0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views20 pagesBiology Classification for Grade VII
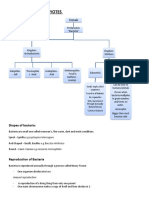
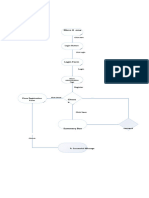
This document provides information about biological classification. It discusses the kingdoms Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Within the animal kingdom, it describes the invertebrate phyla including porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminthes, nematoda, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, and echinodermata. It also discusses the characteristics of vertebrates.
Uploaded by
Author ClubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views20 pagesBiology Classification for Grade VII
This document provides information about biological classification. It discusses the kingdoms Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Within the animal kingdom, it describes the invertebrate phyla including porifera, cnidaria, platyhelminthes, nematoda, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, and echinodermata. It also discusses the characteristics of vertebrates.
Uploaded by
Author ClubCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd