Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ 2 Reviewer
Uploaded by
joashhortillosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesChapter 5 to 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChapter 5 to 6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesEcon 2 Reviewer
Uploaded by
joashhortillosaChapter 5 to 6
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ECON 2 Reviewer
CHAPTER 5: The National Income Approach
National Income Accounting -is the system used to measure the aggregate income and expenditure for a nation
Gross Domestic Product -is the total market or money value of all final goods and services produced in an
economy over a period of one year. Most widely used measure of economic performance.
Approaches in measuring GDP
The Expenditure Approach
GDP = C + I + G + (X - M)
The Income Approach
GDP = NY + IBT + D
NY = W + R + i + P
Industrial Origin or Gross Value Added Approach
GDP = GVA + IBT
GDP Shortcomings
Nonmarket Transactions
Distribution, Kind, and Quality of Products
Neglect of Leisure Time
The Underground Economy
Economic Bads
Nominal or Current GDP -is the value of all final goods and services based on the prices existing during the
time of production.
Formula to convert nominal GDP to real GDP:
Real GDP = Nominal GDP ÷ GDP Deflator × 100
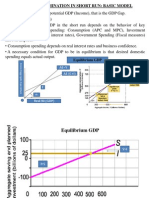
CHAPTER 6: Consumption and Savings
Income -in macroeconomics pertains to economic income which is earned through economic activities
undertaken by the household or business sectors.
Consumption -is the expenditure made by households on goods and services.
The Consumption Function
Consumption and Income: Basic Assumption
Y = Cb + ∆C
Where:
Y = Factor income
Cb = Barrowing from the economy’s stock of savings
∆C = Change in consumption
The Multiplier Concept
K = 1 ÷ 1 – MPC or 1 ÷ MPS
Where:
K = Multiplier coefficient
MPC = Marginal propensity to consume
MPS = 1 – MPC = Marginal propensity to save
MPS + MPC = 1
S=i
i = Y - ∆C
Where additionally:
S = Aggregate savings from currently generated income
i = Inflow
Factors of Consumption
Taste and Preference
Population
Income
Price Level
Innovation and Promotion
You might also like
- Economics HL Formula BookletDocument7 pagesEconomics HL Formula BookletNeha MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Consumption and SavingsDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Consumption and SavingsAngelica Valdez Bauto100% (1)
- Chapter 9EDocument16 pagesChapter 9EMandarin English CentreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - National Income DeterminationDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - National Income DeterminationChelsea Anne VidalloNo ratings yet
- Income, Consumption, Savings & InvestmentDocument23 pagesIncome, Consumption, Savings & InvestmentAurongo NasirNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics:: Current GDP Value $2.264 Trillion Current GDP Growth Rate 7.3%Document11 pagesMacroeconomics:: Current GDP Value $2.264 Trillion Current GDP Growth Rate 7.3%Rithu D.LNo ratings yet
- Consumption and Saving Function: Group MembersDocument23 pagesConsumption and Saving Function: Group MembersSarosh HassanNo ratings yet
- Aggregate DemandDocument19 pagesAggregate Demandriyagrover2004No ratings yet
- Mangerial EconomicsDocument37 pagesMangerial EconomicsevelynNo ratings yet
- Aggregate DemandDocument10 pagesAggregate DemandHarshita NarulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Consumption and SavingsDocument12 pagesChapter 5 - Consumption and SavingsChelsea Anne VidalloNo ratings yet
- Keynesian Consumption ModelDocument46 pagesKeynesian Consumption ModelAnkita MalikNo ratings yet
- Consumption, Saving and Investment FunctionsDocument17 pagesConsumption, Saving and Investment FunctionsSujan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Aggregate Exp SKMDocument78 pagesModule 3 Aggregate Exp SKMVrinda RajoriaNo ratings yet
- Topic (5) - Theory of National Income DeterminationDocument14 pagesTopic (5) - Theory of National Income Determinationfuck offNo ratings yet
- C3 - APE and Fiscal PolicyDocument45 pagesC3 - APE and Fiscal PolicyAnh Ôn KimNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Consumption ExpenditureDocument23 pagesAggregate Consumption ExpenditureHerrika Red Gullon Rosete0% (1)
- Cha-2 Macroeconomics IDocument33 pagesCha-2 Macroeconomics Ilidya berhanemeskelNo ratings yet
- Consumption: Means The Expenditures Made by Household On Goods and ServicesDocument7 pagesConsumption: Means The Expenditures Made by Household On Goods and ServicesAnifahchannie PacalnaNo ratings yet
- Nations Income NotesDocument24 pagesNations Income NotesRitik PatelNo ratings yet
- 5 Aggreagete Expenditures (F19)Document19 pages5 Aggreagete Expenditures (F19)周杨No ratings yet
- Consumption Savings and InvestmentDocument32 pagesConsumption Savings and InvestmentVijay Chelani0% (1)
- Two Sector ModelDocument84 pagesTwo Sector Modelvisha183240No ratings yet
- (KTVM) Kinh Te VI Mo - Pham Xuan Truong - Chap 7Document36 pages(KTVM) Kinh Te VI Mo - Pham Xuan Truong - Chap 7Vũ Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document40 pagesTopic 2玮仪No ratings yet
- Consumption and SavingsDocument17 pagesConsumption and SavingsHardeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Asistensi 1 - PE-2-N - NoteDocument31 pagesAsistensi 1 - PE-2-N - NoteFirda putriNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Overview of Applied EconomicsDocument57 pagesModule 1 Overview of Applied EconomicsAlvin OroscoNo ratings yet
- Session 10 - Fiscal PoliciesDocument17 pagesSession 10 - Fiscal Policiess0falaNo ratings yet
- 2 National Accounting - Lecture 2.Ppt (Autosaved)Document32 pages2 National Accounting - Lecture 2.Ppt (Autosaved)Darren MgayaNo ratings yet
- Income Determination in Short Run: Basic Model: Ae Y AE (C+I) Ae YDocument31 pagesIncome Determination in Short Run: Basic Model: Ae Y AE (C+I) Ae YAman Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- IMPORTANTNIDocument28 pagesIMPORTANTNIVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- MultiplierDocument16 pagesMultiplierNaman LadhaNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes On Unit 9Document4 pagesAdditional Notes On Unit 9Bhavna JoseNo ratings yet
- ECON1011 Principles of Economics Agrarian Reform Taxation: National Income AccountingDocument10 pagesECON1011 Principles of Economics Agrarian Reform Taxation: National Income AccountingJan Mark MujalNo ratings yet
- Income-Expenditure Model of GDP: Reference: Ebook Chapter 4Document57 pagesIncome-Expenditure Model of GDP: Reference: Ebook Chapter 4NormanMichaelNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 NotesDocument15 pagesModule - 4 NotesKrishnaprabha K TNo ratings yet
- Multiplier: MacroeconomicsDocument24 pagesMultiplier: MacroeconomicsBasit IjazNo ratings yet
- Economics FormulasDocument2 pagesEconomics Formulasgay boiNo ratings yet
- The Household-Consumption Sector: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument44 pagesThe Household-Consumption Sector: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinRomaisadawoodAliNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics EBC1018 Summary Author: Ferdinand Kraemer: (Y (T) - Y (t-1) ) / Y (t-1)Document33 pagesMacroeconomics EBC1018 Summary Author: Ferdinand Kraemer: (Y (T) - Y (t-1) ) / Y (t-1)Benedict YeoNo ratings yet
- 2017 Level I Formula SheetDocument28 pages2017 Level I Formula SheetVishal GoriNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For AP EconomicsDocument3 pagesCheat Sheet For AP EconomicsMingrui QianNo ratings yet
- 2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFDocument27 pages2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFShamima YesminNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicDocument34 pagesMacroeconomicSothida SaromNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument18 pagesIlovepdf MergedmazenaymansolimanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro Economics SPCC - 75331bc4 54df 4daa b4db Ab55b4632826Document23 pagesIntroduction To Micro Economics SPCC - 75331bc4 54df 4daa b4db Ab55b4632826Tarun VermaNo ratings yet
- RB CAGMAT REVIEW LEA Review - Macroeconomics - International TradeDocument99 pagesRB CAGMAT REVIEW LEA Review - Macroeconomics - International TradeShainabe RivaNo ratings yet
- 9.7 The Multiplier RSDocument47 pages9.7 The Multiplier RSSyed HaroonNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - C23 To C26 and C28 To C30Document15 pagesSession 3 - C23 To C26 and C28 To C30Nguyệt LêNo ratings yet
- 7 National Income PART I: National Income Accounting: Macro./ Topic 7 / P.1Document6 pages7 National Income PART I: National Income Accounting: Macro./ Topic 7 / P.1ishan_mNo ratings yet
- Lec-12B - Revison - Consumption Savings and InvestmentDocument24 pagesLec-12B - Revison - Consumption Savings and InvestmentMsKhan0078No ratings yet
- MGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Document13 pagesMGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Farhan UL HaqNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics IIDocument35 pagesMacroeconomics IIEmre BüyükbayraktarNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting AbelDocument12 pagesNational Income Accounting AbelKushagra AroraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaDocument16 pagesChapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaYonas AddamNo ratings yet
- Economics FormulasDocument8 pagesEconomics FormulasInam AghaNo ratings yet
- Vĩ MôDocument13 pagesVĩ Môbonglinh2830No ratings yet
- 7 DemandChp5Document9 pages7 DemandChp5sara isazaNo ratings yet