0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views8 pagesJava Class Structure and Basics
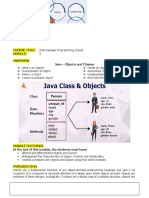
The document discusses the basic building blocks of Java classes including fields, methods, objects, and comments. Some key points:
- Classes are the basic building blocks and contain fields to store data and methods to perform actions.
- An object is an instance of a class that represents real world entities. Objects are created using the new operator.
- Fields store the data/state of an object while methods perform actions on that data.
- Comments are used to explain code and are ignored by the compiler. There are different styles like single-line, multi-line, and Javadoc comments.
- Each class is typically in its own .java file and only one class can be public per file if it
Uploaded by
abilgen006Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views8 pagesJava Class Structure and Basics
The document discusses the basic building blocks of Java classes including fields, methods, objects, and comments. Some key points:
- Classes are the basic building blocks and contain fields to store data and methods to perform actions.
- An object is an instance of a class that represents real world entities. Objects are created using the new operator.
- Fields store the data/state of an object while methods perform actions on that data.
- Comments are used to explain code and are ignored by the compiler. There are different styles like single-line, multi-line, and Javadoc comments.
- Each class is typically in its own .java file and only one class can be public per file if it
Uploaded by
abilgen006Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd