Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KDIGO BP Guideline Top 10 Takeaway
Uploaded by
gordongmdrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KDIGO BP Guideline Top 10 Takeaway
Uploaded by
gordongmdrCopyright:
Available Formats
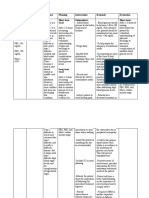
Top Takeaways for Clinicians from the
10
KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline
for Blood Pressure Management in CKD*
1
Standardized office BP measurement
Standardized BP measurement emphasizes the importance of appropriate prepara-
tions and the measurement technique, not the type of device. The relationship
between routine office BP and standardized office BP is highly variable; therefore, it
is not possible to apply a correction factor to translate a given routine BP value to a
standardized BP value.
Home BP monitoring
2
HBPM may be particularly important for the management of BP when a
clinic visit is not practical, for example, during the coronavirus disease 2019
• Quiet room (no talking by patient or observer)
(COVID-19) pandemic. However, at present, HBPM should only be used to • No smoking, caffeine, or exercise for ≥30 min
complement standardized office measurement and not guide treatment before measurement
• Empty bladder
decisions, if standardized office BP is available. • Relax for >5 min
BP target in CKD not treated with dialysis
3
Adults with high BP and CKD should be treated to a target SBP <120 mm Hg No talking during rest period
which must be measured using standardized office BP preparations and and between measurements
Cuff to fit arm size (small, usual, large)
techniques. When measured under standardized conditions, targeting SBP
Arm bare and resting.
<120 mm Hg reduces the risks of CV events and all-cause mortality in CKD; Mid-arm at midpoint of the sternum
however, the effects on progression of kidney disease are uncertain.
Back
4
BP target in CKD subgroups supported
The SBP target of <120 mm Hg also applies to the subgroups of older Validated oscillometric
or manual auscultatory
adults and those with increased albuminuria. The balance of benefits device2,3, calibrated
and harms is less certain in people with CKD G5 and in those with severe- periodically
ly increased albuminuria (A3). Feet flat on floor
5
BP target in patients with diabetes
The benefits of intensive BP lowering are less certain among patients
with concomitant CKD and diabetes, compared to patients with CKD Lifestyle
without diabetes. • Salt intake <2 g/d (<90 mmol/d)
• Physical activity: 150 min/week moderate-intensity
6
Antihypertensive agents in CKD
Pediatric patients
RASi (ACEi or ARB) should be used in patients with CKD and increased
albuminuria, with or without diabetes. The evidence for use of RASi in 24 h MAP by ABPM
≤50th percentile for ACEi or ARB
patients with moderately increased albuminuria is lower in quality than
age, sex, and height
in severely increased albuminuria.
Adults with CKD with and without diabetes
7
Lifestyle interventions ACEi or ARB
Low sodium intake (<2 g/day) and moderate-intensity physical activity SBP <120 mm Hg • G1–G4, A3 without
(≥150 min/week) are suggested in accordance with recommendations for diabetes (1B)
the general population. • G1–G4, A2 without
diabetes (2C)
• G1–G4, A2 or A3
with diabetes (1B)
8
BP target in KTR
For adult kidney transplant recipients, a target of <130/<80 mm Hg, using
standardized office measurement, is still a reasonable goal. A lower SBP Adult kidney transplant recipients
goal (<120 mm Hg) for kidney transplant recipients would require
additional data on the risks and benefits in this population. Dihydropyridine
<130/<80 mm Hg
CCB or ARB
Targets Preferred drugs
9
Antihypertensive agents in KTR
Dihydropyridine CCB or ARB should be used as the first-line antihyper-
tensive agent in adult kidney transplant recipients given their efficacy in
and the importance of preventing graft loss.
10
BP management in children
BP target in children with high BP and CKD should be lowered to ≤50th
percentile for age, sex, and height according to 24-hour MAP by ABPM.
When ABPM is not available, standardized auscultatory office measure-
ment should be used to target SBP <90th percentile.
*The KDIGO Guideline for the Management of BP is applicable to patients with CKD not receiving dialysis. ABPM, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring;
ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; BP, blood pressure; CCB, calcium channel blocker; CKD, chronic kidney
disease; CV, cardiovascular; HBPM, home blood pressure monitoring; KTR, kidney transplant recipient(s); MAP, mean arterial pressure; RASi, renin-angiotensin
system inhibitor; SBP, systolic blood pressure
You might also like
- Blood Pressure Management in The Patient With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure Management in The Patient With Chronic Kidney DiseaseMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- 7-Treatment of HypertensionDocument4 pages7-Treatment of HypertensionOmnia ElsaftyNo ratings yet
- NCP Roldan OncoDocument6 pagesNCP Roldan OncoCeegi Arville RoldanNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Adults With Hypertension: Michigan Quality Improvement Consortium GuidelineDocument1 pageMedical Management of Adults With Hypertension: Michigan Quality Improvement Consortium GuidelinedennisNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in 2017-What Is The Right Target JAMA 2017Document2 pagesHypertension in 2017-What Is The Right Target JAMA 2017JulianNo ratings yet
- 2020 - 2022 Hypertension HighlightsDocument15 pages2020 - 2022 Hypertension HighlightsDuaa ShamiehNo ratings yet
- RBS - Random Blood Sugar PDFDocument4 pagesRBS - Random Blood Sugar PDFKrishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Slide Speaker Candesartan For Hypertension in CKD PatientsDocument43 pagesSlide Speaker Candesartan For Hypertension in CKD Patientsesdras pramuditaNo ratings yet
- What's New?: Canadian Recommendations For The Management of HypertensionDocument9 pagesWhat's New?: Canadian Recommendations For The Management of HypertensionM Naeem ArhamNo ratings yet
- CKD Algorithm Final - 2011 - May 18Document1 pageCKD Algorithm Final - 2011 - May 18AnjaniNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument30 pagesPrevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsShazi AliNo ratings yet
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Document4 pagesRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Ace Khiel Peralta50% (2)
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Management of Progression and Compl 2013 Kidney International SupDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Management of Progression and Compl 2013 Kidney International SupwardaninurindahNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPDocument4 pagesUncontrolled Blood Sugar NCPRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- CKD Kdigo 2012Document27 pagesCKD Kdigo 2012giggs_libraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationHanna La MadridNo ratings yet
- HTTPSWWW - Moh.gov - mymohresourcesPenerbitanCPGEndocrineQR T2DM 6th Edition QR Guide Digital PDFDocument8 pagesHTTPSWWW - Moh.gov - mymohresourcesPenerbitanCPGEndocrineQR T2DM 6th Edition QR Guide Digital PDFFiqa KusrinNo ratings yet
- JR InternaDocument24 pagesJR InternaYuhan NizNo ratings yet
- Stoplight Tool DiabetesDocument1 pageStoplight Tool DiabetesbarbaraNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- DR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020Document34 pagesDR - Antonia Anna Lukito Slide - Webinar 18 April 2020fairuzNo ratings yet
- SHANZ - MED II DIABETES MELLITUS Fixed (Merged)Document11 pagesSHANZ - MED II DIABETES MELLITUS Fixed (Merged)Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1AGUSTIN PRECIOUS JOY CNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanDienizs Labini Tadena100% (1)
- 2.5.3.1 Hipertensi EsensialDocument156 pages2.5.3.1 Hipertensi Esensialshafiqah zawiraNo ratings yet
- Optimum Way BP 2023Document37 pagesOptimum Way BP 2023herryaptNo ratings yet
- 2nd Case Session ToT CPG HPTDocument127 pages2nd Case Session ToT CPG HPThakimahsNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Blood GlucosaDocument8 pagesMonitoring Blood GlucosaMabe AguirreNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument8 pagesNCP Drug StudyLaila V. MananonNo ratings yet
- Medical Check Up Standard Operating Procedure For Diagnosis 1. BMIDocument25 pagesMedical Check Up Standard Operating Procedure For Diagnosis 1. BMIlita agustinNo ratings yet
- ISH Hypertension 2020Document6 pagesISH Hypertension 2020drguillermomoNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmacological Treatment of HypertensionDocument25 pagesNon-Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertensionastrid abrahams0% (2)
- M1 Kamad - G26 NCPDocument3 pagesM1 Kamad - G26 NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- KDIGO 2022 Diabetes Guideline Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesKDIGO 2022 Diabetes Guideline Quick Reference GuideChristian Risco QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Update Management DMDocument27 pagesUpdate Management DMnando8396No ratings yet
- Nidus MonDocument18 pagesNidus MonpriyankaswaminathanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Q and A For Nov2015 Oct16updates - LHDocument5 pagesPharmacy Q and A For Nov2015 Oct16updates - LHManilynNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Diabetes LectureDocument65 pagesDiabetes LecturebailovinaflorNo ratings yet
- Diabetes & AgingDocument2 pagesDiabetes & AgingAnn DahngNo ratings yet
- DR - Dr. Seobagijo Adi, SpPD-KEMD-Segi Prakteis Panduan Pemilihan Obat Oral Anti DiabetesDocument31 pagesDR - Dr. Seobagijo Adi, SpPD-KEMD-Segi Prakteis Panduan Pemilihan Obat Oral Anti DiabetesraraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal InternaDocument11 pagesJurnal InternaRamlah AndariasNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Studies Purpose Results Interpretation Patient'S Reading Normal ValuesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Studies Purpose Results Interpretation Patient'S Reading Normal ValuesasdadadadasdNo ratings yet
- HTN managment-JNC7Document37 pagesHTN managment-JNC7Vaibhav KaroliyaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Geriatrics Evaluation & ManagementDocument4 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Geriatrics Evaluation & ManagementAngeles SlzrNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Management: Is Beta Blockers Still EffectiveDocument55 pagesHypertension Management: Is Beta Blockers Still EffectiveRidyahningtyas SintowatiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Article EssentialPointsFromEvidence-baDocument15 pages2019 Article EssentialPointsFromEvidence-baNur RahmahNo ratings yet
- Diabetes OPD ดีมากกกDocument5 pagesDiabetes OPD ดีมากกกPonpimol Odee BongkeawNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Inpatient Management of Diabetes and HyperglycemiaenesNo ratings yet
- AMH Hypertension PrintDocument4 pagesAMH Hypertension PrintMusharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Medication Hypertension OlaDocument13 pagesMedication Hypertension OlaNoor AliNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Takeaways Clinicians - UpdatedDocument1 pageTop 10 Takeaways Clinicians - UpdatedBea Barbara CarrascalNo ratings yet
- Best Practice For Diabetic Patients On Hemodialysis 2012 (TAD19-S1)Document27 pagesBest Practice For Diabetic Patients On Hemodialysis 2012 (TAD19-S1)Anonymous uuP28GXyNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Guidelines PDFDocument10 pagesHypertension Guidelines PDFARAVINDANo ratings yet
- Glycemic Management Guideline: General PrinciplesDocument8 pagesGlycemic Management Guideline: General PrinciplesJon KnezevichNo ratings yet
- BP Target in CKDDocument70 pagesBP Target in CKDAnitha SNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Guidline Hipertensi Dengan DiabetesDocument5 pagesGuidline Hipertensi Dengan DiabetesTri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Hospital and Research Centre: - Thesis ProposalDocument39 pagesAyurvedic Hospital and Research Centre: - Thesis ProposalgunjanNo ratings yet
- Cell DyneDocument12 pagesCell DyneLia WieNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms in Arts MAPEH 9Document12 pagesGlossary of Terms in Arts MAPEH 9vicaliezaNo ratings yet
- BSR - 20 Element RBPS Training - 14september2017 PDFDocument399 pagesBSR - 20 Element RBPS Training - 14september2017 PDFDuy DangNo ratings yet
- Salvia For Dementia Therapy: Review of Pharmacological Activity and Pilot Tolerability Clinical TrialDocument9 pagesSalvia For Dementia Therapy: Review of Pharmacological Activity and Pilot Tolerability Clinical TrialAleksa LukicNo ratings yet
- Activity Design For Orientation.Document4 pagesActivity Design For Orientation.Ricky Canico Arot50% (2)
- Cardiac Disease and Pregnancy RCOG GuidelineDocument18 pagesCardiac Disease and Pregnancy RCOG GuidelinedanielsusenoNo ratings yet
- Human Subjects Research CST PresentationDocument33 pagesHuman Subjects Research CST Presentationapi-529961637No ratings yet
- Contact Us: The Cathay Drug Company IncorporatedDocument3 pagesContact Us: The Cathay Drug Company IncorporatedSirhc CelioteNo ratings yet
- Al-Dumaini - 2018 - A Novel Approach For Treatment of Skeletal Class II Malocclusion - Miniplates-Based Skeletal AnchorageDocument9 pagesAl-Dumaini - 2018 - A Novel Approach For Treatment of Skeletal Class II Malocclusion - Miniplates-Based Skeletal AnchoragefishribbonNo ratings yet
- Living Things and Their Environment: Quarter 1: Module 1-4Document30 pagesLiving Things and Their Environment: Quarter 1: Module 1-4ar0411No ratings yet
- Mutu Bakso Ikan Patin Yang Diiradiasi Dengan Sinar Gamma (60CO)Document8 pagesMutu Bakso Ikan Patin Yang Diiradiasi Dengan Sinar Gamma (60CO)MagrisaNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM614 - Work Life Balance Report and Action PlanDocument4 pagesBSBHRM614 - Work Life Balance Report and Action PlanReine WenceslaoNo ratings yet
- Arellano University Jose Rizal High School Gov. Pascual Avenue, Malabon City Telefax 921 - 27 - 44Document4 pagesArellano University Jose Rizal High School Gov. Pascual Avenue, Malabon City Telefax 921 - 27 - 44Rogue CuberNo ratings yet
- Arm PlyometricsDocument5 pagesArm PlyometricsGhita Marius GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Ap Practice Exam With FRQDocument41 pagesAp Practice Exam With FRQVanessa LuoNo ratings yet
- The Art of Critical ThinkingDocument2 pagesThe Art of Critical ThinkingAmeer Youseff MarotoNo ratings yet
- Rating of Perceived Exertion For Quantification of The Intensity of Resistance Exercise 2329 9096.1000172Document4 pagesRating of Perceived Exertion For Quantification of The Intensity of Resistance Exercise 2329 9096.1000172joseNo ratings yet
- Gastric LavageDocument19 pagesGastric LavageAnita Santiago Soguilon100% (1)
- Philippine Canadian Inquirer #434Document32 pagesPhilippine Canadian Inquirer #434canadianinquirerNo ratings yet
- Female External GenitaliaDocument6 pagesFemale External GenitaliaTeeNo ratings yet
- Cisco Healthcare SolutionsDocument4 pagesCisco Healthcare SolutionsHassan AlsafiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Vermicompost and Biofertilizers On Yield and Soil PDFDocument3 pagesEffect of Vermicompost and Biofertilizers On Yield and Soil PDFAgricultureASDNo ratings yet
- PLPFDocument88 pagesPLPFcartelperiodoncia100% (3)
- Bayanihan To Recover As One (Bayanihan 2) BillDocument54 pagesBayanihan To Recover As One (Bayanihan 2) BillRappler100% (6)
- Acute Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Current LiteratureDocument9 pagesAcute Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Current LiteratureUlos BenardNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument65 pagesMicroHafiz UllahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 10 - Making ChoicesDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 10 - Making ChoicesPrincess Annie100% (1)
- Training New Staff Checklists: © Linda Drevenstedt, MSDocument12 pagesTraining New Staff Checklists: © Linda Drevenstedt, MSLinda DrevenstedtNo ratings yet
- Mannitol Baxter Viaflo Sol F Inf ENGDocument10 pagesMannitol Baxter Viaflo Sol F Inf ENGBojan BjelajacNo ratings yet