Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 - JEE - Maths - Quadratic Equation - Wavy Curve Method
Uploaded by
Prateek JainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11 - JEE - Maths - Quadratic Equation - Wavy Curve Method
Uploaded by
Prateek JainCopyright:
Available Formats
Wavy Curve Method.
Let f (x ) (x a1 )k1 (x a 2 )k 2 (x a 3 )k 3 .......( x an 1 )k n 1 (x an )k n …..(i)
Where k 1 , k 2 , k 3 ..., k n N and a1 , a 2 , a 3 , ......, a n are fixed natural numbers satisfying the
condition
a1 a 2 a 3 ..... a n 1 a n
First we mark the numbers a1 , a 2 , a 3 , ......, a n on the real axis and the plus sign in the interval of
the right of the largest of these numbers, i.e. on the right of a n . If k n is even then we put plus
sign on the left of a n and if k n is odd then we put minus sign on the left of a n . In the next
interval we put a sign according to the following rule :
When passing through the point a n 1 the polynomial f(x) changes sign if k n 1 is an odd number and
the polynomial f(x) has same sign if k n 1 is an even number. Then, we consider the next interval and
put a sign in it using the same rule. Thus, we consider all the intervals. The solution of f ( x ) 0 is the
union of all intervals in which we have put the plus sign and the solution of f ( x ) 0 is the union of
all intervals in which we have put the minus sign.
You might also like
- Singapore Mathematical Olympiads 1994-1997Document9 pagesSingapore Mathematical Olympiads 1994-1997Niki ChanNo ratings yet
- Competition Corner (Tay Tiong Seng) PDFDocument13 pagesCompetition Corner (Tay Tiong Seng) PDFGV Nguyen ChuNo ratings yet
- Catalan Numbers and Random MatricesDocument7 pagesCatalan Numbers and Random MatricesruntoyNo ratings yet
- 3 SequencesDocument15 pages3 SequencesMJHabibiNo ratings yet
- BW 04 ProblDocument2 pagesBW 04 ProblThai An NguyenNo ratings yet
- DIE - Arthur T. Benjamin, Jennifer J. Quinn - XDocument12 pagesDIE - Arthur T. Benjamin, Jennifer J. Quinn - XDavid DavidNo ratings yet
- ArctanDocument18 pagesArctanFlorinNo ratings yet
- Senior Solutions 1996: SolutionDocument4 pagesSenior Solutions 1996: SolutioncuongaccNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Combinatorics Problems & Solutions: NZ Math Olympiad Training Programme 2004Document8 pagesAssignment 2: Combinatorics Problems & Solutions: NZ Math Olympiad Training Programme 2004ssshhhkiNo ratings yet
- Berkeley Math Circle - Monthly Contests - Solutions (1999-00)Document4 pagesBerkeley Math Circle - Monthly Contests - Solutions (1999-00)ElevenPlus ParentsNo ratings yet
- IMO Shortlist 1994: AlgebraDocument5 pagesIMO Shortlist 1994: Algebraquaned2k5No ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument4 pagesBinomial Theoremsamsonhatyoka100No ratings yet
- 3.2 Limit Theorems - Group 7 - PresentationDocument24 pages3.2 Limit Theorems - Group 7 - PresentationRembulan Permata OctaliaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document8 pagesLesson 4Udeshika WanninayakeNo ratings yet
- Generating FunctionsDocument13 pagesGenerating Functionskhanh truongNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Questions and Fill in Your Responses in The Corresponding Boxes On The Answer SheetDocument4 pagesAnswer The Following Questions and Fill in Your Responses in The Corresponding Boxes On The Answer SheetDiana paredes acostaNo ratings yet
- Binomial TheoremDocument14 pagesBinomial Theoremkarinavihta100% (1)
- HarmonicDocument9 pagesHarmonicOscar HernandezNo ratings yet
- Holder Inequality 2Document3 pagesHolder Inequality 2HenriNo ratings yet
- Curve TracingDocument4 pagesCurve Tracingsurekha surekha0% (1)
- Sol Welcome UsamoDocument6 pagesSol Welcome UsamoHiba EL KasimiNo ratings yet
- MarkovDocument46 pagesMarkovAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- 4) Pascals TriangleDocument56 pages4) Pascals TriangleMadhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Proof: Euler S TheoremDocument20 pagesProof: Euler S TheoremNeelam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Logistic FibonacciDocument4 pagesLogistic FibonacciSabzgostar Avande ParsNo ratings yet
- IrrationalDocument13 pagesIrrationalKhushbakht QureshiNo ratings yet
- Vietnam TST 1999-2009Document22 pagesVietnam TST 1999-2009Phạm Thế SơnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Order Statistics: 6.1 The Multinomial FormulaDocument19 pagesLecture 6. Order Statistics: 6.1 The Multinomial FormulaLya Ayu PramestiNo ratings yet
- KC Border - More Than You Wanted To Know About Quadratic Forms, CaltechDocument17 pagesKC Border - More Than You Wanted To Know About Quadratic Forms, CaltechDarabaGabriellNo ratings yet
- Training RecDocument6 pagesTraining RecRijal AbedinNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Export PDFDocument246 pagesCal1 Export PDFamarNo ratings yet
- 696696969Document6 pages696696969tempmail user 69No ratings yet
- ELMO 2011 Sols PDFDocument10 pagesELMO 2011 Sols PDFJavad Rahmany FardNo ratings yet
- Math 25800: Homework 7: Peter Boyajian April 7, 2017Document5 pagesMath 25800: Homework 7: Peter Boyajian April 7, 2017Peter BoyajianNo ratings yet
- AsymptotesDocument17 pagesAsymptotesPriyanka HaldarNo ratings yet
- Sequences (Part 1)Document69 pagesSequences (Part 1)tejaswini muralidharanNo ratings yet
- 80 ProblemsDocument9 pages80 Problemsjuliet holbNo ratings yet
- 10 HL SummarymathsDocument143 pages10 HL SummarymathsMariana Salazar BaqueroNo ratings yet
- Counting MappingsDocument6 pagesCounting MappingsOsho Arun LoveNo ratings yet
- Aime 2000iDocument2 pagesAime 2000ianantyantoNo ratings yet
- Probability Handout PART3Document9 pagesProbability Handout PART3Scarlet leeNo ratings yet
- Catalan Numbers: Frazer JarvisDocument7 pagesCatalan Numbers: Frazer JarvisGeorge TedderNo ratings yet
- Really Cool Billiards PaperDocument7 pagesReally Cool Billiards PaperNikhil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Shannon-Fano-Elias CodingDocument3 pagesShannon-Fano-Elias CodingKristina RančićNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Catalan Numbers and Recurrence RelationsDocument6 pagesLecture 1: Catalan Numbers and Recurrence RelationsNameet JainNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong Mathematics Olympiad (2022/23) Finals (Group - Event 1)Document9 pagesHong Kong Mathematics Olympiad (2022/23) Finals (Group - Event 1)shenkaheiNo ratings yet
- Finally: Partial FractionsDocument10 pagesFinally: Partial FractionsPrabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- 2010 U of I Mock Putnam Exam SolutionsDocument3 pages2010 U of I Mock Putnam Exam SolutionsGag PafNo ratings yet
- RecurrenceDocument5 pagesRecurrenceDenzel Ivan PalatinoNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Their Limits: The Limit IdeaDocument31 pagesSequences and Their Limits: The Limit IdeaPaulino AdaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 10 Real Analysis IBADocument9 pagesLecture - 10 Real Analysis IBAWisha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Exceedingly Luck-Based Math Olympiad SolutionsDocument6 pagesExceedingly Luck-Based Math Olympiad SolutionsJavad Rahmany FardNo ratings yet
- The Probabilistic Method - ProbabilisticMethodDocument9 pagesThe Probabilistic Method - ProbabilisticMethodNguyễn YsachauNo ratings yet
- CLRS Solution Chapter 33Document15 pagesCLRS Solution Chapter 33Kawsar AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 The Euler Phi FunctionDocument19 pages1 The Euler Phi FunctionRico LeeNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument45 pagesDiscrete MathematicsDilip KdNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong Mathematics Olympiad (2022/23) Finals (Group - Event 1)Document9 pagesHong Kong Mathematics Olympiad (2022/23) Finals (Group - Event 1)shenkaheiNo ratings yet
- Step Cambridge 1999 Paper IDocument5 pagesStep Cambridge 1999 Paper IsmadhyasNo ratings yet
- Elgenfunction Expansions Associated with Second Order Differential EquationsFrom EverandElgenfunction Expansions Associated with Second Order Differential EquationsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Corporate FinanceDocument47 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Corporate FinancePrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Vs ProfitabilityDocument14 pagesLiquidity Vs ProfitabilityPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument6 pagesAccounting CyclePrateek JainNo ratings yet
- MS 109 - Unit IDocument33 pagesMS 109 - Unit IPrateek JainNo ratings yet
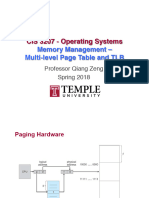
- 17 Multilevel Page Table TLBDocument32 pages17 Multilevel Page Table TLBPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- CUET 2023 PG COMPLETE COURSE With TEST SERIES MCA SCQP09 1681301272969Document1 pageCUET 2023 PG COMPLETE COURSE With TEST SERIES MCA SCQP09 1681301272969Prateek JainNo ratings yet