0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views8 pagesSI Units and Measurement Dimensions Guide
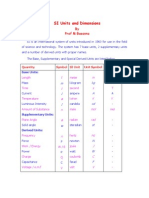
This document discusses dimensions, SI units, and prefixes of SI units. It defines dimensions as physical quantities being measured, such as length, mass, and time. It describes base quantities that cannot be defined in terms other quantities, and derived quantities that are defined in terms of base quantities. The document also outlines the International System of Units (SI units) that are used as standards for measurement. Examples of SI units provided are meters, kilograms, and seconds. Finally, it lists the common prefixes used for positive and negative powers when modifying SI units.
Uploaded by
ernestnyondo63Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views8 pagesSI Units and Measurement Dimensions Guide
This document discusses dimensions, SI units, and prefixes of SI units. It defines dimensions as physical quantities being measured, such as length, mass, and time. It describes base quantities that cannot be defined in terms other quantities, and derived quantities that are defined in terms of base quantities. The document also outlines the International System of Units (SI units) that are used as standards for measurement. Examples of SI units provided are meters, kilograms, and seconds. Finally, it lists the common prefixes used for positive and negative powers when modifying SI units.
Uploaded by
ernestnyondo63Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd