Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Job Analysis
Uploaded by
Bheiybie Jayne Frias0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesThe document summarizes the process of job analysis, which involves gathering information about a job's components, characteristics, and requirements in order to determine the work activities and write an accurate job description. An effective job analysis is important for tasks like employee selection, training, and compliance with legal guidelines. The key sections of a job description are the job title, work activities, tools/equipment, work context, performance standards, and compensation. Structured methods for conducting a job analysis include questionnaires, surveys, and collecting critical incidents from employees.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the process of job analysis, which involves gathering information about a job's components, characteristics, and requirements in order to determine the work activities and write an accurate job description. An effective job analysis is important for tasks like employee selection, training, and compliance with legal guidelines. The key sections of a job description are the job title, work activities, tools/equipment, work context, performance standards, and compensation. Structured methods for conducting a job analysis include questionnaires, surveys, and collecting critical incidents from employees.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesJob Analysis
Uploaded by
Bheiybie Jayne FriasThe document summarizes the process of job analysis, which involves gathering information about a job's components, characteristics, and requirements in order to determine the work activities and write an accurate job description. An effective job analysis is important for tasks like employee selection, training, and compliance with legal guidelines. The key sections of a job description are the job title, work activities, tools/equipment, work context, performance standards, and compensation. Structured methods for conducting a job analysis include questionnaires, surveys, and collecting critical incidents from employees.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Job Analysis ● Job evaluation results
● Gathering, analyzing, and structuring ● Employees feelings of
information about a job’s personal worth
components, characteristics, and - Affects clarity of resumes
requirements (Sanchez & Levine,
2000). Brief Summary
● It is the process of determining the - Useful for recruitment advertising
work activities and requirements, - Should be written in an easy to understand
and the job description is the written style
result of the job analysis. - Jargon and abbreviations should not be
used
Importance of Job Analysis
● Writing job descriptions Work Activities
● Employee selection - Organize by dimensions
● Training ● Similar activities
● Personpower planning ● Similar KSAOs (Knoledge, skills,
● Performance appraisal abilities, and other characteristics
● Job Classification ● Temporal order
● Job evaluation Task statements
● Job design ● List only one activity per statement
● Compliance with ● Statements should be able to “stand
● Legal guidelines alone”
● Organizational ● Should be written in an easy to
● Analysis understand style
● Use precise rather than general
Job Description Sections words
● Job Title “Responsible for”
● Brief summary “Oversees”
● Work activities “Handles accounts”
● Tools and equipment used
● Work context Work Context
● Work performance - Work schedule
● Compensation information - Degree of supervision
● Job Competencies - Ergonomic information
● Physical and Psychological Stress
Job Title ● Indoors v. outdoors
- Describes the nature of the job ● Lighting/heat/noise/physical space
- Assists in employee selection and ● Clean v. dirty environment
recruitment ● Standing/sitting/bending/lifting
Work Performance
- Affects perceptions of job worth and status - Describes how performance is evaluated
- This section might include ● Human resources
● Standards used ● Compensation
● Frequency of evaluation ● Training
● Evaluation dimensions ● Engineering
● The person doing the evaluating
- Internal task force
Compensation Information - Supervisors
● Job evaluation dimensions - Employees
● Exempt status - Consultants
● Pay grade - Interns/class projects
● Job group
Which Employees Should Participate?
EEO-1 Category - Choices
1. Officials and managers ● All employees
2. Professionals ● Random sample
3. Technicians ● Representative sample
4. Sales workers ● Convenience sample
5. Office and clerical
6. Craft workers - Potential Differences
7. Operatives ● Job competence
8. Laborers ● Race
9. Service workers ● Gender
● Education level
Job Competencies ● Viewpoint
- Common Names
What Type of Information Should be
● Job competencies Gathered?
● Knowledge, skill, ability, and other
characteristics (KSAOs) Types of Requirements
● Job specifications - Formal
- Informal
- Competencies should be separated
Level of Specificity
● Those needed before hire ● Job- Loan officer
● Those that can be learned after hire ● Position- Loan officer at the Boone
branch
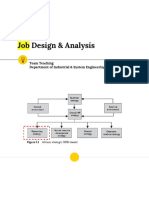
Preparing for a Job Analysis ● Duty- Approval of loans
Who Will Conduct the Job Analysis? ● Task -Investigates loan history to
determine if applicant has bad credit
- Internal Department ● Activity- Runs credit histories on
credit machine
● Element- Enters applicant’s SSN ● The statement should make sense by
into credit machine itself
● Sub element- Elevates finger 30 ● All statements should be written in
degrees before striking key the same tense
● Should include the tools and
Conducting a Job Analysis equipment used to complete the task
Basic Steps ● Task statements should not be
Step 1: Identify tasks performed competencies
● Task statements should not be
Step 2: Write task statements policies
—Step 3: Rate Task Statements—
Step 3: Rate task statements - Tasks can be rated on a variety of scales
Step 4: Determine essential KSAOs ● Importance
● Part-of-the-job
Step 5: Select tests to tap KSAOs ● Frequency of performance
● Time spent
—Step 1: Identify Tasks Performed— ● Relative time spent
- Gathering existing information ● Complexity
- Interviewing subject matter experts ● Criticality
(SMEs) - Research shows only two scales are
● Individual interviews necessary
● SME Conferences ● Frequency
● Ammerman Technique ● Importance
- Observing incumbents
- Job participation Using the Ratings
- Create a chart summarizing the ratings
—Step 2: Write Task Statements— - Add the frequency and importance ratings
- Required elements to a task statement to form a combined rating for each task
● Action - Include the task in the final task inventory
● Object if:
- Optional elements ● Average rating is greater than .5 for
● Where the task is done both frequency and importance {or}
● How it is done ● Combined rating is 2.0 or higher
● Why it is done
● When it is done
- Characteristics of well-written task
statements
● One action and one object
● Appropriate reading level
- Job Adaptability Inventory
Structured Job Analysis Methods
- 132 items
General Information about Worker
- 8 adaptability dimensions
Activities
● Handling emergencies
- Position Analysis Questionnaire
● Handling work stress
- 194 Items
● Solving problems creatively
- 6 main dimensions
● Dealing with uncertainty
● Information input
● Learning
● Mental processes
● Interpersonal adaptability
● Work output
● Cultural adaptability
● Relationships with others
● Physically orienting adaptability
● Job context
- Personality-Related Position Requirements
● Other
Form
- Easy to use
● 107 items items
- Standardized
● 12 personality dimensions
- Difficult to read for average employee
- Fleishman Job Analysis Survey
- Job Structure Profile
● 72 abilities
● Designed as a replacement for the
● Good reliability
PAQ
- Critical Incident Technique
● Easier to read than the PAQ
● Job incumbents generate incidents of
● Good reliability
excellent and poor
- Job Elements Inventory
● performance
● 153 items
● Job experts examine each incident to
● 10th grade readability level
determine if it is an
● Correlates highly with PAQ
● example of good or poor
- Functional Job Analysis
performance
● Data
● 3 incumbents sort incidents into
● People
categories
● Things
● Job analyst combines and names
categories
● 3 incumbents resort incidents into ● Master’s degree
combined categories - Responsibility
● Number of incidents per category ● Makes no decisions
provides an idea of the importance of ● Makes decisions for self
each category ● Makes decisions for 1-5 employees
● Makes decisions for more than 5
The Ideal Compensation System employees
- Will attract and retain desired employees - Physical demands
- Will motivate current employees while ● Lifts no heavy objects
also providing security ● Lifts objects between 25 and 100
- Is equitable pounds
- Is in compliance with ● Lifts objects more than 100 pounds
legal guidelines
Determining Internal Pay Equity
- Determine compensable factors
- Determine levels for each factor
- Assign weights to each factor
- Convert weights to points for each factor
- Assign points to each level within a factor
- Assign points to jobs
- Run regression to determine how well
points predict salary midpoints
Step 1: Determining Compensable
Factors
- Compensable Factors
Examples
- responsibility
- complexity/difficulty
- skill needed
- physical demands
- work environment
Step 2: Determine Levels for Each
Compensable Factor
- Education
● High school degree or less
● Two year college degree
● Bachelor’s degree
- Does high compensation for CEOs actually
increase company performance?
- Should a company’s number one focus be
n making money for its shareholders?
- What might be other ethical factors
surrounding this issue?
Determining External Pay Equity
- Worth based on external market
- Determined through salary surveys
- Information obtained
● salary range
● starting salary
● actual salaries paid
● Benefits
Potential Salary Survey Problems
- Response rate
● organization conducted
● trade group conducted
- Finding comparable jobs
- Do salary surveys
perpetuate discrimination?
- Do salary surveys “fix”
salaries at low levels?
Focus on Ethics
Compensating CEOs and Executives
- Are CEOs being paid too much or are they
worth the high compensation packages they
receive?
- Is it ethical that a CEO receives a bonus
when employees are being laid off or having
their benefits reduced?
You might also like
- Business Level and Corporate Level StrategiesDocument9 pagesBusiness Level and Corporate Level StrategiesFun Toosh345No ratings yet
- 1,2&3 SQandSQADocument25 pages1,2&3 SQandSQASandy CyrusNo ratings yet
- Louis Vuitton Case StudyDocument27 pagesLouis Vuitton Case StudyUry Suryanti Rahayu AdzaniNo ratings yet
- Forwarder Certificate of Receipt (FCR)Document2 pagesForwarder Certificate of Receipt (FCR)Hua WeiNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 13Th Edition by RomneyDocument18 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 13Th Edition by Romneyyebegashet100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - JOB ANALYSIS AND JOB EVALUATION - Feb.9.2021Document95 pagesChapter 2 - JOB ANALYSIS AND JOB EVALUATION - Feb.9.2021Sofia Garchitorena SerranoNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis QuirinDocument67 pagesJob Analysis Quirinbushra asad khanNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis QuirinDocument67 pagesJob Analysis QuirinPriyanka ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis QuirinDocument67 pagesJob Analysis QuirinmimichurNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 HRMDocument8 pagesChap 3 HRMK59 HOANG THANH THUYNo ratings yet
- Independent University School of Business and EntrepreneurshipDocument18 pagesIndependent University School of Business and EntrepreneurshipSEERAT HASSAN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- HRM351 Job AnalysisDocument19 pagesHRM351 Job AnalysisAndrea Lộc Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Job Analysis and DesignDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Job Analysis and Designjemilart4realNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis Criteria Reliability ValidityDocument7 pagesJob Analysis Criteria Reliability ValidityMitraNo ratings yet
- HR Management: Dr. Nora MashhourDocument23 pagesHR Management: Dr. Nora Mashhour0sama HamedNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis: Becamex Business SchoolDocument27 pagesJob Analysis: Becamex Business SchoolNguyễn Thị Thanh ThúyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Job Design and Job AnalysisDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Job Design and Job Analysisdautron147No ratings yet
- Sem1 I O-PsychDocument40 pagesSem1 I O-PsychKenny CrosmonerNo ratings yet
- Review Class Part 2 For Industrial Psychology JOB ANALYSIS and EVALUATION - AdditionalDocument47 pagesReview Class Part 2 For Industrial Psychology JOB ANALYSIS and EVALUATION - AdditionalMary Ann AmbitaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Psychology NotesDocument7 pagesIndustrial Psychology NotesApple Joyce CañeteNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter 03Document54 pagesHRM Chapter 03Shewa DenekNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 I O PsychDocument4 pagesChapter 2 I O Psychchristineruthfare03No ratings yet
- Chap 02 - Job Analysis and EvaluationDocument52 pagesChap 02 - Job Analysis and EvaluationRen TengedanNo ratings yet
- M2. Analyzing Work and Designing Jobs - PPT 2Document40 pagesM2. Analyzing Work and Designing Jobs - PPT 2rj batiyegNo ratings yet
- HRM - 02 - HR Planning & Diversity Management PDFDocument23 pagesHRM - 02 - HR Planning & Diversity Management PDFmikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Job AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Job AnalysisAlthea GacilanNo ratings yet
- Chap 02 - Job Analysis and EvaluationDocument52 pagesChap 02 - Job Analysis and EvaluationMATHILDA ANGELA DENISE R. REYESNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Job Desing Job Analysis - 5f41fd2b91c2eDocument27 pagesSession 2 - Job Desing Job Analysis - 5f41fd2b91c2eIreshaNadeeshaniNo ratings yet
- HR Hand BookDocument23 pagesHR Hand BookMd. Rahat KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Job Analysis and EvaluationDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Job Analysis and EvaluationRhaylyn AranasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Organizational Structures and SystemsDocument147 pagesChapter 2 - Organizational Structures and SystemsLovely Jelliane UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Job AnalysisDocument35 pagesPart 3 - Job Analysis22002862No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Job Analysis and DesignDocument28 pagesChapter 3 Job Analysis and DesignafityzolaNo ratings yet
- L2 3-JobAnalysisTalentManagementDocument57 pagesL2 3-JobAnalysisTalentManagementChíi KiệttNo ratings yet
- Assessing Workplace Learning NeedsDocument7 pagesAssessing Workplace Learning NeedsTaranom BakhtiaryNo ratings yet
- OKE Job Analysis and EvaluationDocument52 pagesOKE Job Analysis and EvaluationLazain ZulhamNo ratings yet
- Employee Evaluation FormDocument1 pageEmployee Evaluation FormcruznoreenmNo ratings yet
- Building Internal EquityDocument38 pagesBuilding Internal EquityPK AAMIRNo ratings yet
- Building Internal EquityDocument38 pagesBuilding Internal EquitySaurabh Kulkarni 23No ratings yet
- Job As Determinant of Financial CompensationDocument24 pagesJob As Determinant of Financial CompensationRISHITHAKURNo ratings yet
- Job Description SchoolDocument37 pagesJob Description Schoolrenee brielle angelo duranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Job Analysis & DesignDocument40 pagesChapter 2 Job Analysis & DesignEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- Full Course AgileDocument126 pagesFull Course AgileOmnia RaafatNo ratings yet
- HRM Uint 2Document61 pagesHRM Uint 2Nazir Ahmed100% (1)
- Itmax System BerhadDocument6 pagesItmax System BerhadMuhammad DanialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Job AnalysisDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Job AnalysisNorjiella Binti Mohd NurdinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document67 pagesChapter 2Jordan ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Chap 02 - Analyzing and Evaluating JobsDocument13 pagesChap 02 - Analyzing and Evaluating JobsMichael Angelo Uy100% (1)
- Week 4 Personnel Selection 1011Document9 pagesWeek 4 Personnel Selection 1011Hieu HoangNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis: Presented by Sunil Amaan Indrajit Neetu ArunDocument35 pagesJob Analysis: Presented by Sunil Amaan Indrajit Neetu ArunSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Ew Stein Job DesignDocument10 pagesEw Stein Job DesignRohini KumarNo ratings yet
- Job Their RequirementsDocument8 pagesJob Their RequirementsAngel MalahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Developing Job ExpectationsDocument21 pagesChapter 5: Developing Job ExpectationsSyed Nagma ShabnamNo ratings yet
- (2021) Week#10 MosdmDocument37 pages(2021) Week#10 MosdmanshariNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal HandoutsDocument10 pagesPerformance Appraisal HandoutsPrabhat SahooNo ratings yet
- Job Design and Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningDocument40 pagesJob Design and Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningKalindu LiyanageNo ratings yet
- HRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJDocument14 pagesHRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJVijay prasadNo ratings yet
- HRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJDocument14 pagesHRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJVijay prasadNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument18 pagesJob AnalysisREHANRAJNo ratings yet
- 4 - Job Evaluation - 23 - 29 Jan2024Document18 pages4 - Job Evaluation - 23 - 29 Jan2024Sahil SinghhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.0 Job AnalysisDocument42 pagesChapter 3.0 Job AnalysisDeadLy PerformersNo ratings yet
- Job Design and Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningDocument40 pagesJob Design and Job Analysis and Human Resource PlanningKalindu LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - 30th SepDocument60 pagesSession 2 - 30th SepHashane PereraNo ratings yet
- Io PsychDocument7 pagesIo PsychPrecious KayeNo ratings yet
- Practical Project Management: Learning to Manage the Professional, Second EditionFrom EverandPractical Project Management: Learning to Manage the Professional, Second EditionRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Introduction To SwapsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To SwapsAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Declaration Format Loss of SV TVDocument1 pageDeclaration Format Loss of SV TVArivaazhi PeriyaswamyNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document221 pagesBook 1amiramohaaamed12No ratings yet
- The Collection by MacKinseyDocument124 pagesThe Collection by MacKinseyAbdel AzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Creative StrategiesDocument52 pagesChapter 9 Creative StrategiesVC LodewijkNo ratings yet
- Denise Nelson Operates Interiors by Denise An Interior Design ConsultingDocument2 pagesDenise Nelson Operates Interiors by Denise An Interior Design ConsultingAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2019 ECO State Rank Essay Plan BOP Lucas LinDocument2 pages2019 ECO State Rank Essay Plan BOP Lucas LinAbishek KarnanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Jamuna Group Financial Statement AnalysisDocument13 pagesA Case Study of Jamuna Group Financial Statement AnalysisMD. ISRAFIL PALASH100% (2)
- Cemco Holdings, Inc., G.R. No. 171815Document17 pagesCemco Holdings, Inc., G.R. No. 171815JaylordPataotaoNo ratings yet
- Models of HRMDocument9 pagesModels of HRMMd SaifNo ratings yet
- Woodbois Annual Report 2022Document61 pagesWoodbois Annual Report 2022Suresh PoojariNo ratings yet
- Crown Cork and Seal inDocument22 pagesCrown Cork and Seal inMuhammad Wahyu PriyambudiNo ratings yet
- HRM PPT Sem 4Document10 pagesHRM PPT Sem 4Palak LambaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Situasi Penerapan Kesehatan Kerja Pada Puskesmas Di Wilayah Jakarta Barat Tahun 2018Document7 pagesAnalisis Situasi Penerapan Kesehatan Kerja Pada Puskesmas Di Wilayah Jakarta Barat Tahun 2018nanikNo ratings yet
- Market Cap To GDP RatioDocument8 pagesMarket Cap To GDP RatiokalpeshNo ratings yet
- Cottage and Small Scale IndustryDocument23 pagesCottage and Small Scale IndustryMuhammad Shahzaib YousafNo ratings yet
- FPIP Vehicle Sticker Application FormDocument2 pagesFPIP Vehicle Sticker Application FormBryan Amerna100% (2)
- Iso 4379 1993Document9 pagesIso 4379 1993gökhan tanrıseverNo ratings yet
- Maize, Wheat, Soya Beans, Sugar Beans, Cowpeas, Sorghum, Groundnuts and VegetablesDocument2 pagesMaize, Wheat, Soya Beans, Sugar Beans, Cowpeas, Sorghum, Groundnuts and Vegetablescretu gabiNo ratings yet
- 94 - Reyes V TanDocument2 pages94 - Reyes V Tanmimiyuki_No ratings yet
- 6 Untapped Traffic Sources in 2020 That Convert With ANY NicheDocument22 pages6 Untapped Traffic Sources in 2020 That Convert With ANY Nichehamza driouchNo ratings yet
- Invoice TBC CHH Conex LTDDocument1 pageInvoice TBC CHH Conex LTDAnna MingulovaNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Nomor 2, Desember 2019 E-ISSN: 2655-7347: Keywords: Defect, Compensation, Gojek, Negligence, ShipmentDocument17 pagesVolume 2 Nomor 2, Desember 2019 E-ISSN: 2655-7347: Keywords: Defect, Compensation, Gojek, Negligence, ShipmentMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Distributed Ledger Identification Systems in The Humanitarian SectorDocument42 pagesDistributed Ledger Identification Systems in The Humanitarian SectorSamir BennaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eleven: Pricing StrategiesDocument47 pagesChapter Eleven: Pricing StrategiesBhaneka CreationsNo ratings yet