Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hardening
Uploaded by
madzieuuuuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hardening
Uploaded by
madzieuuuuCopyright:
Available Formats
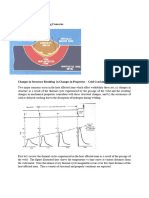
Hardening is a metallurgical process which we use where we want to increse
the hardness of the metal at the expense of plasticity. Due to this, the metal is
more resistant to wear, erosion, and it doesn’t elongate as much when exposed
to tensile stress.
Types of hardening
We have 2 main types of hardening with and without the use of a heat.
To the type that doesn’t involve heat we can include
work hardening and shot -peening
The types that involve heat are
Quenching, tempering, precipitation hardening and case hardening
Of course there are many more types of the same process that differienties in
how it goes or how the end piece will behave but it would take too much time
to include all of these in this presentation.
Work hardening is a a metal working technique that in the process also hardens
the metal. The structure of the metal gets stronger because of the compression
we’re putting it under. The structure and atoms are closer together, making it
more coherent. In addition to that the pressure breaks down the grain into
smaller grains which also increses the strength of the metal. This result can be
achived also by rolling or hammering the workpiece. Which means we don’t
have to change the shape of the component in order to harden it.
Shot peening is a similar proces to work hardening, that means the reason why
the metal gets harder is the same. Shot-peening involves shooting small metal
balls at the Surface of a workpiece. Because of that only the top layer of the
material changes it’s properties, leaving the core more elastic which can be
beneficial in use of tools, making them last longer without breaking.
Quenching is a heat treatment technique. In short this process relies on heating
a metal to high, given for that type of material temperature (for steel it is 30-50
degrees above Ac3, ac1,3 line) and quickly cooling it by dipping it in water or
oil. After this we get a material that is much stronger but of course more brittle
than before. The microstructure we get after this is martensite or bainite, it
depends on how quickly we cooled the metal.
Tempering is an additional process that is done after Quenching in order to get
a bit more elastic and less brittle material. It involves reheating a workpiece to
high, but not as high as in quenching temperature. The temperature depends
on what type of tempering we want to do. We have high, medium and low
tempering. Since we’re focusing on hardness of a metal we’ll Focus more on
low tempering. With combination of quenching and low tempering we get a
process called heat hardening. It relivies the stress in the workpiece but at a
cost we have slightly more ductile material, which of course means it’s not as
hard as before, however it is still much stronger than not doing nothing.
precipitation hardening also called age hardening is very similar to tempering,
however the heat is maitained for much longer period of time, often reaching
days or weeks. It involves formation of fine precipitates within the metal matrix.
The precipitates formed during this process is what gives the metal it’s new
hardness. The product we recive at the end is much stronger than what we
could get with tempering. The strength i also dependend on how long we keep
the material in given teperature. Generally lower temperature in longer periods
of time gives us better results. Of course we can make the process be done in
few hours in higher temperaturę but it’ll have worse qualities than the one that
is maintained in low temperature for a few days. It’s mostly used in alluminium
and copper alloys instead of steel, but
case hardening is a process in which heat up the metal in a mixture of gases
(not in the air).
Examples of what these gases can contain is carbon, boron or nitrogen.
The exact processes in which we achive given layers on the Surface of the
material are in order, Carburizing, Boring and Nitriding. These elements form a
bond with the exposed atoms of the metal we want to case harden. Which
harden the outer layer of the work piece, it’s Surface hardened. Unfortunatelly
this type of heat treatment needs specialized type of furnace that can introduce
the atmosphere with previously mentioned elements.
You might also like
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment (Annealing)Document6 pagesHeat Treatment (Annealing)arhummajeed751No ratings yet
- The Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Heat TreatmentDocument6 pagesHeat TreatmentVarun KavvampalliNo ratings yet
- Annealing (Metallurgy)Document3 pagesAnnealing (Metallurgy)shofira zuhrahNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment is the Process of Heating Metal Without Letting It Reach Its Molten, Or Melting, Stage, And Then Cooling the Metal in a Controlled Way to Select Desired Mechanical Properties. Heat Treatment is Used ToDocument14 pagesHeat Treatment is the Process of Heating Metal Without Letting It Reach Its Molten, Or Melting, Stage, And Then Cooling the Metal in a Controlled Way to Select Desired Mechanical Properties. Heat Treatment is Used Toxy zNo ratings yet
- Crystalline vs Non-Crystalline Materials and Heat Treatment ProcessesDocument19 pagesCrystalline vs Non-Crystalline Materials and Heat Treatment ProcessesAlhaj MassoudNo ratings yet
- Annealing (Metallurgy)Document5 pagesAnnealing (Metallurgy)Vijay Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Annealing (Metallurgy) : Merged DiscussDocument5 pagesAnnealing (Metallurgy) : Merged DiscussDia Andrita RahmanNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of MetalsDocument7 pagesHeat Treatment of MetalsGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Explained: What It Is and Why It's ImportantDocument12 pagesHeat Treatment Explained: What It Is and Why It's ImportantGanesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Effects on Material PropertiesDocument5 pagesHeat Treatment Effects on Material PropertiesArgha DasNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatments PDFDocument2 pagesHeat Treatments PDFJhony BhatNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Processes and Metal Plating Methods ExplainedDocument5 pagesHeat Treatment Processes and Metal Plating Methods Explainedanon_294705394No ratings yet
- Heat Treating: Training ObjectiveDocument7 pagesHeat Treating: Training ObjectiveDaniel GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Mt14 ReviewerDocument16 pagesMt14 ReviewerMichelle TuballaNo ratings yet
- What Is Heat Treatment?: Written By: Johnsinit - Edited By: Lamar Stonecypher - Updated: 1/8/2011Document2 pagesWhat Is Heat Treatment?: Written By: Johnsinit - Edited By: Lamar Stonecypher - Updated: 1/8/2011విష్ణువర్ధన్రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals: Ali RazaDocument18 pagesMechanical Engineering Fundamentals: Ali RazaAhmad ButtNo ratings yet
- 202 Out2Document8 pages202 Out2professorNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment ServisDocument10 pagesHeat Treatment ServisMuhammad SyameerNo ratings yet
- Annealing (metallurgy) - Heat treatment softens metalsDocument4 pagesAnnealing (metallurgy) - Heat treatment softens metalsStephen MontelepreNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of MetalsDocument3 pagesHeat Treatment of MetalsIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- Basic Heat Treatment of MetalsDocument5 pagesBasic Heat Treatment of MetalscalliepearsonNo ratings yet
- Hot Working & Cold WorkingDocument34 pagesHot Working & Cold Workingavutu_kunduruNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of SteelDocument3 pagesHeat Treatment of SteelpramodNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document3 pagesLab Report 3John HowellNo ratings yet
- Ayu Anjelia CH - 43219055 - 4B Alih Jenjang - Heat Treament of SteelDocument4 pagesAyu Anjelia CH - 43219055 - 4B Alih Jenjang - Heat Treament of SteelAnanda WulandariNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process - Module2.0Document33 pagesManufacturing Process - Module2.0Fiza KamaNo ratings yet
- Brass AnnealingDocument11 pagesBrass AnnealingChristos KalavrytinosNo ratings yet
- Discuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsDocument3 pagesDiscuss at Least Four Techniques in Forming MetalsJeffrey JimenezNo ratings yet
- Strain Hardening MechanismsDocument9 pagesStrain Hardening MechanismsRho AsaNo ratings yet
- Basic Heat TreatmentDocument12 pagesBasic Heat Treatmentpramod_goswamiNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Processes GuideDocument18 pagesHeat Treatment Processes GuideShyam PatidarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 HeatTreatmentDocument7 pagesLesson 6 HeatTreatmentupenderNo ratings yet
- Metals and AlloysDocument13 pagesMetals and Alloyswoi mariaNo ratings yet
- Completely Describe The Iron-Carbon Diagram With HelpingDocument5 pagesCompletely Describe The Iron-Carbon Diagram With HelpingwaqarNo ratings yet
- ENGR3526 - Heat Treatment LabDocument3 pagesENGR3526 - Heat Treatment LabStephanie BoatengNo ratings yet
- Annealing Process ExplainedDocument5 pagesAnnealing Process ExplainedAntonius TanNo ratings yet
- Tempering (Metallurgy)Document11 pagesTempering (Metallurgy)apa605No ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Ferrous MetalsDocument8 pagesHeat Treatment of Ferrous Metalsarchangeluriel06No ratings yet
- Fundmentals of ManufacturingDocument4 pagesFundmentals of ManufacturingBivas PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Objectives and ProcessesDocument6 pagesHeat Treatment Objectives and ProcessesAdaitaChowdhury100% (1)
- Heat TreatmentDocument30 pagesHeat TreatmentDr-Bharath Vedashantha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Question 3Document4 pagesQuestion 3Fazerin ShahNo ratings yet
- Tempering (Metallurgy)Document12 pagesTempering (Metallurgy)rochmat sawaludinNo ratings yet
- Iare Amp Lecture NotesDocument98 pagesIare Amp Lecture NotesDeepika PandeyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and Production Lecture NotesDocument98 pagesAircraft Materials and Production Lecture NotesRadhika AmmuluNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon SteelDocument12 pagesHeat Treatment of Plain Carbon Steelweda walata heduwaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Machine Design by R.S.khurMI and J.K.guptA (Tortuka)Document3 pagesTextbook of Machine Design by R.S.khurMI and J.K.guptA (Tortuka)Sln RjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2Document43 pagesChapter 2 2Borokinni ToluNo ratings yet
- Metalurgi FisikDocument8 pagesMetalurgi FisikAgustine SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Processes Affecting Changes in PropertiesDocument13 pagesProcesses Affecting Changes in PropertiesMark julius garciaNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Techniques Alter Metal PropertiesDocument6 pagesHeat Treatment Techniques Alter Metal PropertiesAHMAD NAIM BIN AHMAD NAZRI / UPMNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment (Slide)Document13 pagesHeat Treatment (Slide)Afiq SaimiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Alloying Elements on Fe-Fe3C SystemDocument62 pagesEffect of Alloying Elements on Fe-Fe3C SystemHarsha MallaNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming and Heat TreatmentDocument75 pagesMetal Forming and Heat Treatmentkenneth iyahenNo ratings yet
- Welding Metallurgy 2Document12 pagesWelding Metallurgy 2mmr315No ratings yet
- Dual PhaseDocument3 pagesDual Phaseahmed ezwaiNo ratings yet
- Api 571Document41 pagesApi 571majid100% (1)
- TLE SMAW For DemoDocument3 pagesTLE SMAW For DemoRobin Rafael PescaderoNo ratings yet
- Lathe Machine OperationDocument13 pagesLathe Machine OperationRizuanul Arefin EmonNo ratings yet
- Recommended KISWEL Products As Per ASTMDocument21 pagesRecommended KISWEL Products As Per ASTMSun SunNo ratings yet
- Shackles: 5150 - Nut & Bolt Bow ShackleDocument1 pageShackles: 5150 - Nut & Bolt Bow ShackleAlthaf R100% (1)
- Balusters and Balustrade - Components, Types and DetailsDocument17 pagesBalusters and Balustrade - Components, Types and DetailsAnqa ParvezNo ratings yet
- Geostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesDocument1 pageGeostats Pty LTD: Base Metal AnalysesJhony Enrique Morales LauraNo ratings yet
- Astm A131Document5 pagesAstm A13109122912680100% (5)
- Syi Cata GeneDocument1 pageSyi Cata Genebelay agaNo ratings yet
- JWS-165 Well Service Pump: Parts ListDocument13 pagesJWS-165 Well Service Pump: Parts ListGildardo Mora100% (2)
- Ramset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ - EPCON C8 Anchor StudsDocument8 pagesRamset Specifiers Anchoring Resource Book ANZ - EPCON C8 Anchor Studsyyanan1118No ratings yet
- Cutting - in - Practice - Blades IndicationsDocument24 pagesCutting - in - Practice - Blades IndicationsHector Elias Mercedes HazimNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Is A Domain Of: Etymology and PronunciationDocument10 pagesMetallurgy Is A Domain Of: Etymology and Pronunciationprashantbaid05No ratings yet
- Technical Sheet ALOCROM 1200: PropertiesDocument2 pagesTechnical Sheet ALOCROM 1200: Propertiesvijay yadavNo ratings yet
- 215-Astm A 394 2000 Steel Transmission Tower Bolt, Zinc Coated - Bare PDFDocument7 pages215-Astm A 394 2000 Steel Transmission Tower Bolt, Zinc Coated - Bare PDFgraduateNo ratings yet
- Progress in Materials Science: Lenka Kunc Ická, Radim Kocich, Terry C. LoweDocument49 pagesProgress in Materials Science: Lenka Kunc Ická, Radim Kocich, Terry C. LoweDaniel FridmanNo ratings yet
- M525 Application Guide - Speed & Feed (Inch) : Common Machining FormulasDocument1 pageM525 Application Guide - Speed & Feed (Inch) : Common Machining FormulasRobotNo ratings yet
- What is Q345 Steel? Guide to Properties and SpecificationsDocument15 pagesWhat is Q345 Steel? Guide to Properties and SpecificationsDESIGNNo ratings yet
- GR 5 Term 2 2020 Ns T Resource PackDocument38 pagesGR 5 Term 2 2020 Ns T Resource PackLorraine NoloNo ratings yet
- Separate Chemistry: Higher Tier in BoldDocument16 pagesSeparate Chemistry: Higher Tier in BoldzipperNo ratings yet
- Sae Ams 5796D 2000 (En) PDFDocument6 pagesSae Ams 5796D 2000 (En) PDFWilliam LooNo ratings yet
- Band Gang Saw Blades 2008 en PDFDocument15 pagesBand Gang Saw Blades 2008 en PDFZokac TeoNo ratings yet
- High Temperature Brazing AlloysDocument0 pagesHigh Temperature Brazing AlloysvkmsNo ratings yet
- Kirsch® Architrac® Series 9600 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesKirsch® Architrac® Series 9600 Spec SheetznvwvsixNo ratings yet
- Albrecht Precision Drill Chucks: The World'S Most Consistently Accurate Drill ChucksDocument10 pagesAlbrecht Precision Drill Chucks: The World'S Most Consistently Accurate Drill ChucksfgrefeNo ratings yet
- AH MergedDocument6 pagesAH MergedReginaldo SantosNo ratings yet
- Goulds IC Pump BulletinDocument24 pagesGoulds IC Pump BulletinSergio E. Marchetti Newco S. A.100% (1)
- Ti SPC Ohe Atd 0060Document16 pagesTi SPC Ohe Atd 0060pradeeepgarg100% (1)
- CE 2101: Engineering Materials: Rumana AfrinDocument18 pagesCE 2101: Engineering Materials: Rumana AfrinRumana AfrinNo ratings yet
- Miners' Guild - Mining in LythiaDocument16 pagesMiners' Guild - Mining in LythiaA.J. GrundNo ratings yet
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesFrom EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- Exercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandExercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesFrom EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Handbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesFrom EverandHandbook of Fire and Explosion Protection Engineering Principles: for Oil, Gas, Chemical and Related FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionFrom Everand3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionArnaud PerrotNo ratings yet
- Autophagy in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAutophagy in Health and DiseaseBeverly RothermelNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceFrom EverandEnvironmental and Health and Safety Management: A Guide to ComplianceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849From EverandSafety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- General Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismFrom EverandGeneral Orders for Security Personnel: A Guide to Maintaining Discipline and ProfessionalismNo ratings yet
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet