0% found this document useful (0 votes)
217 views13 pagesSolving Convolution Integrals
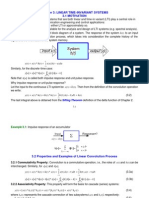
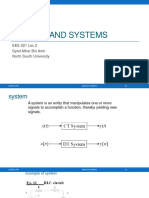
This document contains 4 problems involving convolution integrals. For each problem, it provides the steps to (1) sketch the signals, (2) integrate the convolution integral by breaking it into cases based on the limits of integration, and (3) combine the cases to obtain the final solution. It works through each step methodically and shows the detailed working to arrive at solutions for different signals and systems.
Uploaded by
ahmad mzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
217 views13 pagesSolving Convolution Integrals
This document contains 4 problems involving convolution integrals. For each problem, it provides the steps to (1) sketch the signals, (2) integrate the convolution integral by breaking it into cases based on the limits of integration, and (3) combine the cases to obtain the final solution. It works through each step methodically and shows the detailed working to arrive at solutions for different signals and systems.
Uploaded by
ahmad mzCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd