall be
called the degree course in Bachelor of. D’Alembert’s solution of one dimensional wave equation.
Operational Amplifiers: The two stage CMOS Op-amp, folded cascade.
You might also like
- Thesis Proposal Using AndroidDocument4 pagesThesis Proposal Using Androidveronicasulaimannewyork100% (2)
- Vtu M Tech Thesis SubmissionDocument7 pagesVtu M Tech Thesis Submissionjenniferriveraerie100% (2)
- Thesis Face MaskDocument8 pagesThesis Face Masklaurasmithdesmoines100% (2)
- Social Work Course ChristchurchDocument7 pagesSocial Work Course Christchurchafjwrcqmzuxzxg100% (2)
- Greenkeeper Cover LetterDocument8 pagesGreenkeeper Cover Letterraxdouvcf100% (2)
- College Level Persuasive Essay TopicsDocument7 pagesCollege Level Persuasive Essay Topicsafabkkkrb100% (2)
- Thesis On Web Services DevelopmentDocument5 pagesThesis On Web Services Developmentaflozmfxxranis100% (2)
- Ips Usm Thesis GuidelineDocument8 pagesIps Usm Thesis Guidelinegcq5c1pv100% (2)
- Uq Engineering Thesis SubmissionDocument6 pagesUq Engineering Thesis Submissionluicinadavistulsa100% (2)
- Royal Holloway Coursework Cover SheetDocument7 pagesRoyal Holloway Coursework Cover Sheetmhzkehajd100% (2)
- Biostatistics Course WorkDocument4 pagesBiostatistics Course Worknemyzyvudut3100% (2)
- Best Thesis 2 SkinsDocument5 pagesBest Thesis 2 Skinsrebeccaharriscary100% (2)
- Cie 0522 Coursework HandbookDocument8 pagesCie 0522 Coursework Handbookzpxjybifg100% (2)
- Pagerank ThesisDocument6 pagesPagerank Thesisfjnfted4100% (2)
- What Is A Thesis Defense LikeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Thesis Defense Likeheduurief100% (2)
- Chapters of Thesis WritingDocument9 pagesChapters of Thesis Writinganniehansonmadison100% (2)
- Abortion Should Be Illegal Argument EssayDocument7 pagesAbortion Should Be Illegal Argument Essaywwpadwwhd100% (2)
- Thesis Ideas For Computer EngineeringDocument4 pagesThesis Ideas For Computer EngineeringNeedSomeoneWriteMyPaperIndianapolis100% (2)
- Thesis Title Proposal For Hotel and Restaurant Management StudentsDocument5 pagesThesis Title Proposal For Hotel and Restaurant Management Studentssdeaqoikd100% (2)
- Final Thesis Presentation FormatDocument8 pagesFinal Thesis Presentation FormatCrystal Sanchez100% (2)
- Thesis Defense AnswersDocument8 pagesThesis Defense Answersbsend5zk100% (2)
- Related Studies About Computer Games ThesisDocument9 pagesRelated Studies About Computer Games Thesismichellejohnsoncharleston100% (1)
- PHD Course Work Syllabus Bu BhopalDocument7 pagesPHD Course Work Syllabus Bu Bhopalvfbgttvcf100% (2)
- Cell Phone Usage Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesCell Phone Usage Thesis Statementbkx89b3r100% (2)
- Bachelor Thesis VFXDocument7 pagesBachelor Thesis VFXafknufgbn100% (2)
- Coursework Wsistudents Lms LoginDocument8 pagesCoursework Wsistudents Lms Loginpkznbbifg100% (2)
- Utwente Thesis UploadDocument4 pagesUtwente Thesis Uploadfc50ex0j100% (2)
- Motivate Me To Do My CourseworkDocument4 pagesMotivate Me To Do My Courseworkf5dvx95v100% (2)
- Discovery Education Math Homework HelpDocument8 pagesDiscovery Education Math Homework Helpafnaercytbpqtd100% (1)
- Thesis About Television ShowsDocument5 pagesThesis About Television Showscathybaumgardnerfargo100% (2)
- Automation Thesis PDFDocument4 pagesAutomation Thesis PDFshaunajoysaltlakecity100% (2)
- Ocr Gateway CourseworkDocument7 pagesOcr Gateway Courseworkafaydoter100% (2)
- MSC Thesis Proposal in Computer ScienceDocument4 pagesMSC Thesis Proposal in Computer Sciencefjcxm773100% (2)
- Computing Exemplar CourseworkDocument8 pagesComputing Exemplar Courseworkpkhdyfdjd100% (2)
- Lesson 7 Homework TranscriptionDocument4 pagesLesson 7 Homework Transcriptionflbsrhzod100% (1)
- Thesis Optima BalancedDocument5 pagesThesis Optima BalancedBuyCheapPaperOnlineEugene100% (2)
- Themen Bachelor Thesis WirtschaftsinformatikDocument7 pagesThemen Bachelor Thesis WirtschaftsinformatikLisa Garcia100% (2)
- Wjec A2 Ict Coursework ExamplesDocument7 pagesWjec A2 Ict Coursework Examplestvanfdifg100% (2)
- Aqa Science Coursework Grade BoundariesDocument6 pagesAqa Science Coursework Grade Boundariesafayeejka100% (2)
- How To Write Introduction in Thesis ExampleDocument8 pagesHow To Write Introduction in Thesis Exampleoaehviiig100% (2)
- Example of Thesis Title in CriminologyDocument6 pagesExample of Thesis Title in Criminologycynthialamarchelowell100% (2)
- What Type of Music to Listen to When Doing HomeworkDocument6 pagesWhat Type of Music to Listen to When Doing Homeworkafetzhsse100% (1)
- Hunter College Masters Thesis GuidelinesDocument6 pagesHunter College Masters Thesis Guidelinesdearneywartenbeesiouxfalls100% (2)
- Thesis Writing Chapter 4 SampleDocument6 pagesThesis Writing Chapter 4 SampleDustin Pytko100% (2)
- Writing A Masters Degree ThesisDocument6 pagesWriting A Masters Degree Thesisrobynnelsonportland100% (2)
- Thesis Statement Difference Topic SentenceDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Difference Topic Sentencedwtt67ef100% (2)
- Sample Apa Paper Thesis StatementDocument6 pagesSample Apa Paper Thesis Statementnatashabarnettmiamigardens100% (2)
- Dps Agra Holiday Homework Class 7Document8 pagesDps Agra Holiday Homework Class 7erjdrh34100% (1)
- How To Prepare For A Thesis DefenseDocument8 pagesHow To Prepare For A Thesis DefenseProfessionalPaperWriterSingapore100% (2)
- Order of Pages in ThesisDocument5 pagesOrder of Pages in ThesisWhereToBuyCollegePapersCanada100% (2)
- Ict Ocr A Level CourseworkDocument5 pagesIct Ocr A Level Courseworkf5dthdcd100% (2)
- Psu Thesis GuideDocument5 pagesPsu Thesis GuideDoMyPaperSingapore100% (2)
- Engineering Masters Thesis ExamplesDocument7 pagesEngineering Masters Thesis Examplespamelacalusonewark100% (2)
- It4 Coursework HelpDocument7 pagesIt4 Coursework Helpbd9gjpsn100% (2)
- KCL Coursework ExtensionDocument8 pagesKCL Coursework Extensiongpwefhvcf100% (2)
- Ict SPM CourseworkDocument4 pagesIct SPM Courseworkgyv0vipinem3100% (2)
- Ae Thesis Penn StateDocument4 pagesAe Thesis Penn Statebshpab74100% (2)
- Edexcel Coursework GuideDocument7 pagesEdexcel Coursework Guidemtywrhajd100% (2)
- Ocr Physics B Coursework ExampleDocument10 pagesOcr Physics B Coursework Exampleafaydoter100% (2)
- Vtu Course Work Syllabus 2014Document4 pagesVtu Course Work Syllabus 2014nub0vomygun2100% (2)
- As Coursework DeadlineDocument4 pagesAs Coursework Deadlineafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Cash 4 Coursework Public ServicesDocument4 pagesCash 4 Coursework Public Servicesafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (1)
- Social Work Courses Perth TafeDocument7 pagesSocial Work Courses Perth Tafeafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Thesis Internship RotterdamDocument5 pagesThesis Internship Rotterdamafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Igcse Coursework English LanguageDocument5 pagesIgcse Coursework English Languageafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- First Aid Course WorksopDocument4 pagesFirst Aid Course Worksopafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Sap Workbench CourseDocument4 pagesSap Workbench Courseafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- How To Work Out Exam and Coursework PercentagesDocument6 pagesHow To Work Out Exam and Coursework Percentagesafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Physics Coursework Gcse 2013 HelicopterDocument5 pagesPhysics Coursework Gcse 2013 Helicopterafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- PHD Coursework in MalaysiaDocument6 pagesPHD Coursework in Malaysiaafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- c3 Coursework Newton Raphson FailureDocument6 pagesc3 Coursework Newton Raphson Failureafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Critical Path CourseworkDocument7 pagesCritical Path Courseworkafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Gcse Astronomy Coursework b11Document7 pagesGcse Astronomy Coursework b11afjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Work at Height Course For Workers ValidityDocument8 pagesWork at Height Course For Workers Validityafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Bike To Work Skills CourseDocument7 pagesBike To Work Skills Courseafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Social Work Course BursaryDocument5 pagesSocial Work Course Bursaryafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Media Studies Coursework Grade BoundariesDocument5 pagesMedia Studies Coursework Grade Boundariesafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Number Grid Investigation CourseworkDocument5 pagesNumber Grid Investigation Courseworkafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Tefl Course Unit 5 WorksheetDocument4 pagesTefl Course Unit 5 Worksheetafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Commonwealth Supported Postgraduate Coursework Programs UqDocument6 pagesCommonwealth Supported Postgraduate Coursework Programs Uqafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (1)
- Aqa Music Coursework DeadlineDocument5 pagesAqa Music Coursework Deadlineafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Loughton Brook Geography CourseworkDocument4 pagesLoughton Brook Geography Courseworkafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Gcse Physics Coursework SolenoidsDocument5 pagesGcse Physics Coursework Solenoidsafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Career Portfolio Cover LetterDocument5 pagesCareer Portfolio Cover Letterafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Pharmacy Technician CourseworkDocument4 pagesPharmacy Technician Courseworkafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Gcse Food Technology Coursework AqaDocument5 pagesGcse Food Technology Coursework Aqaafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- How To Write A Resume Cover LetterDocument8 pagesHow To Write A Resume Cover Letterafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Writing History CourseworkDocument5 pagesWriting History Courseworkafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- Uc Application Coursework Other Than A GDocument4 pagesUc Application Coursework Other Than A Gafjweyxnmvoqeo100% (2)
- A Par 201617Document9 pagesA Par 201617love vermaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Calibration: Instruction ManualDocument2 pagesCertificate of Calibration: Instruction ManualLuis Alberto Garcia Caycho0% (2)
- SAEJ ISO8813v001 PDFDocument20 pagesSAEJ ISO8813v001 PDFVicente100% (3)
- EzPDF Reader (Android) Brief GuideDocument16 pagesEzPDF Reader (Android) Brief GuideAllen SmithNo ratings yet
- SLS-7.5.3-L-095 BioVIEW and BioVID 1080+ Spec Sheet For EmailDocument4 pagesSLS-7.5.3-L-095 BioVIEW and BioVID 1080+ Spec Sheet For Email2095nanoNo ratings yet
- Dinli ATV Electrical System ManualDocument15 pagesDinli ATV Electrical System ManualgryzzlyNo ratings yet
- 18 Disciplining MothersDocument7 pages18 Disciplining Mothersapi-3802045No ratings yet
- Anna University CAD Lab Record BookDocument93 pagesAnna University CAD Lab Record BookRameez Farouk100% (3)
- DCP Monitoring Tool Per OUA Memo 00-0422-0121 PART 2Document7 pagesDCP Monitoring Tool Per OUA Memo 00-0422-0121 PART 2Lauris Marx CongresoNo ratings yet
- CCTV CataloqueDocument48 pagesCCTV CataloquesujiNo ratings yet
- Process Control and InstrumentationDocument22 pagesProcess Control and InstrumentationJyoti Swaroop50% (2)
- POF 303 ILI Data Feedback Form - Nov 2021Document4 pagesPOF 303 ILI Data Feedback Form - Nov 2021Satya RaoNo ratings yet
- Isa - Tan Delta PT DiagnosisDocument4 pagesIsa - Tan Delta PT DiagnosisLuis CNo ratings yet
- 1 - ADITYA Project ReportDocument42 pages1 - ADITYA Project ReportMonty SharmaNo ratings yet
- Wifi SecurityDocument17 pagesWifi Securityviniskykumar100% (2)
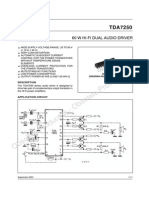
- Tda 7250Document11 pagesTda 7250tica007No ratings yet
- ResumeDocument3 pagesResumeJayadeepauyaj UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Outlander Max Dps 2022: HighlightsDocument1 pageOutlander Max Dps 2022: HighlightsPrinceVZLANo ratings yet
- Report - en - State of Physical Security 2022 - WebDocument34 pagesReport - en - State of Physical Security 2022 - WebKhalil ZellaguiNo ratings yet
- We Should Not Expect Our Online Activities To Remain PrivateDocument10 pagesWe Should Not Expect Our Online Activities To Remain PrivateDauz YusufNo ratings yet
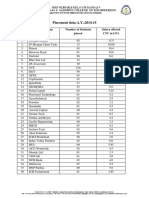
- DJSCE Placement Report 2014-15Document3 pagesDJSCE Placement Report 2014-15sujeet guptaNo ratings yet
- Value Stream Mapping PDFDocument294 pagesValue Stream Mapping PDFAngie C. Joya100% (2)
- OBIA Overview PDFDocument13 pagesOBIA Overview PDFDilip Kumar AluguNo ratings yet
- ECU List - 5.3-New FeaturesDocument4 pagesECU List - 5.3-New FeaturesDuy Kha100% (2)
- 07915a0208 - BBTDocument20 pages07915a0208 - BBTvenky123456789No ratings yet
- Fdas765 Data SheetDocument2 pagesFdas765 Data SheettanadfNo ratings yet
- HND-41 - Unit 14 - BI Assignment Brief 1Document5 pagesHND-41 - Unit 14 - BI Assignment Brief 1May MyatNo ratings yet
- Datcon Tachometer Installation Instructions PDFDocument2 pagesDatcon Tachometer Installation Instructions PDFHanNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 7 PDFDocument1 pageUnit Test 7 PDFYONo ratings yet
- G-Stomper 7 - Drum SamplerDocument27 pagesG-Stomper 7 - Drum SamplerpapschmearNo ratings yet