Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxidation Number Rules
Uploaded by
suvodeep715Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oxidation Number Rules
Uploaded by
suvodeep715Copyright:
Available Formats
Determining Oxidation Numbers
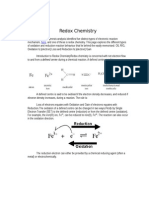
Rule #1: The oxidation state of an uncombined element not possessing an electric charge is always zero.
This is true regardless of whether the element exists as an atom or a polyatomic molecule. This means
that O2 (oxygen), Mg2 (magnesium), Al (aluminum), He (helium), and S8 (sulfur) have the oxidation
number zero, because the oxidation state of the individual atoms wasn’t changed during the formation
of the molecule. The bonds between atoms of the same element are always covalent, wherein electrons
are shared, rather than ionic, wherein electrons are passed from one reagent to another. The question
of oxidation states only applies to reactions where ionic bonds are formed.
Rule #2: The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to the charge on it. For instance, Na + (sodium
ion with one electron missing), Al3+ (aluminum ion with three electrons missing), and Cl– (chlorine ion
with one extra electron) have the oxidation numbers +1, +3, and -1, respectively. However, many metals
as well as nonmetals can form different ions (notably carbon, sulfur, and iron), and can have multiple
oxidation states. So, though the charge is equal to the oxidation state, it may not be consistent.
Rule #3: The oxidation number of oxygen is almost always -2. The only time oxygen’s oxidation number
shifts is when it is part of a class of compounds called ‘peroxides’. In that case, it becomes -1.
Rule #4: Similarly, the oxidation number of hydrogen is almost always +1. The only time this is altered is
if hydrogen forms a transitional binary hydride with a metal. In this rare event, it becomes -1.
Rule #5: Lying in the same group of the periodic table as hydrogen, alkali metals such as lithium, sodium,
and potassium also have an oxidation number of +1. The only time this changes is when the metals are
in the elemental form, in which case their oxidation state is zero.
What is the oxidation number of phosphorus in H3PO2 molecule? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Oxidation number of H is +1
Oxidation number of O is -2
H3PO2
3 + x- 4 = 0 or x – 1 = 0 ∴ x = + 1
Thus oxidation number of P in H3PO2 = +1.
You might also like
- 0007190-Fundamentals of Corrosion and Corrosion Control ForDocument25 pages0007190-Fundamentals of Corrosion and Corrosion Control ForPDHLibraryNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument41 pagesElectro Chemistrysrik1376No ratings yet
- Unit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesUnit I. Electrochemistry: Learning ObjectivesArdenz Emrey LagascaNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds PDFDocument18 pagesNaming Compounds PDFJohn Jade BasuelNo ratings yet
- Oxidation NumberDocument19 pagesOxidation NumbershruthiNo ratings yet
- L Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R EductionDocument10 pagesL Oss of E Lectrons Is O Xidation G Ain of E Lectrons Is R Eductionherman lewisNo ratings yet
- RedoksDocument33 pagesRedokssanty_vanftowsNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument34 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentचौकीदार गोपाल भार्गवNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument6 pagesRedox ReactionsManda BaboolalNo ratings yet
- As Chapter 6a ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesAs Chapter 6a ElectrochemistryNazil HaziqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Document22 pagesChemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Document22 pagesChemistry For Engineers: CHEM 114Ivyy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- 3830 Lecture Notes Part4 - 2008 - RedoxDocument18 pages3830 Lecture Notes Part4 - 2008 - RedoxKola PattabhiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationDocument5 pagesChemistry Handout 12 REF #: 012: Reduction and OxidationNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Forming Redox EquationDocument17 pagesForming Redox EquationfatiniNo ratings yet
- Valency & Bonding, Oxidation States and Redox ReactionDocument18 pagesValency & Bonding, Oxidation States and Redox ReactionRufus TsaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesUnit 4 ElectrochemistryElaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- #1 Soal Diskusi RedoksDocument8 pages#1 Soal Diskusi RedoksAlfi FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12oxidation and ReductionDocument17 pagesChapter 12oxidation and ReductionSiyabonga MaphsaNo ratings yet
- ppt6 REDOX PDFDocument17 pagesppt6 REDOX PDFOscar Kelvin NsituNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecule and Chemical ReactionDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecule and Chemical ReactionSolomon BinutuNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument5 pagesRedox ReactionsAthulRKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University: Term PaperDocument15 pagesLovely Professional University: Term PaperhemantNo ratings yet
- Oxidation States (Oxidation Numbers) - ChemistryDocument1 pageOxidation States (Oxidation Numbers) - Chemistrydonya2dhNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryTan Li XinNo ratings yet
- 2-Electrochemistry: Week 3 - Topic 2Document65 pages2-Electrochemistry: Week 3 - Topic 2ClarkNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument4 pagesRedox Reactionsronique sanchoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document6 pagesLecture 13provanowrin5No ratings yet
- Oxidation State: N.B. Errors in This Entry in The Printed Version of The CompendiumDocument1 pageOxidation State: N.B. Errors in This Entry in The Printed Version of The CompendiumVibhor SahajiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.4 Redox Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Oxidising and Reducing Agents Redox ReactionsDocument7 pagesTopic 2.4 Redox Reactions Oxidation and Reduction Oxidising and Reducing Agents Redox ReactionsranazikriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chemistry Class 11Document27 pagesChapter 8 Chemistry Class 11Ravinder singhNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 Definitions: Oxidation and Reduction Take Place Together at The Same Time in The SameDocument22 pages9.1 Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 Definitions: Oxidation and Reduction Take Place Together at The Same Time in The SameJaimin SuraniNo ratings yet
- Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Document34 pagesOxidation-Reduction Reactions Princess...Warren Mark ManguneNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Notes Redox EquilibriaDocument21 pages5.3 Notes Redox EquilibriaDiego Istheillest HinesNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Numbers (Oxidation States)Document18 pagesOxidation Numbers (Oxidation States)ArtiChamoliNo ratings yet
- chm022L Redox LecDocument39 pageschm022L Redox LeckeishasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Baldwin Girls' High School, Bengaluru-25 STD: 7, Subject: Chemistry Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesBaldwin Girls' High School, Bengaluru-25 STD: 7, Subject: Chemistry Atomic StructureSanhitha RameshNo ratings yet
- 1 Principle of Chemistry 2Document12 pages1 Principle of Chemistry 2Thu ReinNo ratings yet
- 11oxida PDFDocument3 pages11oxida PDFThuvarakaNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument5 pagesChem NotesShanel WisdomNo ratings yet
- 1-Basic of CorrosionDocument41 pages1-Basic of CorrosionMohamed Gawad ARayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Redox and Electrochemistry NotesDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Redox and Electrochemistry NotesspotifyNo ratings yet
- Redox Chemistry: Background To Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesRedox Chemistry: Background To Redox ReactionAhmed Mohamed EwisNo ratings yet
- Manila CityDocument14 pagesManila Cityapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Class XI Redox Reactions NotesDocument5 pagesClass XI Redox Reactions NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: Classical Idea of Redox ReactionDocument10 pagesRedox Reactions: Classical Idea of Redox ReactionRohan ThomasNo ratings yet
- L-15 Electro ChemistryDocument29 pagesL-15 Electro ChemistryAkhilesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Electrochemistry - Modified - GutoDocument35 pagesLecture 5 - Electrochemistry - Modified - GutoSamwel MwetichNo ratings yet
- Reductive EliminationDocument14 pagesReductive EliminationAɞdȗl NąvêêdNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Bonds and Groups Chapter 1 - Atoms and ReactionsDocument2 pagesAtoms, Bonds and Groups Chapter 1 - Atoms and ReactionsEleanorNo ratings yet
- (Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Document14 pages(Week 5) - Module 5-Gen - Chem. 2Diana Joy Ancheta CldheiNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Numbers: Oxidation Numbers Are Made-Up or Hypothetical Numbers Assigned To Each AtomDocument4 pagesOxidation Numbers: Oxidation Numbers Are Made-Up or Hypothetical Numbers Assigned To Each AtomYuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSDocument6 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Notes Anil CH 8. REDOX REACTIONSKrishnendu NairNo ratings yet
- L14 - Reduction and OxidationDocument50 pagesL14 - Reduction and OxidationNur AishahNo ratings yet
- 2020F CHM102 E4 RedoxDocument18 pages2020F CHM102 E4 Redoxpdchemigcse1786No ratings yet
- RedoxDocument51 pagesRedoxsankarNo ratings yet
- Chemical FormulasDocument12 pagesChemical FormulasApple PinpinNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument13 pagesRedox ReactionforbeskaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Biology (10) Question Paper NidtemDocument4 pagesBiology (10) Question Paper Nidtemsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Biology (10) Question Paper NidtemDocument4 pagesBiology (10) Question Paper Nidtemsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Circular Motion of A Car On A Level RoadDocument2 pagesCircular Motion of A Car On A Level Roadsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Class X CH 10Document3 pagesClass X CH 10suvodeep715No ratings yet
- Half Yearly QUESTION PAPER Science Class IXDocument6 pagesHalf Yearly QUESTION PAPER Science Class IXsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Pulley Problems IIT JEE - JEE MainDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion - Pulley Problems IIT JEE - JEE Mainsuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Class 12 Term 2 Physics ActivityDocument8 pagesClass 12 Term 2 Physics Activitysuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Class 12 CH 1 QuestionsDocument4 pagesClass 12 CH 1 Questionssuvodeep715No ratings yet