Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INEA Assignment
Uploaded by
Gaurav Poddar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesINEA Assignment
Uploaded by
Gaurav PoddarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
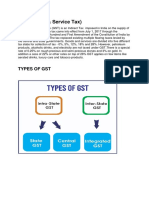
What is GST?
GST is levied on every stage of manufacturing and sales of goods and services across India.
This tax is levied when the goods or services are consumed. There are three subcategories to
GST-
CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax) is collected by the Central Government on interstate
sale of goods and services.
SGST (State Goods and Services Tax) is collected by the State Government on intrastate
sales.
IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax) is collected when a supply of products and
services is supplied from one state to another. The taxes collected are shared both by the
Central and State Government.
Indian Economy Before GST
It has been found that the cascading effect of taxes was one of the major drawbacks of
indirect taxation system followed by the country before GST. This is mainly due to
the taxation structure that both the Central and State Government to levy taxes
separately on goods and services at different stages of production to consumption.
The cascading effect of this tax was hindrance to GDP Growth rate in India
It is critical to revive domestic investments and further ease of doing business in the
country to attract foreign investors. The low growth of FDI in the consumer and retail
sectors can be due to uncertainty and complexity of the FDI policy. While the
government has taken substantial efforts in relaxing the regulations as well as
removing ambiguities, global consumer and retail companies were still
hesitant to take decisions to invest in India.
The Retail inflation has declined to a six-year low of 3.3 per cent in 2017-
18, with the economy moving towards a more stable tax regime.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) averaged 3.3 per cent during the period,
which was the lowest in the last six financial years.
The export industry faced tough times till GST was implemented, due to non-
availability of refunds under the VAT tax system. India’s exports rose 9.8%
during 2017-18, the highest growth rate in six years, while imports went up
nearly 20% after the GST implication
Impact of GST on our economy
1. Simpler tax structure
With GST, the taxation system of our country has become simpler. It is a
single tax, ensuring easier calculation. With this tax, the buyer gets a clear
idea of the amount paid as tax when purchasing certain products. This is
crucial when considering GST and its impact on the GDP.
2. More funds for production
Another effect of GST on the Indian economy has been the reduction in the
total taxable amount. This saved fund can again be invested back into the
production cycle to foster production.
3. Support for small and medium enterprises
Based on the size of your organization, the amount of GST depends on
your firm's annual turnover, provided you have been registered under the
Composition Scheme introduced by GST. Enterprises with a yearly
turnover of 50 lakhs have to pay 6% GST whereas enterprises with 1.5
crores worth of turnover have to pay 1% GST.
4. Increased volume of export
When considering GST and its impact on the Indian economy, customs
duty on exporting goods has reduced. So now production units save money
while producing goods and also while shipping them. This two-way savings
has lured many production units to export their goods, increasing the export
quantity.
5. Enhanced operations throughout India
With a unified taxation system, transporting goods around India has now
become easy, boosting operations throughout the country.
6. No more cascading effect
With GST, taxes of the State and Central Government have been merged.
This has removed the cascading effect of taxes, reducing the burden on the
buyer and the seller. So even if it may look like one big chunk of tax to be
paid, you pay lesser hidden taxes.
The impact of GST on the common man’s pocket
If you see the short-term impacts, customers now shall need to pay more
taxes on goods and services they purchase. A majority of essential
consumables will input either the same or a higher amount of tax. The
benefits of GST to the common man are plentiful.
Small-scale trades also have to bear the cost of compliance, which may
raise the prices of their produce, affecting the consumer.
Nevertheless, in the long term, GST also promises several benefits. With
the decrease of payable taxes for producers of consumer goods like
FMCG, the automotive sector will have to reduce the prices of their
commodities. This will allow the consumer to pay less while trying to avail
of these services.
A drop in prices will show an immediate surge in demands, boosting the
production cycle bringing in more profits. With this, both the buyer and the
seller get to save a fair share of money eventually, and the economy, too,
shall be boosted.
A boost in production shall also pave the way for expansion, leading to
more employment and increased income. This not only creates a better
scope for the common man but also strengthens the economy.
The implementation of GST also implies raising an invoice for the purchase
of any goods and services. With a proper billing system, the prospect of
black money and corruption shall also go down. These have been troubling
aspects for the common man in India.
How does GST affect the other sectors?
Till now, we discussed the small, medium, and large scale manufacturers
and the real estate sector; let’s now take a look at the impact of GST on
businesses other than real estate-
Logistics
In a country as big as ours, logistics plays a key contribution to the
economy. A well-organized and structured logistics industry can grow
exponentially, especially under the Make in India banner.
E-commerce
E-commerce has high growth potential. However, e-commerce companies
shall have to bear with tax collected at source factor for GST.
Pharma
The pharma and healthcare sector shall have a positive impact on GST
with its simplified tax structure. It will also be availing a tax respite in lieu of
making healthcare cheaper and accessible to people of all income groups.
Telecom
A drop in prices can be expected in the telecom sector, as costs like
warehousing, logistics, etc., will reduce.
Textile
Indian textile is one of the largest employers of skilled and unskilled labour.
With the textile industry also making 10% of total exports in India, the
numbers are likely to increase with the removal of customs duties. GST
shall also affect the value of cotton, a material on which most small-scale
textile industries depend. These are some of the impacts of GST on small
traders.
Agriculture and farming
Agriculture is the biggest contributor to India's GDP, covering more than
16%. With the ease of logistics, transportation costs of agricultural produce
will also go down. Thus, the impact of GST on wholesalers has been
greatly positive.
FMCG
With GST eliminating the need for multiple sales depots, FMCG shall save
a lot on logistics and distribution costs.
Automobile
Under the previous taxation system, several taxes like excise, VAT, sales
tax, road tax, motor vehicle tax, registration duty were applicable, which
has now been replaced by GST. Automobile prices are likely to drop as the
producers are saving more in the form of taxes now.
Startups
GST has tremendously benefitted Indian startups with perks like a DIY
compliance model, increased limits for registration, a free flow of goods and
services and tax credit on purchases. It has also become easier for
companies with a pan India presence to calculate taxes, especially if
belonging to the e-commerce sector. Understand the impact of GST on
small-scale industries if you are a part of this sector.
Self-employed individuals
Self-employment or freelancing is a young industry in our country, but filing
for taxes has become easier as they fall under service providers with GST
implementation. Understanding the impact of GST on micro small and
medium enterprises is important for such individuals.
Entrepreneurs engaged in the hospitality sector should also check out the
impacts of GST on the hospitality industry.
GST comes with its set of pros and cons, affecting both buyers and sellers.
One must be aware of GST’s negative impact on the GDP as well. So one
side, when taxes have become simplified, they have also led to a rise in
compliance costs.
You might also like
- How to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)From EverandHow to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- How GST Will Benefit the Indian Economy and BusinessesDocument5 pagesHow GST Will Benefit the Indian Economy and BusinessesvasanthisbNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Small and Medium EnterprisesDocument19 pagesImpact of GST On Small and Medium EnterprisesEswari Gk100% (1)
- GST and Its Impact On Various Sectors of Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesGST and Its Impact On Various Sectors of Indian EconomyRandy DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On The Indian EconomyDocument16 pagesImpact of GST On The Indian EconomySandeep TomarNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PRAPOSALDocument4 pagesPROJECT PRAPOSALprasadNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Indian Economy: Keywords: GST, Consumer, Producer, Centre, StateDocument4 pagesImpact of GST On Indian Economy: Keywords: GST, Consumer, Producer, Centre, StateSonam KumariNo ratings yet
- IMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMY CovidDocument6 pagesIMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMY CovidArushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Swot 2 Eco 2Document6 pagesSwot 2 Eco 2Amrutha GayathriNo ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of GST On RetailersDocument9 pagesA Study On Impact of GST On RetailersKrishna Nandhini VijiNo ratings yet
- Harsh Kandele-19mbar0242-Cia2-ItDocument9 pagesHarsh Kandele-19mbar0242-Cia2-ItHarsh KandeleNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST on India's EconomyDocument11 pagesImpact of GST on India's EconomyabcNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of GSTDocument7 pagesCritical Analysis of GSTPooja BhagatNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST on Retail SectorDocument5 pagesImpact of GST on Retail SectormariyaNo ratings yet
- IMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMYDocument10 pagesIMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMYbijay2022No ratings yet
- Impact of GST Implementation On Automobile IndustryDocument22 pagesImpact of GST Implementation On Automobile IndustryvasanthisbNo ratings yet
- GST's Impact on Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesGST's Impact on Indian EconomyKetan YadavNo ratings yet
- GST Data CollectedDocument11 pagesGST Data CollectedtpplantNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Indian Economy PaperDocument10 pagesImpact of GST On Indian Economy PaperDevil DemonNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Service Providers: LogisticsDocument4 pagesImpact of GST On Service Providers: LogisticsAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- GST Search Dimensions Original ArticleDocument17 pagesGST Search Dimensions Original Articleratneet_dhaliwalNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument6 pagesGSTahamadsameer391No ratings yet
- GST Impact on Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesGST Impact on Indian EconomyUrvashi RaoNo ratings yet
- impactofgstonindianeconomypaperDocument10 pagesimpactofgstonindianeconomypaperharshitverma1762No ratings yet
- The GST and Economic GrowthDocument4 pagesThe GST and Economic GrowthEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Good and Services TaxDocument5 pagesGood and Services TaxJoydeep SenguptaNo ratings yet
- The GST Effect - ZohoDocument6 pagesThe GST Effect - ZohoKrupal PatelNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Goods and Services Tax (GST)Document11 pagesImplementation of Goods and Services Tax (GST)NATIONAL ATTENDENCENo ratings yet
- Sector-Wise Impact Analysis: LogisticsDocument3 pagesSector-Wise Impact Analysis: LogisticsAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Indian Economy PaperDocument13 pagesImpact of GST On Indian Economy Papertani boyNo ratings yet
- GST - An Overview of India's Indirect Tax ReformDocument7 pagesGST - An Overview of India's Indirect Tax ReformshashankNo ratings yet
- GST Impact Analysis Across Key Sectors (35Document4 pagesGST Impact Analysis Across Key Sectors (35Ankit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Method of Collecting Data Primary DataDocument8 pages2.1 Method of Collecting Data Primary Datadeepak sipaniNo ratings yet
- NeerajMandhan - Vinayak - GST AND INDERECT TAXESDocument33 pagesNeerajMandhan - Vinayak - GST AND INDERECT TAXESkanikaNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument24 pagesProject ReportanilNo ratings yet
- Article1Document5 pagesArticle1SatendraNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Manufacturers, Distributor, and RetailersDocument4 pagesImpact of GST On Manufacturers, Distributor, and RetailersAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- GST Overview: Benefits, Impact and ImplementationDocument17 pagesGST Overview: Benefits, Impact and ImplementationSivaraman Santhosh100% (1)
- Impact of GST On Manufacturers, Distributor, and RetailersDocument4 pagesImpact of GST On Manufacturers, Distributor, and RetailersAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- GST: Understanding India's Indirect Tax SystemDocument4 pagesGST: Understanding India's Indirect Tax SystemShubham GargNo ratings yet
- Concept Of: Goods & Service TaxDocument23 pagesConcept Of: Goods & Service Taxraginikumarithakur45No ratings yet
- GST - Write Up - 2 - 22.4.2020Document5 pagesGST - Write Up - 2 - 22.4.2020Rajamohan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- A Short Case Study On The Ten Principles of EconomicsDocument8 pagesA Short Case Study On The Ten Principles of EconomicsRaunak ThakerNo ratings yet
- UTKARSH YADAV (Sec - B) (Research Paper)Document8 pagesUTKARSH YADAV (Sec - B) (Research Paper)UTKARSH YADAVNo ratings yet
- GD Topic - All About GSTDocument10 pagesGD Topic - All About GSTShubham PalNo ratings yet
- ECO_V5_N1_010Document9 pagesECO_V5_N1_010debadattakumbha13No ratings yet
- GST Is Known As The Goods and Services TaxDocument33 pagesGST Is Known As The Goods and Services TaxR. YashwanthiniNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Limitations of GSTDocument7 pagesBenefits and Limitations of GSTGovernment Ramanarayan chellaram collageNo ratings yet
- GST-a Single Point Efficient Tax System or An Economic Disaster?Document2 pagesGST-a Single Point Efficient Tax System or An Economic Disaster?AngelNo ratings yet
- 88 1 407 2 10 20170909 PDFDocument13 pages88 1 407 2 10 20170909 PDFJazz JuniorNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument6 pagesGSTpranaynagrale876No ratings yet
- GST On FMCGDocument24 pagesGST On FMCGRajendra NishadNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On GSTDocument15 pagesA Project Report On GSTAnjali RatudiNo ratings yet
- GST Lab 2022Document78 pagesGST Lab 2022Sreeja Reddy100% (1)
- GST Impact on Corporate IndiaDocument2 pagesGST Impact on Corporate IndiaApoorav PawarNo ratings yet
- Goods and Service TaxDocument12 pagesGoods and Service Taxshourima mishraNo ratings yet
- GST Assignment 1Document7 pagesGST Assignment 1Tapasya Nirmal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Name-Dipesh Bhattacharyya Roll No-03 Course-BBA LLB Subject-Accountancy Topic-Goods and Service Tax (GST) Adamas University DatedDocument12 pagesName-Dipesh Bhattacharyya Roll No-03 Course-BBA LLB Subject-Accountancy Topic-Goods and Service Tax (GST) Adamas University DatedDIPESH BHATTACHARYYANo ratings yet
- Types of Taxes Under GSTDocument4 pagesTypes of Taxes Under GSTDiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tour Contract Receipt / Tax Invoice: TOTAL BOOKING AMOUNT: 850.00 + 0.00 (GST) 850.00Document1 pageTour Contract Receipt / Tax Invoice: TOTAL BOOKING AMOUNT: 850.00 + 0.00 (GST) 850.00PrabhuYechhiNo ratings yet
- Digitally Signed Tax Invoice for Wall Fan PurchaseDocument1 pageDigitally Signed Tax Invoice for Wall Fan PurchaseashishvasekarNo ratings yet
- MC List3186837121838048305Document124 pagesMC List3186837121838048305maveryqNo ratings yet
- Invoice No. - 409851Document2 pagesInvoice No. - 409851Ajay rawatNo ratings yet
- OCT 2020 eBill-VodafoneDocument10 pagesOCT 2020 eBill-Vodafonearvindgangwar80No ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceManabendra SinghaNo ratings yet
- Supadha Work Order Copy 325 Keerthana ConstructionsDocument5 pagesSupadha Work Order Copy 325 Keerthana Constructionstripl.kmvNo ratings yet
- Invoice2022 2023 07307 001Document2 pagesInvoice2022 2023 07307 001bapi sahuNo ratings yet
- Rdso Revised Help For Filling Online Vendor Registration - QAMVRDocument4 pagesRdso Revised Help For Filling Online Vendor Registration - QAMVREr. Vicky MakawanaNo ratings yet
- Sub:Risk Assumption Letter: Insured Vehicles DetailsDocument4 pagesSub:Risk Assumption Letter: Insured Vehicles DetailskamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Jio Invoice 290323Document2 pagesJio Invoice 290323Deepak KiniNo ratings yet
- 5459XXXXXXXXXX79 - 23 10 2023Document2 pages5459XXXXXXXXXX79 - 23 10 2023chagusahoo170No ratings yet
- TKT 17sept23Document2 pagesTKT 17sept23mangb161No ratings yet
- Indirect Tax GST BookDocument106 pagesIndirect Tax GST BookDancer Vijay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 04 Input Tax CreditDocument20 pagesUnit 04 Input Tax CreditSathya saiNo ratings yet
- Pods InvoiceDocument1 pagePods InvoicealishaNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Er Sachin SafaleNo ratings yet
- Od 226670539882013000Document2 pagesOd 226670539882013000சற்குணத்தமிழன் செNo ratings yet
- Train TicketsDocument1 pageTrain TicketsBhavesh PoojariNo ratings yet
- Reliance Insurance - Payment Receipt (1) 1Document1 pageReliance Insurance - Payment Receipt (1) 1dinesh.pyreddyNo ratings yet
- Swimming Membership Receipt-MulundDocument1 pageSwimming Membership Receipt-Mulundchithur DevarajNo ratings yet
- Super Stockist (IMU) Bill Format PDFDocument1 pageSuper Stockist (IMU) Bill Format PDFAnkit PradhanNo ratings yet
- Outward Supply Replated - GST Audit 9C by CA Venugopal Gella - Ver1.0Document34 pagesOutward Supply Replated - GST Audit 9C by CA Venugopal Gella - Ver1.0Kishan M Mehta CoNo ratings yet
- Tally Ledger List in Excel Format TeachooDocument12 pagesTally Ledger List in Excel Format TeachooDINESH CHANCHALANINo ratings yet
- Admission Fee ReceiptDocument2 pagesAdmission Fee ReceiptshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Book InvoiceDocument1 pageBook InvoiceKaushik DasNo ratings yet
- SMPSDocument1 pageSMPSvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Sanghamitra Exp Third Ac (3A)Document1 pageSanghamitra Exp Third Ac (3A)akssharmamobileNo ratings yet
- General Conditions of ContractDocument29 pagesGeneral Conditions of ContractShubham DubeyNo ratings yet
- GST Receipt Voucher TemplateDocument2 pagesGST Receipt Voucher TemplateUNEXPECTEDNo ratings yet
- Small Business Taxes: The Most Complete and Updated Guide with Tips and Tax Loopholes You Need to Know to Avoid IRS Penalties and Save MoneyFrom EverandSmall Business Taxes: The Most Complete and Updated Guide with Tips and Tax Loopholes You Need to Know to Avoid IRS Penalties and Save MoneyNo ratings yet
- How to Pay Zero Taxes, 2020-2021: Your Guide to Every Tax Break the IRS AllowsFrom EverandHow to Pay Zero Taxes, 2020-2021: Your Guide to Every Tax Break the IRS AllowsNo ratings yet
- What Your CPA Isn't Telling You: Life-Changing Tax StrategiesFrom EverandWhat Your CPA Isn't Telling You: Life-Changing Tax StrategiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesFrom EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNo ratings yet
- Lower Your Taxes - BIG TIME! 2019-2020: Small Business Wealth Building and Tax Reduction Secrets from an IRS InsiderFrom EverandLower Your Taxes - BIG TIME! 2019-2020: Small Business Wealth Building and Tax Reduction Secrets from an IRS InsiderRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Invested: How I Learned to Master My Mind, My Fears, and My Money to Achieve Financial Freedom and Live a More Authentic Life (with a Little Help from Warren Buffett, Charlie Munger, and My Dad)From EverandInvested: How I Learned to Master My Mind, My Fears, and My Money to Achieve Financial Freedom and Live a More Authentic Life (with a Little Help from Warren Buffett, Charlie Munger, and My Dad)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (43)
- Tax Strategies: The Essential Guide to All Things Taxes, Learn the Secrets and Expert Tips to Understanding and Filing Your Taxes Like a ProFrom EverandTax Strategies: The Essential Guide to All Things Taxes, Learn the Secrets and Expert Tips to Understanding and Filing Your Taxes Like a ProRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (43)
- Deduct Everything!: Save Money with Hundreds of Legal Tax Breaks, Credits, Write-Offs, and LoopholesFrom EverandDeduct Everything!: Save Money with Hundreds of Legal Tax Breaks, Credits, Write-Offs, and LoopholesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- What Everyone Needs to Know about Tax: An Introduction to the UK Tax SystemFrom EverandWhat Everyone Needs to Know about Tax: An Introduction to the UK Tax SystemNo ratings yet
- Founding Finance: How Debt, Speculation, Foreclosures, Protests, and Crackdowns Made Us a NationFrom EverandFounding Finance: How Debt, Speculation, Foreclosures, Protests, and Crackdowns Made Us a NationNo ratings yet
- How to get US Bank Account for Non US ResidentFrom EverandHow to get US Bank Account for Non US ResidentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Hidden Wealth of Nations: The Scourge of Tax HavensFrom EverandThe Hidden Wealth of Nations: The Scourge of Tax HavensRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Bookkeeping: Step by Step Guide to Bookkeeping Principles & Basic Bookkeeping for Small BusinessFrom EverandBookkeeping: Step by Step Guide to Bookkeeping Principles & Basic Bookkeeping for Small BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Stiff Them!: Your Guide to Paying Zero Dollars to the IRS, Student Loans, Credit Cards, Medical Bills and MoreFrom EverandStiff Them!: Your Guide to Paying Zero Dollars to the IRS, Student Loans, Credit Cards, Medical Bills and MoreRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Tax Savvy for Small Business: A Complete Tax Strategy GuideFrom EverandTax Savvy for Small Business: A Complete Tax Strategy GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Taxes for Small Business: The Ultimate Guide to Small Business Taxes Including LLC Taxes, Payroll Taxes, and Self-Employed Taxes as a Sole ProprietorshipFrom EverandTaxes for Small Business: The Ultimate Guide to Small Business Taxes Including LLC Taxes, Payroll Taxes, and Self-Employed Taxes as a Sole ProprietorshipNo ratings yet
- Tax Accounting: A Guide for Small Business Owners Wanting to Understand Tax Deductions, and Taxes Related to Payroll, LLCs, Self-Employment, S Corps, and C CorporationsFrom EverandTax Accounting: A Guide for Small Business Owners Wanting to Understand Tax Deductions, and Taxes Related to Payroll, LLCs, Self-Employment, S Corps, and C CorporationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Freight Broker Business Startup: Step-by-Step Guide to Start, Grow and Run Your Own Freight Brokerage Company In in Less Than 4 Weeks. Includes Business Plan TemplatesFrom EverandFreight Broker Business Startup: Step-by-Step Guide to Start, Grow and Run Your Own Freight Brokerage Company In in Less Than 4 Weeks. Includes Business Plan TemplatesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)