Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A
A
Uploaded by
aminqasm1110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesOriginal Title
a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesA
A
Uploaded by
aminqasm111Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
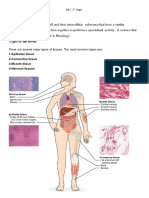
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
CHAPTER NO:12
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Prepared by,
RAMDAS BHAT
Associate Professor
Karavali college of Pharmacy
Mangalore
7798772463
Ramdas21@gmail.com
RAMDAS BHAT
KARAVALI COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 1
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
GIT is the route through which the Nutrierits such as vitamins, minerals and fluid enters
into the body.
GIT is 10mt in length from one end to another
Starts from mouth then to pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, stamach, small intestine, large
intestine and ending with rectum finally into the Anus,
From the mouth the food mixed with the saliva move to the pharynx, oesophagus (25em
long) by the heig of the peristalsis the food reaches the stomach.
From stomach food will move on to the 5. then inta Lending up with rectum
Undigested food will then be excreted through the Anus.
UsumSmall intestine).
Caecum
\Vesmiform Appencx
ORAL CAVITY:
first part of the digestive system.
Opens up at the lips
Has a dome roof called as Palate
Anteriorly lips posteriorly the pharynx
Contains the UVULA at the centre surraund by the pharyngeal tonsils on either side (2)
‘The mechanism in the oral cavities is grinding, tearing of food and mixing of the foods and
saliva produces moistens the food and oral cavity.
The food mass in the oral cavity is called as BOLUS (food +saliva)
The bolus can move in the mouth with the use of the tongue the process is called as the
chewing or MASTICATION.
RAMDAS BHAT
KARAVALI COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 2
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
Jonaue
It forms the base of the mouth
Muscular-membranous structure
‘They contain taste buds and the
papillae’s
‘The tongue helps in speech and mixing
of the food.
TEETH:
‘There are 16416 Teeths in mouth fixed to the
sockets in maxilla and mandible,
Arranged curved form
Helpful in tearing, crushing and grinding of the
food.
‘The Teeths are INCISORS (4+4), CANINES (242),
PREMOLARS (444), MOLARS (6+6)..
wo
sate
KARAVAL! COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
ian
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
SALIVARY GLAND:
3 pairs are seen,
PAROTID, SUBMAXILLARY OR SUBMANDIBULAR AND
SUBLINGUAL
‘These glands open up in the oral cavity
PAROTID GLAND: they are situated in front and below to
ear, they secrete Ptyalin, these glands open up into the
cheeks of mouth on either side
SUBMAXILLARY OR SUBMANDIBULAR: situated at bottom
of the mouth on either side, they are mixed gland i.e.,
seromucouis and these glands open up in the mouth
SUBLINGUAL: situated below to tongue, mixed in nature,
open up at the base of tongue.
© Pravided with sym. and parasym, Nervous system.
HISTOLOGY:
* Tubiilo-alveolar exocrine gland
* Has lobules made of alveoli and supporting
connective tissue called as INTERLOBULAR
SEPTUM,
Alveoli contain secretory cells je. Serous and
the mucous
Nucleus of the Serous cells are round and are
present at the base, nucleus of the mucous
cells is flat and are present at the base.
Parotid gland contains more of the serous
‘gland
Sublingual contain more of the mucous gland
and
‘Submaxillary/ submandibular has both
serous and the mucaus/ mixed gland.
KARAVALI COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
SALI
© Mixed secretion of the salivary gland
COMPOSITION:
Water (99.5%)
SOLIDS LIKE INORGANIC SALTS
SOD. CHL, KCL
ORGANIC COMPONENTS Li
Enzymes such as ptyalin (salivary amylase),
Phosphatase, lipase and mucin
Urea, uric a
JgA antibodies
Ph is neutral or slightly acidic 6.0-7.0.
FUNCTION OF SALIVA:
«The salivary amylase acts on the boiled starch and converts it to maltose and dextrin
Contains the enzyme lysozyme that kills micro-organism
Slight acidic Ph of the sativa kills Micro organism
Mucin in the saliva helps in the lubrication and helps in passage of the food
Helps as the buffer for acid base balance
Decrease the temperature of food that are hot when taken in mauth.
‘PHARYNS:
Common tube for both food and the air
Starts from the nasal cavity and ends till the C6 vertebrae
‘They are connected to the oesophagus
They are different type
Nasophatynx, oropharynx, larynigopharynx
They help in the transportation of the food from the oral cavity to the oesophagus
‘They also help in the transport of the air into the lungs
‘They help in the hearing process.
KARAVAL! COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NOTES
OESOPHAGUS:
Tube like structure extending from the pharynx to the stomach
They are 25 cm in length
‘They have 3 parts
1, CERVICAL (4 em} 2, Thoracic (20 cm) 3, ABDOMINAL(Zem)
Extend from the C6 vertebrae upto the Cardia end of Stomach
‘The microscopy of the oesophagus shows: mucosal layer (has 3 layersa) lining epitheliurn,
b) famina propria c) muscularis mucosa), Submucous layer, muscularis externa, fibrous
J shaped structure
Connected to the esophagus at the Cardia end
Itdistends when filled
Capacity is 1-2 Lt
It stores the food and partly digests the food due to the presence of the gastric secretions
ie, gastric juice
‘The digestion happens by the contractions of the muscles of the stomach
‘They have 2 sphincters a) cardiac sphineter and b) pyloric sphincter
KARAVALI COLLEGE OF PHARMACY 6
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 1.2A Pictures of Glassware and EquipmentDocument2 pages1.2A Pictures of Glassware and Equipmentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Sectioning: Paraffin Section CuttingDocument12 pagesSectioning: Paraffin Section Cuttingaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab InustrumentDocument7 pagesLab Inustrumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0303243420300192 Mainaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830Document15 pages242c1789-05b6-4fe7-8bf8-aa9bb7961830aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Lab 3 HistologyDocument10 pagesLab 3 Histologyaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffDocument21 pages43ea5612-5704-41d8-96f4-b0cef6d6bdffaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Proteins-Ppt From Search 3Document6 pagesProteins-Ppt From Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument23 pagesDocumentaminqasm111No ratings yet
- 3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFDocument17 pages3rd Basic Laboratory Operations PDFaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Introduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3Document6 pagesIntroduction To Argos Software 13051467 - From - Search 3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.7.Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.7.aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Lec-1Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Lec-1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- 1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024Document8 pages1st Semester General Chemistry Course Catalogue Morning 2023 2024aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Computer Essentials - Chapter1Document38 pagesComputer Essentials - Chapter1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- CamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41Document13 pagesCamScanner 07 28 2023 21.41aminqasm111No ratings yet