Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Indian Philosophy Pointers
Uploaded by
Winston QuilatonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Philosophy Pointers
Uploaded by
Winston QuilatonCopyright:
Available Formats
Indian Philosophy Pointers
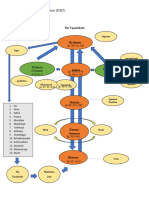
Hindu - Sanskrit Sindhu meaning “the Indus River valley” Trimurti (BVS) – primary natures of Brahman (Brahma, Vishnu
and Shiva)
Dharma or Hindu dharma
Brahma – uncreated creator
instead of Hinduism
Vishnu – preserver of universe (10x reincarnated)
henotheism – superior to lesser divine
- Rama - 7th Vishnu (Ramayana)
polytheistic – belief on many gods
Shiva – destroyer and dancer (8x reincarnated)
rta – a cosmic principle of harmony, regularity and right order
Avatar or avatara - take a flesh on knowable form (incarnation)
sacred texts:
Atman – soul
shruti (VEDAS)- “heard” from the gods Hanuman – monkey-faced god in Ramayana
smriti - “remembered” by ancient human sages
aum/om – essence of Brahman (creation, preservation,
Vedas - collections of devotional hymns, ceremonial guidelines destruction)
and philosophical reflections
Basic Tenets/Doctrines:
Four Sections of Vedas (MBAU):
1. Samsara – reincarnation of soul (cycle of rebirth)
1. Mantras – religious poetry address to the gods 2. Moksha – liberation from samsara
2. Brahmanas – ceremonial guidelines 3. Karma – every thought or deed, it has a consequence
3. Aranyakas – material for ascetic
4. Upanishads – philosophical commentaries Four Yogas (KJRB):
Four Vedas (RYSA): 1. Karma – path of work and service
2. Jnana – path of knowledge “not seeing”
1. Rig Veda – devotional hymns 3. Raja – path of meditation; Samadhi - intense mental
2. Yajur Veda – ritual hymns concentration
3. Sama Veda – chant hymns 4. Bhakti – path of love and devotion to God
4. Atharva Veda – magical hymns
Vedic gods:
Smritis (LRBM):
Indra – thunder, rain, and war,
1. Laws of Manu – code of ideal behavior
Agni – fire
2. Ramayana – journey of Rama
Varuna – cosmic order and righteousness
3. Bhagavad-Gita – essence of the Vedas
Surya – sun
4. Mahabharata - contains the Bhagavad Gita
Vayu – wind
Four Periods (VESS): Ushas – dawn
Saraswati – knowledge, speech, and music
1. Vedic (1500 to 600 BC) – writing of sacred Vedic Texts
2. Epic (500 to 200 BC) – writing of Epic literatures 6 Orthodox (Astika)
3. Sutra (200 BCE to 5 AD) – systematic philosophical
1. Nyaya
discourse
2. Vaisesika
4. Scholastic (16 CE onwards) – elaborate commentaries
3. Samkhya
and debates
4. Yoga
Caste system (BKVS): 5. Purva Mimamsa
6. Uttara Mimamsa or Vedanta
1. Brahmins/Brahmanas– priests
2. Kshatriyas – rulers and warriors 3 Heterodox (Nastika)
3. Vaishyas – commoners
1. Buddhism
4. Shudras – servants/slaves
2. Jainism
Brahman – ultimate reality 3. Charvaka
Namaste
- Literally means “I bow to you”
- Greeting the god within you
Dark Night of Soul – John of the Cross
Metanoia – change of heart
Mystical Union with God Book
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Articulating Filipino Philosophies OrigiDocument209 pagesArticulating Filipino Philosophies OrigiWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Ecclesiology - Quilaton AssignmentDocument2 pagesEcclesiology - Quilaton AssignmentWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Kierkegaard SummaryDocument25 pagesKierkegaard SummaryWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Ecclesiology PointersDocument1 pageEcclesiology PointersWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Karol WoytylaDocument2 pagesKarol WoytylaWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Church As...Document1 pageChurch As...Winston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Ecclesiology - Quilaton Term PaperDocument18 pagesEcclesiology - Quilaton Term PaperWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Ecclesiology - Quilaton Term PaperDocument6 pagesEcclesiology - Quilaton Term PaperWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Quilaton - Indian Philo - Ass3Document4 pagesQuilaton - Indian Philo - Ass3Winston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Part Ii - Body (Introtophilo)Document5 pagesPart Ii - Body (Introtophilo)Winston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Dec 2 Thesis Defense ProposalDocument47 pagesDec 2 Thesis Defense ProposalWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- St. Anselm's Ontological Argument On The Existence of GodDocument4 pagesSt. Anselm's Ontological Argument On The Existence of GodWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- DeanonDocument37 pagesDeanonWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Augustine, On Free Choice of The WillDocument5 pagesAugustine, On Free Choice of The WillWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Christmas LetterDocument1 pageChristmas LetterWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Copy St. Anselm's Ontological Argument On The Existence of GodDocument3 pagesCopy St. Anselm's Ontological Argument On The Existence of GodWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 - Political Life of Cross Cultural CommunicationDocument19 pagesLesson 11 - Political Life of Cross Cultural CommunicationWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- A Memoir of Happines That Turned Into GriefDocument10 pagesA Memoir of Happines That Turned Into GriefWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- EXECUTIVE SUMARY Second RoundDocument13 pagesEXECUTIVE SUMARY Second RoundWinston Quilaton0% (1)
- Human ActsDocument2 pagesHuman ActsWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- The Holy Rosary As The Narrative of My OwnDocument3 pagesThe Holy Rosary As The Narrative of My OwnWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Global Warming SummaryDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming SummaryWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- "Kuya Winnie, Tell Me": The Wisdom of Student and CareerDocument1 page"Kuya Winnie, Tell Me": The Wisdom of Student and CareerWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Culture (QUILATON)Document7 pagesEthics and Culture (QUILATON)Winston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Cultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The Philippines: Challenge and Implications in Genetic CounselingDocument10 pagesCultural Beliefs On Disease Causation in The Philippines: Challenge and Implications in Genetic CounselingWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- El Filibusterismo (Settings)Document4 pagesEl Filibusterismo (Settings)Winston Quilaton0% (1)
- Module 1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 1 AssignmentWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Hume's Theory of KnowledgeDocument2 pagesHume's Theory of KnowledgeWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Locke's Theory of KnowledgeDocument3 pagesLocke's Theory of KnowledgeWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)