Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CamScanner 03-11-2024 20.38
CamScanner 03-11-2024 20.38
Uploaded by
AIRUNI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views18 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views18 pagesCamScanner 03-11-2024 20.38
CamScanner 03-11-2024 20.38
Uploaded by
AIRUNICopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Cambridge Assessment
@ a rtonall Education
Cambridge IGCSE™
a holm
CENTRE CANDIDATE |
NUMBER NUMBER
PHYSICS 0625/44
Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MaylJune 2023,
‘hour 15 minutes
‘You must answer on the question paper.
‘No additional materials are needed.
INSTRUCTIONS
‘Answer all questions.
Use a black or dark blue pen. You may use an HB pencil for any diagrams or graphs.
‘Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes atthe top ofthe page,
Write your answer to each question in the space provided,
Do not use an erasable pen or correction fluid.
Do not write on any bar codes.
You may use a calculator.
You should show all your working and use appropriate units,
‘Tako the weight of 1.0kg to be 9.8N (acceleration of free fall = 9.8m/s").
INFORMATION
© The total mark for this paper is 80.
‘© The number of marks for each question or part question is shown in brackets [|
‘This document has 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated.
xen ttumowr
Scanned with CamScanner
2
eros a svaight section of aver where the wate is owing from ght ole at a spoed of
vis
fier
o54mis
_
a
swimaver
Fig. 4.4 (not to scale)
‘Aswimmer starts at point P and swims at a constant speed of 0.72m/s relalive to the water and at
right angles tothe current.
(a) (Determine, relative to the river bank, both the magnitude and direction ofthe swimmer's
velocity.
K attbtec®
O74 on prerenie
ost ag
ost
of
magnitude of velocity =
rection of velocity
(i) After 1.5 minutes, the swimmer reaches point Q.
Calculate the distance between P and Q.
gs Didone \trbp=4e
time
distance :
ods -
oRrfe =P {4.8 -0
Scanned with CamScanner
3
When the swimmer is crossing the river, his actions produce a constant forward force on his,
Explain why he moves at a constant speed.
[Total: 9}
Scanned with CamScanner
4
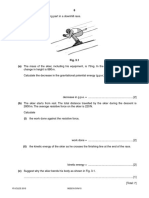
Fig. 2.1 shows a motorcyclist accelerating along a straight horizontal section of track.
re
Fig. 2.1
‘The motorcyclist and motorcycle have a combined mass of 240kg.
{a) On oe horizontal section of the track, the motorcyclist accelerates from rest at
72mI/s*.
(i) The motorcyclist reaches the end of the straight section of track in 5.38.
Calculate the speed of the motorcyclist at the end of the straight section.
oo
Ae T 70x53 = 3814
Axis poets DE: Lr
(ii) Calculate the resultant force on the motorcyclist and motorcycle on the straight section
of track.
re
te 79x 240 resultant force = ..
= ig!
Scanned with CamScanner
5
} At tho end of the stralght section, the track remains horizontal but bends to the right, as,
shown in Fig. 2.1.
When the motorcyclist reaches the bend, she travels around the bend in a circular path at a
constant speed.
(W)_ Velocity Is a vector quantity
State how a vector quantity differs from a scalar quantity.
hi
fi (ii) Describe what happens to the velocity of the motorcyclist as she travels around the bend
q at constant speed.
\ f
» {f]
(ili) Explain why there must be a resultant force on the motorcyclist as she travels around the
bend.
Scanned with CamScanner
6
Ant
bbar balloon is inated with hollum and sealed so that no houm escapes,
The balloon is positioned immediately bolow the ceiling In a room.
Heaters are switched on and the temperature of the air In the room increases.
(a) When the heaters are first switched on, the temperature of tho air immediately below tho
colling increases more quickly than the temperature of the alr in tho rost of the room.
Explain why this happens.
tele 2
Jo 1h buy 21 He Gl) oir
(b) The temperature of the helium in the balloon increases and as the rubber stretches, the I the.
‘volume occupied by the helium increases. a
+) Hee
(1) State what happens to the motion of the helium particles as the temperature Increases. ib
. “ he
aa
(ll) As the rubber stretches and the volume of the helium increases, the pressure of the
helium remains constant.
Explain, in terms of the particles of helium, how the pressure of the helium remains
constant.
8
Total: 6)
iene
Perper tral
Preston
het kecoue
Ove Inver.
(when vobewe — 1A1G0 305 Pree Sess
ot te enperr Facrtey ¢ Pee Taceeer hee
Ofileme ub
hems — Oloartnt «
Scanned with CamScanner
1, Susie envestiyhers tes Hidericy A a Marvent tang, Fig 4.4 shavers tee Saerert ‘ancy wi) ts
fa tasty ierareotsecd in wien i 9 teecheer,
tracrmcmratec
to pomen supty
wales:
— flamert tarp
Fig. 44
The reading on the thermometer in the water 1s 19.0°C.
Only the glass of the lamp is in contact whth the water and the electrical connections are completely
insulated,
‘The lamp is suttched on,
‘Al the end of the experiment, the temperature of the water is 21.5°C.
(2) The mass of the water in the beaker is 600g.and the specific heat capacity of water is
4200 149"C)
0) “tu ta increase nt ea energy ofthe waters 6900! 6
Ez: mest
291 6 aml ¥ seen xs 14
eq 6300 8)
(il) In tho experiment, the lamp is switched on for 500s. The power supplied to the filament
famp 1s 13W. The useful energy from the lamp is transferred as light. The energy that
Increases the temperature of the water is wasted energy.
Determine the maximum possible efficiency of the filament lamp.
: Etmecine 2 Cee lou
/ 7 Efhecienty « sai fo
+7 e a alse
bin. P
pus : t1 fy 47h
la.La maximum possible efficiency = «. 17% - 4)
Scanned with CamScanner
9
(6) The efficiency of the lamp is less than the value determined in (a\(ll).
Suggest one reason for this.
Oy
[Total: 8}
ZL
Scanned with CamScanner
0
"lg, 6.4 shows @ tock HECD made oh cfoos that has 3 refcacss
ved side hE ond tees strap sides, BC, CD and DAL ex Of 1.5. The Bock has one
monochromatic apt
Fig. 5.41
‘There are right angles at C and D. The curved side AB is one quarter of the circumference of a
circle that has its centre at point P.
Aray of monochromatic light enters the block through the curved side AB and strikes side BC at P.
‘Some light emerges into the air and some is reflected.
(a) State what is meant by monochromatic. < 1
Lig tah oe. Ctlor:
(c) Show that the critical angle c for glass of refractive index,
|
= singe
[eS xsin@e Il
ey
HX jn sino a
ie a
(nif cx siete)
ce 42°
(0625/4123
Scanned with CamScanner
"
(4) Fig. 5.1 shows that the angle between the ray of ight and tine AP is
wijes as aide BC. light @, where line AP ts at right
Angle @ increases to 45°.
(State and explain what happens to the light that strikes P.
(ll) When @= 45°, the reflected light strikes side CD.
Describe what happens when this reflected light strikes side CO.
tt)
[Total: 8)
Scanned with CamScanner
2
A mobile phone (cell phone) network uses microwaves of frequency 1.9 x 10°Hz to transmit and
receive signals.
‘The speed of microwaves in air is 3.0 x 108m/s.
(@) Calculate the wavelength of these microwaves in air.
lt 3 xlo%
ew Ts alet
ck Os> 1b
(b) State two reasons why microwaves are used for mobile phone (cell phone) signals.
13
(c) All mobile phone (cell phone) networks use digital signals to communicate with the phone.
(Describe, with the aid of a diagram, how a digital signal differs from an analogue signal.
Digiber were a logic ime
tales ite. chAs.
eighth
(i) State two advantages of using digital signals rather than analogue signals.
Tb bole
Total:
Scanned with CamScanner
B
RUT gh 9 cre hat cons a bat. @ switch, a voltmeter and three 40 resistors.
Fig. 7.4
‘The switch is open and resistors R, and R, form a potential divider.
(2) Describe what is meant by a potential divider.
{b) The reading on the voltmeter is 7.5V.
(Calculate the electromotive force (e.m4.) of the battery.
emf.=
(il) The switch is closed.
Calculate the resistance of the complete Or
Ly RRs Gevir [e |
sae hr Wry.
da
7 i ot He: 6 resistance = ..
-
[Total: 8]
Scanned with CamScanner
lhe , 4
lm has een town is tansited using a tg vtogo cai, A nslomar i tho
simple iron-cored transformer.
(a) Explain the principle of operation of
(b) The transformer steps the supply voltage down from 220000V to 33000V.
vielbe
(i) There are 450 tums on the secondary coll.
Caloulate the number of tums on the primary col, ts -
poco X 109
\s_Ni Vane > VpNy = = a3 pote
vp Ne ve 2 Bae
number of turns = ove.
oe (2)
(a) The clctical power transferred tothe transformer by the high-voltage cable Is 77 MW.
few
T1x/08 : oo
Calculate the current in the primary coll.
Ar yo
see BY
Total: 9}
Scanned with CamScanner
16
5
"9.9.1 represents all the particles in a neutral atom of a radioactive isotope x1,
Fig. 9.1 (not to scale)
(a) Determine the number of neutrons in this atom and explain how the answer is obtained.
the number of neutror
explanation
ttr..S tector dence oveleer alll be dees. 6. fhe
ble cles, eprops. and bests. Bty. del?
—ramber of neutrons =
1). The isotope X1 is a beta emitter that decays to the stable isotope X2.
(i) Describe how a nucleus of X2 differs from a nucleus of X1.
Drofsn bet
Scanned with CamScanner
ww
(©) The hal.ite of X1 ts apgroximstely 20.5,
(1) Define the term hait-tte, Lime
The_aneunt. ct tstsbeadiion..
Dtbirbestle Etta bent cba ‘ua
wlbeibtes 3 Se el de topes
(li) Suggest one reason why isotopes witty very short half-lives are especially hazardous.
Scanned with CamScanner
a
7
+) The half-life of X1 is. ana 20ms,
(i) Define the term half-life.
awneunt.
The...
(li) Suggest one reason why isotopes with very short halflives are especially hazardous.
Total: 8
Scanned with CamScanner
18
Pluto is a dwarf planet. Fig. 10.1 shows the direction of motion of Pluto as it follows its elliptical
orbit around the Sun.
ale
[> +>
‘of motion
Fig. 10.1 (not to scale)
(a) Point X is the point in the orbit closest to the Sun and point Y is the point furthest away.
‘The orbital speed of Pluto varies as it orbits the Sun.
()_ Describe how the speed of Pluto varies as it moves from X to Y and then back to X.
(ii) Explain, in terms of energy transfers, why the speed of Pluto varies in this way.
Scanned with CamScanner
9
(b
The average temperature on the surface of Pluto is 43K.
(1) Convert this temperature toa value in degrees Celsius (1c)
igo oa
temperature = alt 3I “cit
(li) Pluto has a white surface, as shown in Fig. 10.2. As Pluto rotates, the white surface
altemately faces towards and away from the Sun.
Fig. 10.2
Explain how this affects the temperature of Pluto as it rotates on its own axi
a
o The whib suche foe Leas feaporie thn Qe ota 7)
Gyter $Me dh fle feb vtm s! Soam eh Sen
ft ehedts wt Ale velaten 4 Mt
Sun *
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Time Line Physics O LevelDocument1 pageTime Line Physics O LevelAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/21Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/21AIRUNINo ratings yet
- New Doc 10-30-2023 19.47Document2 pagesNew Doc 10-30-2023 19.47AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Test 07-04-2022Document5 pagesTest 07-04-2022AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Test 06-04-2022Document5 pagesTest 06-04-2022AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Particle Model of MatterDocument2 pagesTopic 3: Particle Model of MatterAIRUNINo ratings yet
- The Orion Academy Name: - 06-04-2022 Test: Speed Runner 1 Runner 2Document3 pagesThe Orion Academy Name: - 06-04-2022 Test: Speed Runner 1 Runner 2AIRUNINo ratings yet
- CamScanner 10-18-2023 21.34Document1 pageCamScanner 10-18-2023 21.34AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-03Document1 pagePages From 0625 - w15 - QP - 31-03lelon ong0% (1)
- FLYERDocument2 pagesFLYERAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Changes of State and The Particle Model 2 MSDocument9 pagesChanges of State and The Particle Model 2 MSAIRUNINo ratings yet
- ATP - QP - 04.07.2020Document3 pagesATP - QP - 04.07.2020AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Definitions and Concepts For AQA Physics GCSE: Topic 3: Particle Model of MatterDocument2 pagesDefinitions and Concepts For AQA Physics GCSE: Topic 3: Particle Model of MatterAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity PracticalDocument6 pagesHeat Capacity PracticalAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Class Test 28 July 2020 PDFDocument5 pagesClass Test 28 July 2020 PDFAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Secure Estimation and Attack Detection in Cyber-Physical Systems With Switching AttackDocument6 pagesSecure Estimation and Attack Detection in Cyber-Physical Systems With Switching AttackAIRUNINo ratings yet
- 162Document20 pages162AIRUNINo ratings yet
- ShareDocument1 pageShareAIRUNINo ratings yet
- Grade Thresholds - March 2017: Cambridge IGCSE Physics (0625)Document1 pageGrade Thresholds - March 2017: Cambridge IGCSE Physics (0625)AIRUNINo ratings yet
- Control Loops Thermostat Industrial Control Systems Processes Feedback Controller Process Variable SetpointDocument1 pageControl Loops Thermostat Industrial Control Systems Processes Feedback Controller Process Variable SetpointAIRUNINo ratings yet
- 0625 m17 Ms 12 PDFDocument3 pages0625 m17 Ms 12 PDFAIRUNINo ratings yet
- ShareDocument1 pageShareAIRUNINo ratings yet