Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supplementary Protocol
Uploaded by
suryaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supplementary Protocol
Uploaded by
suryaCopyright:
Available Formats
1 PROTOCOL FOR:
2 Simple, inexpensive and RNase-free purification of plasmid DNA by fractional precipitation with
3 isopropanol
4 Viiu Paalme and Mart Speek*
5 Department of Chemistry and Biotechnology, Tallinn University of Technology, Akadeemia tee
6 15, Tallinn 12618, Estonia
7 *Corresponding author: Mart Speek (mart.speek@ttu.ee)
8 LEGEND
9 ATTENTION
10 * HINT
11 REST
12 REAGENTS AND MATERIALS
13 Reagents
Chemicals Abbreviation Manufacturer Catalog Number
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid EDTA-Na2 Sigma-Aldrich E9884
disodium salt dihydrate
Isopropanol (2-propanol) Honeywell Riedel-de Haën 24137
Potassium acetate KOAc Sigma-Aldrich 236497
Sodium hydroxide NaOH Sigma-Aldrich S8045
Sodium dodecyl sulfate SDS Sigma-Aldrich 436143
BioTechniques protocol template
Tris base, Tris Sigma-Aldrich T1503
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
14
Solutions Abbreviation Ingredients
Alkaline lysis solution I Sol I 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10 mM EDTA-Na2, pH 8.0
Alkaline lysis solution II Sol II 0.1N NaOH, 1% SDS
Alkaline lysis solution III Sol III 3M KOAc, pH 5.5
70% Ethanol Ethanol/water (v/v 70/30)
TE 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA-Na2
15
16 Materials
Pipettes, tubes and tips Manufacturer (product code)
PIPETMAN P1000, 100-1000 µL Gilson (F144059M)
PIPETMAN P200, 20-200 µL Gilson (FA10005M)
1.5 mL Microcentrifuge Tubes Axygen (MCT-150-C)
200 µl Yellow Reference Tips Axygen (TR-222-Y)
1000 µl Blue Pipet Tips Axygen (T-1000-B)
17
18 PROCEDURE
19 The following protocol is a modification of alkaline lysis procedure for plasmid minipreparation described in {1] and
20 is based on classical works of Birnboim and Doly 1979 [2] and Ish-Horowicz and Burke 1981 [3]. Schematic
21 illustration of the protocol is shown in Fig. 1 (see below).
22 All centrifugation steps are carried out at room temperature
23
24 Steps (1-12):
25
26 (1) Transfer 1.4 ml overnight bacterial culture into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at maximum speed
27 (12,100 x g) for 1 min to pellet bacteria.
28
29 (2) Remove the supernatant by aspiration and resuspend the pellet in 200 µl of Solution I by vigorous vortexing.
BioTechniques protocol template
30 To facilitate resuspension use pipette tip.
31
32 (3) Add 400 µl of Solution II. Mix end-over-end by hand 5-6 times and place on ice for 2-3 min. Do not vortex.
33
34 (4) Add 300 µl of ice-cold Solution III and mix by inverting the tube several times. Note the complete and
35 uniform formation of white pellet. Let stand on ice for 2-3 min.
36
37 (5) Centrifuge at maximum speed for 5 min.
38
39 (6) Transfer 875 µl of the supernatant to a new tube containing 290 µl of isopropanol (0.33 volume) and mix.
40
41 (7) Centrifuge at max speed for 5 min.
42
43 (8) Carefully remove the supernatant (1150 µl) and transfer to a new tube containing 30 µl of isopropanol
44 (0.36 volumes of the initial solution) and mix immediately. *Avoid touching the pellet, containing RNA, bacterial
45 DNA and polysaccharides.
46
47 (9) Centrifuge at maximum speed for 8 min.
48
49 (10) Remove most of the supernatant by aspiration, quick spin and very carefully remove the remaining 100-150
50 µl portion with a pipette. Avoid touching the transparent pellet, normally containing 10-20 µg of plasmid DNA.
51
52 (11) Wash the pellet with 200-400 µl of 70% Ethanol, centrifuge and remove supernatant completely from the
53 opposite side of the pellet.
54
55 (12) Dissolve the pellet in 50 µl TE and analyse about 1/50 of plasmid DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis using
56 appropriate standards.
57
BioTechniques protocol template
58
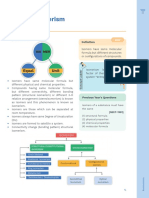
Figure 1. Schematic representation of purification of plasmid DNA by fractional precipitation
with isopropanol. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and RNA are removed after first and plasmid (p)DNA
after second precipitation with isopropanol. Addition of potassium acetate (Sol III) results in the
59 EQUIPMENT
precipitation of bacterial proteins, chromosomal (c)DNA and potassium dodecyl sulfate (KDS).
Equipment Manufacturer
BioTechniques protocol template
MiniSpin personal microcentrifuge Eppendorf
Icebox containing wet ice
60
61 TROUBLESHOOTING
62 To guarantee rapid mixing, and avoid oversaturation and/or precipitation at the interphase between alcohol and
63 aqueous solution (Steps 6 and 8), it is important to add the aqueous solution to the isopropanol, not vice versa.
64 This is opposite to traditional precipitation with alcohol where the latter is added to the aqueous solution. Care
65 must be taken in washing the pellet with 70% Ethanol (Step 11).
66 REFERENCES
67 [1] Green MR, Sambrook J. Preparation of Plasmid DNA by Alkaline Lysis with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate:
68 Minipreps. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 10, 911-916 (2016).
69 [2] Birnboim HC, Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic
70 Acids Res. 7(6), 1513-1523 (1979).
71 [3] Ish-Horowicz D, Burke JF. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 9(13), 2989-2998 (1981).
BioTechniques protocol template
You might also like
- Supplementary Protocol123Document5 pagesSupplementary Protocol123suryaNo ratings yet
- Formulations ToiletriesDocument13 pagesFormulations ToiletriesErrol FernandesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization of Sorghum Using RAPD and ISSR MarkerDocument12 pagesMolecular Characterization of Sorghum Using RAPD and ISSR Markersaikripa121No ratings yet
- Estrogens, ConjugatedDocument10 pagesEstrogens, ConjugatedJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Palladium Nanoparticles in Carbon Thin Film Lined SBA-15 Nanoreactors EfficientDocument6 pagesPalladium Nanoparticles in Carbon Thin Film Lined SBA-15 Nanoreactors EfficientDana MateiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Carbovir and Abacavir From A Carbocyclic PrecursorDocument8 pagesSynthesis of Carbovir and Abacavir From A Carbocyclic PrecursorDANNA SOFIA SANCHEZ CAMACHONo ratings yet
- B AcephateDocument5 pagesB Acephatejessica montielNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesTwo-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresisbiosa45100% (1)
- Biochemical Markers AnalysisDocument11 pagesBiochemical Markers AnalysisFakhar ShahNo ratings yet
- Oin-ops-chem-017-Analytical Test Procedures For Water and SteamDocument166 pagesOin-ops-chem-017-Analytical Test Procedures For Water and SteamraniNo ratings yet
- Helpful Edman Degradation Sample Preparation ProtocolsDocument7 pagesHelpful Edman Degradation Sample Preparation ProtocolsThis guyNo ratings yet
- Reductive Methylation of Primary and Secondary Amines and Amino Acids by Aqueous Formaldehyde and ZincDocument3 pagesReductive Methylation of Primary and Secondary Amines and Amino Acids by Aqueous Formaldehyde and Zincjavasolo100% (1)
- 1 (α PYRIDYL) 2 PROPANOLDocument4 pages1 (α PYRIDYL) 2 PROPANOLAlex CumbaNo ratings yet
- A Practical Synthesis of (-) - Kainic AcidDocument11 pagesA Practical Synthesis of (-) - Kainic AcidNikhil SarpateNo ratings yet
- Supporting Information: © Wiley-VCH 2009Document28 pagesSupporting Information: © Wiley-VCH 2009Nguyễn Viết HiếuNo ratings yet
- Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis (Comet) AssayDocument5 pagesSingle Cell Gel Electrophoresis (Comet) AssayCoțovanu IulianNo ratings yet
- Scifinder®: Mild and Efficient Iodination of Aromatic and Heterocyclic Compounds With The Naclo2/Nai/Hcl SystemDocument2 pagesScifinder®: Mild and Efficient Iodination of Aromatic and Heterocyclic Compounds With The Naclo2/Nai/Hcl SystemJesus Garcia PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Surtec 966: Activator With Palladium/Tin ColloidDocument4 pagesSurtec 966: Activator With Palladium/Tin Colloidfrankpwang100% (1)
- MCP 1 AuteurDocument28 pagesMCP 1 AuteurTri Seto Putra HermawanNo ratings yet
- Biomaghreb PRICE QUALITY and SERVICESDocument59 pagesBiomaghreb PRICE QUALITY and SERVICESbigweb100% (2)
- Bio Protocol233Document6 pagesBio Protocol233yusufNo ratings yet
- Synthesis, Characterization and Properties of Polysiloxane-Based Episulfide ResinDocument12 pagesSynthesis, Characterization and Properties of Polysiloxane-Based Episulfide ResinFadli IkhsanNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology and Energy Storage Lab Manual - 2Document30 pagesNanotechnology and Energy Storage Lab Manual - 2Sunskrati PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cianeto Total - SFADocument4 pagesCianeto Total - SFAAndré SchikierskiNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Plant Genomic DNADocument10 pagesIsolation of Plant Genomic DNAChris PenielNo ratings yet
- tmp6BC3 TMPDocument16 pagestmp6BC3 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Lab ManualDocument11 pagesGenetic Engineering Lab ManualGeetanjali GorainNo ratings yet
- Supporting Information Synthesis of Benzimidazoles From AmidinesDocument38 pagesSupporting Information Synthesis of Benzimidazoles From AmidinesNickly NickNo ratings yet
- Adipic Acid - Wikipedia PDFDocument24 pagesAdipic Acid - Wikipedia PDFKalpesh DetheNo ratings yet
- 04nDocument35 pages04nJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of (3Z) Dodecenyl (E) 2 ButenoateDocument6 pagesSynthesis of (3Z) Dodecenyl (E) 2 ButenoatedangchihienNo ratings yet
- Acetone - WikipediaDocument65 pagesAcetone - WikipediaDylNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Analitik Jahlela Sari Kimia Bahasa InggrisDocument14 pagesJurnal Analitik Jahlela Sari Kimia Bahasa InggriskhairiyatiNo ratings yet
- CN Total New 3837mthdDocument36 pagesCN Total New 3837mthdYean CarlosNo ratings yet
- Aoac 991.07Document7 pagesAoac 991.07Javier muñozNo ratings yet
- METHOD 130.2: TOTAL HARDNESS BY EDTA TITRATIONDocument5 pagesMETHOD 130.2: TOTAL HARDNESS BY EDTA TITRATIONCosmina PapaNo ratings yet
- MiMB Sample ChapterDocument10 pagesMiMB Sample ChapterSinivas ParthaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of The Algicide BacillamideDocument7 pagesSynthesis of The Algicide Bacillamiderajesh kothariNo ratings yet
- (Chem 36) Expt 4 Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateDocument34 pages(Chem 36) Expt 4 Reduction of Methyl AcetoacetateStudent 10% (1)
- Derivados PetroleoDocument48 pagesDerivados PetroleoCarlos TimanaNo ratings yet
- Pallavi Appasaheb KamandarDocument36 pagesPallavi Appasaheb KamandarsahilNo ratings yet
- Proposed Project - EthylDocument19 pagesProposed Project - EthylAnkur gautamNo ratings yet
- Deg Lab Manual WWT Sept 2018Document21 pagesDeg Lab Manual WWT Sept 2018areripelmyNo ratings yet
- Book Chapter Haider, Reid, SharpDocument17 pagesBook Chapter Haider, Reid, SharpmlNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Materials and Experimental ProceduresDocument9 pagesChapter Three Materials and Experimental Proceduresntahapa99No ratings yet
- 015 PCR Protocols 1st EditionDocument386 pages015 PCR Protocols 1st EditionmuyeedahmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Report SBT Sem 5 ProteinDocument11 pagesLab Report SBT Sem 5 ProteinIyana RazaliNo ratings yet
- SDS-PAGE Separation of Viral ProteinsDocument4 pagesSDS-PAGE Separation of Viral ProteinsAbiNo ratings yet
- 1kb Plus LadderDocument4 pages1kb Plus LadderPedro SoaresNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Lab Manual: 6 Experiments for Testing & Treating WaterDocument21 pagesWastewater Lab Manual: 6 Experiments for Testing & Treating Waterfatin naziraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Materials and MethodsDocument13 pagesChapter-2: Materials and Methodsdalton2003No ratings yet
- Hydration of Propylene Via Sulfation HydrationDocument4 pagesHydration of Propylene Via Sulfation HydrationDineshNo ratings yet
- Oh DeterminationDocument1 pageOh DeterminationUsama AwadNo ratings yet
- Effect of Poly (Acrylic Acid) End-Group Functionality On Inhibition of Calcium Oxalate Crystal GrowthDocument7 pagesEffect of Poly (Acrylic Acid) End-Group Functionality On Inhibition of Calcium Oxalate Crystal GrowthPencils SharpenerNo ratings yet
- PLA PresentationDocument43 pagesPLA PresentationPooja DadlaniNo ratings yet
- Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchFrom EverandApplication of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchRajmund MichalskiNo ratings yet
- GC/LC, Instruments, Derivatives in Identifying Pollutants and UnknownsFrom EverandGC/LC, Instruments, Derivatives in Identifying Pollutants and UnknownsNo ratings yet
- Gel Electrophoresis of ProteinsFrom EverandGel Electrophoresis of ProteinsMichael J DunnNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- PremiumReceipt PR1808493400012324Document1 pagePremiumReceipt PR1808493400012324suryaNo ratings yet
- Invitation Seminar Feb 2024 - HyderabadDocument1 pageInvitation Seminar Feb 2024 - HyderabadsuryaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary DataDocument2 pagesSupplementary DatasuryaNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Absorbance Standards for SpectrophotometersDocument6 pagesUltraviolet Absorbance Standards for SpectrophotometerssuryaNo ratings yet
- Review Preparation of Methacrylate Monoliths: Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, St. Petersburg, RussiaDocument13 pagesReview Preparation of Methacrylate Monoliths: Institute of Macromolecular Compounds, St. Petersburg, RussiasuryaNo ratings yet
- Biosafety Considerations For Cell Based Viral Vaccines: Margaret TempleDocument42 pagesBiosafety Considerations For Cell Based Viral Vaccines: Margaret TemplesuryaNo ratings yet
- RSC Advances: PaperDocument12 pagesRSC Advances: PapersuryaNo ratings yet
- Article1380286349 - Lan Et AlDocument6 pagesArticle1380286349 - Lan Et AlsuryaNo ratings yet
- Fbioe 09 630551Document18 pagesFbioe 09 630551suryaNo ratings yet
- Cell Counter That Thinks Like Cell Biologist Countess 3 BrochureDocument12 pagesCell Counter That Thinks Like Cell Biologist Countess 3 BrochuresuryaNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Ijbmr 20180602 14Document7 pages10 11648 J Ijbmr 20180602 14suryaNo ratings yet
- NanoDrop 2000 2000c 1000 Calibration Check Procedure enDocument2 pagesNanoDrop 2000 2000c 1000 Calibration Check Procedure ensuryaNo ratings yet
- Potassium Dichromate235 430nmDocument3 pagesPotassium Dichromate235 430nmsuryaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Dextran-Grafted Agarose Resin For Hydrophobic Charge-Induction ChromatographyDocument10 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Dextran-Grafted Agarose Resin For Hydrophobic Charge-Induction ChromatographysuryaNo ratings yet
- Article1380286349 - Lan Et AlDocument6 pagesArticle1380286349 - Lan Et AlsuryaNo ratings yet
- Index: Manual For (BIG)Document32 pagesIndex: Manual For (BIG)suryaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Dextran-Grafted Agarose Resin For Hydrophobic Charge-Induction ChromatographyDocument10 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Dextran-Grafted Agarose Resin For Hydrophobic Charge-Induction ChromatographysuryaNo ratings yet
- ChemCheckSummary ProchimicaDocument48 pagesChemCheckSummary ProchimicaMd.Ifrith RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2011 - SANDIA - Steam Cycles For Molten Salt Plants PDFDocument121 pages2011 - SANDIA - Steam Cycles For Molten Salt Plants PDFDavide FranziniNo ratings yet
- E 355Document3 pagesE 355Mogos PaulNo ratings yet
- EU RoHS Exemption List GuideDocument32 pagesEU RoHS Exemption List GuidecanacNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument42 pagesNuclear ChemistryneerajNo ratings yet
- Calibration of PH MeterDocument4 pagesCalibration of PH MeterMg H75% (4)
- Chapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)Document3 pagesChapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)JayjayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 Solution (Updated)Document7 pagesTutorial 4 Solution (Updated)Jayden Chan33% (3)
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument82 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Reinjeksi PabumDocument34 pagesReinjeksi PabumSkolastikaPradiptaNo ratings yet
- Tabla 8.1 Soldadura de Acero InoxidableDocument1 pageTabla 8.1 Soldadura de Acero InoxidableJuan Alberto Lopez SanchezNo ratings yet
- Justin Brian Chiongson, M. SC., RCH Relicardo M. Coloso, Ph. D., RCHDocument23 pagesJustin Brian Chiongson, M. SC., RCH Relicardo M. Coloso, Ph. D., RCHAiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Microstructure prediction and control in hot strip millsDocument7 pagesMicrostructure prediction and control in hot strip millsAli RayyaNo ratings yet
- Trusted by Engineers for Medium Carbon SteelDocument3 pagesTrusted by Engineers for Medium Carbon SteelVinay BhatiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Safety ValvesDocument15 pagesPressure Safety Valvesh_abdullah100% (2)
- IsomerismDocument61 pagesIsomerismSaket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution Report TemplateDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution Report Templatemhonk479No ratings yet
- Draft StructuralSteel DesignGuideDocument79 pagesDraft StructuralSteel DesignGuideSheila Rose Bacerra-VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 2017 Controlled TestDocument10 pagesGrade 10 2017 Controlled Testrowan chibiNo ratings yet
- Safety in The LaboratoryDocument10 pagesSafety in The LaboratoryRhemia Li CapisanNo ratings yet
- DM Lec 8Document7 pagesDM Lec 8Ali NazarNo ratings yet
- Elite Dangerous Trader's Bible Voice AttackDocument6 pagesElite Dangerous Trader's Bible Voice AttackAaron Orion Chavez100% (1)
- General Instructions: Pie Matlab Assessment For Chemical EngineersDocument6 pagesGeneral Instructions: Pie Matlab Assessment For Chemical EngineersJulia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Agents COP 2016Document56 pagesChemical Agents COP 2016James McloughlinNo ratings yet
- Block 1 - Week 4 PDFDocument60 pagesBlock 1 - Week 4 PDFEvelyn YongNo ratings yet
- GCSE AQA Chemistry 8642 Paper 1Document28 pagesGCSE AQA Chemistry 8642 Paper 1walidabdulrahman96No ratings yet
- Wood Briquette TorrefactionDocument4 pagesWood Briquette TorrefactionJulian Andres PaezNo ratings yet
- Triple Q WatersDocument4 pagesTriple Q Watersendalehadgu2866No ratings yet
- Calculation of Asphalt Concrete PropertiesDocument2 pagesCalculation of Asphalt Concrete PropertiesHAZIQ RAHMANNo ratings yet
- ASTM D974 14 (For Acid and Base Number by Color-Indicator Titration)Document7 pagesASTM D974 14 (For Acid and Base Number by Color-Indicator Titration)Fabian Ricardo100% (1)