0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views2 pagesIntel 8051 Microcontroller Overview
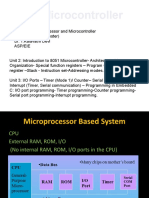
The document discusses the pins and functions of the Intel 8051 microcontroller. It has the following key specifications and features:
- It has 4KB of ROM and 128B of RAM for basic user needs.
- It has 4 ports with a total of 32 input/output lines for interfacing.
- The ports, CPU, and RAM organization allow for upgrades to the microcontroller.
- The pins serve various functions like I/O, interrupts, timers, power supply, and interfacing with external memory and crystals.
Uploaded by
sifunatimothy509Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
113 views2 pagesIntel 8051 Microcontroller Overview
The document discusses the pins and functions of the Intel 8051 microcontroller. It has the following key specifications and features:
- It has 4KB of ROM and 128B of RAM for basic user needs.
- It has 4 ports with a total of 32 input/output lines for interfacing.
- The ports, CPU, and RAM organization allow for upgrades to the microcontroller.
- The pins serve various functions like I/O, interrupts, timers, power supply, and interfacing with external memory and crystals.
Uploaded by
sifunatimothy509Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd