Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transcribe - AnaLab 2 - 23
Uploaded by
katrizmaervillagantolOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transcribe - AnaLab 2 - 23
Uploaded by
katrizmaervillagantolCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
MOINA TIPS ACCORDING TO SIR (except Opponens Digit ➔ Pisiform
Be specific daw! Minimi)
Rule:
Rotates the shoulder medially - NOT CORRECT _______________________________________
Rotates the scapula medially - CORRECT
In the book lahi ang origin, pero ganahan si sir ani
All the thenar eminence OAF
❖ How many intrinsic muscles are there in the - Come from: flexor retinaculum, tubercle of the
hand? trapezium and scaphoid
- 20 muscles (if mu ans kag Flexor retinaculum only, chaktu ra
daw
❖ How many muscles are innervated by the
median nerve? Hypothenar eminence
- 5 muscles - Abductor digiti mini
Other book: Flexor retinaculum
❖ Meaning, out of the 20 muscles of the hand Other Other book: Pisiform
- 15 are innervated by the ulnar nerve
- According to sir,
REVIEW “Basing on that, therefore the muscles of the
Muscles of the Thenar Eminence thenar eminence and hypothenar eminence – all
(All Innervated by the Median Nerve) of them will come from the flexor retinaculum.
- Opponens Pollicis EXCEPT Opponens Digiti Minimi which comes
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis from the pisiform”
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
- Lumbricals 1 and 2 “So probably sa inyung book,
- (Also innervates 3 ½ of sensorium of palm) Ang abductor pollicis originates in the tubercle of the
trapezium and the scaphoid…highly probable.”
Muscles of the Hypothenar Eminence ___________________________________________
(Primarily innervated by the Ulnar Nerve)
- Abductor Digiti Minimi
- Flexor Digiti Minimi
- Opponens Digiti Minimi Note: This is a SUMMARIZED TABLE I based this sa
discussion ni sir
Please refer to the transcription below to read exact
words gi ingon ni sir
Note: This is a SUMMARIZED TABLE I based this sa
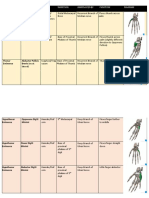
discussion ni sir Muscles Insertion
Please refer to the transcription below to read exact
words gi ingon ni sir All of them insert in the proximal
phalanx either on the
Muscles Origin pollex or the digiti minimi.
All the Thenar ➔ Flexor Opponens attached on the shaft of
eminence retinaculum the pollex or digiti minimi
(OAF) ➔ Tubercle of the
Trapezium and For instance; (Opponens Insertion)
Scaphoid
Opponens digiti minimi metacarpal shaft of the
5th digit
All the Hypothenar ➔ Flexor
eminence retinaculum Opponens pollicis insert the shaft of the 1st
metacarpal.
– –
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 1
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
______________________
For instance; (Majority of the muscle)
All of them insert in the proximal phalanx either on the
Abductor Digiti Minimi anterior surface of the pollex or the digiti minimi. However, your opponens will
base of the proximal attached on the shaft of the pollex or digiti minimi
phalanx of the little finger
So your Opponens digiti minimi will attached on the
Flexor Digiti Minimi anterior surface of the metacarpal shaft of the 5th digit and the Opponens
base of the proximal pollicis will attach or insert the shaft of the 1st
phalanx of the little finger metacarpal.
Abductor Pollicis attached on the Therefore, the Abductor and Flexor digiti minimi will
Brevis anterolateral surface of attached on the proximal phalanx anterior surface of the
the base of the proximal base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
phalanx of the thumb via
sesamoid bone Dri, Abductor pollicis brevis and Flexor pollicis brevis will
attached on the anterolateral surface of the base of the
Flexor Pollicis Brevis attached on the proximal phalanx of the thumb via sesamoid bone
anterolateral surface of
the base of the proximal
phalanx of the thumb via *So naa sya dri* duha gyud na sila. It is the reason
sesamoid bone why your Opponens can flex and your flexor can
also abduct
So all your hypothenar muscles are innervated by the
Lumbricals insert on the extensor Ulnar, thenar muscles are innervated by the Median
expansion via the tendon Nerve
Origin: from the tendon of of the EDC
the FDP This muscle (?) comes from the tendon of the FDP and
“inser– rather will pass on will insert on the extensor expansion via the tendon of
the lateral side because it the EDC
will insert on the extensor
expansion via the tendon So this is your First, second, third, and fourth lumbrical
of the EDC” Notice that all the lumbricals are inser– rather will pass
on the lateral side because it will insert on the extensor
expansion via the tendon of the EDC
Adductor Pollicis Base of proximal phalanx
(Oblique Head) of thumb So meaning ana if I remove this, kani sya is
Origin - the shaft of the already your palmar interossei.
third metacarpal bone,
specifically on the number sa model
anterior surface 72 - volar/ palmar interossei (3rd)
73 - artery
(Transverse Head)
Origin - second and third Oblique head will come on the shaft of the 3rd
metacarpal metacarpal. (Dapat ANTERIOR SURFACE of the 3rd
metacarpal)
— Idk pero lahi ang _____________________
discussion ni sir sa
google ;-;
Q: What nerve innervates the adductor pollicis
A: Ulnar nerve
Hypothenar Muscles - Ulnar nerve
Thenar Muscles - Median nerve Q: What muscle do we used the froment’s test
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 2
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
A: Adductor pollicis
= That is why ang FROMENT’S TEST is
pathognomonic for ulnar nerve innervation
Ulnar nerve
- will pass by the (1) cubital tunnel.
- And then (2) arcade of struthers then (3) cubital
tunnel then ang next niya kay (4) tunnel of
guyon.
Median nerve -
(1) TOS then
(2) ligament of struthers then
(3) tendon of biceps of brachii – if there is trauma, then
ni contract sya…this median nerve will impinge –
(4) then ang pronator teres mu hypertrophy then
(5)sublimis (head coming from the medial epicondyle
that came from the coronoid process) that is why it is
called sublimis arcade – MEDIAN NERVE
Meaning ana, supposedly –
Q: If you have Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome,
will you lose the lateral sensation of the sensorium of
the palm?
A: NO
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 3
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
in px
(Especially, if you
REVIEW asked the patient to
“Dapat everybody should be able to draw the push the upper
brachial plexus by now, If you know how to draw the extremity against the
brachial plexus, you will be able to categorize sets of wall)
nerves” TIPP FROM SIR MAYNARD!
Will have difficulty in
“Katung mga bright dapat mag tutor sa mga ga lisod ABduction because
na classmate WAHAHHA” you need the scapula
to upwardly rotate.
BRACHIAL PLEXUS (This is because you
(proximal to distal insertion) need the glenoid to
(need to be specific!) act as a platform
while the head of the
ROOTS (2) humerus will stand)
- Long Thoracic Nerve
- Dorsal Scapular Nerve If it won't rotate, it will
be difficult because
TRUNKS (2) the head will hit the
- Suprascapular acromion.
- Nerve to subclavius
Dorsal (Superficial If the dorsal scapular
Scapular Back Muscles) nerve is affected, the
LATERAL CORD (3)
Nerve muscles that it
- Lateral pectoral nerve
- Levator innervates will end
- Musculocutaneous nerve
Scapulae
- Lateral cord branch to median
The position of the
- Rhomboid scapula is in lateral
POSTERIOR CORD (5)
Major winging and
- Upper Subscapular
upward winging
- Thoracodorsal
- Rhomboid ( Because this nerve,
- Lower Subscapular
Minor innervates the
- Axillary
muscles that
- Radial
downwardly rotate
the scapula )
MEDIAL CORD (5)
- Medial pectoral nerve
If the trapezius is
- MCNA (brachial)
weak,
- MCNFA (antebrachial)
-then the scapula will
- Ulnar
be in lateral winging
- Medial cord branch to Median
with downward
rotation = DROP
SHOULDER
(Very Important: Enumerate the muscles that this
Note: Once the
nerve innervates)
tendon of the biceps
NERVE MUSCLE THAT Remarks: gets heavy, it will
IT contract. It will
INNERVATES maintain the position
of the head of the
ROOTS humerus against the
Long Thoracic Serratus If SA is weak glenoid. If you have a
Nerve Anterior -medial winging of drop shoulder, it will
scapula is observed also drop. That is
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 4
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
why weakness of the Therefore, you
trapezius will also cannot do sitting
result to subluxation push up
of the head of the
humerus Axillary Deltoid Fracture associated
with: Surgical neck
TRUNKS of the humerus Fx
Lesion:
Suprascapular Supraspinatus You will have ● Difficult
difficulty in ABduction
Infraspinatus ABduction
especially in you can still initiate
Teres Minor shifting(?) abduct but it will not
be enough to bring
NOTE: Because you the upper extremity
need the above your head
supraspinatus for the
first 30 degrees of Radial Nerve Fracture associated
protraction with: Humeral shaft
fx/ spiral groove &
Fracture associated Supracondylar Fx
with: Clavicle Fx
Nerve to Subclavius In the nerve to
Subclavius subclavius, it is okay.
Because you have FRACTURE:
many depressors Axillary nerve - Surgical neck of the humerus Fx
LATERAL CORD Suprascapular nerve - Clavicle Fx
Radial - Humeral shaft Fx ; Spiral groove
Lateral Pectoralis Weakness of the Radial, Ulnar and Median - Supracondylar Fx
Pectoral Nerve Major Pectoralis Major (the
same with medial
pectoral nerve) —----------------------
– Bare with me –
● Difficulty in ULNAR NERVE
Horizontal
ADduction. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) {1}
- It will go out between Anterior and middle
Musculocutaneous Coracobrachialis Problem: scalene and it will enter the Axilla area and then
Elbow Flexion Pectoral area
Biceps Supination (because - Pathway of the neurovascular bundle from the
Brachii the BB is the root of the neck until the pectoral area
strongest supinator
Brachialis of the forearm) - Can be either:
- Vasogenic (involve ang blood supply)
POSTERIOR CORD - Neurogenic (dli involve ang blood
Upper Subscapular Difficulty: supply)
Subscapular ● Internal
Rotation - Symptoms may include:
- Pain (heaviness)
Thoracodorsal Latissimus Difficulty: - Pallor (violet, or white [circulation])
Dorsi ● Cannot - Paresthesia (“Binhod” or “pins and
ADduct needles”)
(Latissimus Dorsi is a
vv strong ADductor) - Common points of compression include;
- Scalene Triangle (Scalenus anticus
and medius)
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 5
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
- Costoclavicular (first rib and clavicle)
- Retroclavicular/ Retropectoral
(underneath/behind the pectoral minor)
For the Common points of compression of TOS
If you…
● Do the Last part of Eden’s Test or
Hyperadduct - retroclavicular/retropectoral
*Eden’s test will test first the costoclavicular and then
the retropectoral
- because the second is to hyperadduct while
taking note if there is pulselessness or So wala pa sya kaabot sa elbow,
reproduction signs and symptoms.
Before the elbow, you have the Arcade of Struthers
Do the Military Brace or first part of Eden’s Test or Arcade of Struthers {2}
Depress - costoclavicular - A aponeurosis or fascia sheath that is a
passageway for your ulnar nerve
Eden’s test will test first the costoclavicular and the
retropectoral
- because the second is to hyperadduct while
taking note if there is pulselessness or
reproduction signs and symptoms.
Do the Adson’s Test or the Neck and look at affected
area- interscalene triangle
So tan.nan (all nerves) can be affected by the TOS
(For examples, axillary has a weakness pero wala
syay surgical intervention so you test it in TOS. So
patient will feel pain and paresthesia in the deltoid So meaning ana, whether arcade struthers or TOS,
area. And if you test it and it worsen, we can conclude both have the same manifestation or same
that the axillary nerve is compressed at the TOS (So it symptoms.
can be either sa TULO na compression points)
Q: How do you differentiate whether it is affected in the
-- So, as physical therapist, we need to localize where TOS or arcade of struthers
is the area is affected because we can do certain - Use the 5 maneuvers to determine TOS. Once
maneuvers or manual therapy to widen the area. Very you duplicate or replicate the sign and
important that we can assess. symptoms, then you are sure that the affectation
is in the TOS
- And if there is no replication of symptoms during
those maneuvers, then you can surmise that the
affectation is in the arcade struthers
5 Manuevers:
- ULTT’s test
- Adson’s
- Wright’s Test
- Eden’s Test
- Roos Test (?)
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Thoracic_Outlet_Syndr
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 6
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
Adductor Pollicis
ome_(TOS)
Lumbricals 3 & 4
ELBOW
Interrossei (Palmar & Dorsal)
Cubital Tunnel [3]
- Depression between the olecranon and medial Sensorium to medial 1 ½ Palmar and Dorsal
epicondyle
- Excess in the cubital angle, whatever the angle (Sensorium - sensation in the skin)
is that is the cubital angle
- (Value: 5 degrees to 15 degrees) If you go Example:
beyond 15 degrees, there is a possibility the At the tunnel of Guyon, if you extend you can bend
ulnar nerve will be stretched or there is arthritis because you have the FDP, You can have claw hands,
or trauma in the area. prevalent in avictation in intrinsic dorsal.
- Called Tardy Ulnar Palsy
Pero if it is in the cubital tunnel, claw hand is not
prevalent
Ulnar ___
(wa dyud ko kasabut) 52:03
Q: What nerve supplies the skin medial ½ dorsum
A: Palmar cutaneous nerve which is a branch of the
ulnar nerve
“Sometimes other nerves are separated that will enter
FCU the tunnel of Guyon pero sometimes the tunnel of Guyon
is not affected, pero most of the time affected dyud daw
FDP (medial 1/2) siya. SO it really depends. You have anatomical
variations.”
After that you are in at the WRIST
—-
Tunnel of Guyon Bare with me pt2
- Hook of the Hamate and Pisiform with the MEDIAN NERVE
palmar carpal ligament.
START WITH TOS AREA (1)
ELBOW
Can be affected in the supracondylar ridge however it
is not impingement, it is trauma
Prior to elbow, (rare case)
We have the ligament of struthers (2)
- Same manifestation with TOS
Same below the elbow or distal to elbow, Bicipital
aponeurosis or lacertus fibrosus syndrome (3)
Hypothenar “OAF” The difference:
- Opponens Digiti Minimi All three of them have the same manifestations
- Abductor Digiti Minimi meaning weakness of all the muscle that the nerve will
- Flexor Digiti Minimi innervate
Palmaris Brevis
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 7
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
➢ Lateral ½ and
Question: How will we know whether the affectation is ➢ Pronator Quadratus
in the TOS, Bicipital aponeurosis, or ligament of
struthers Now prior to that,
You have a nerve, continuation to your median nerve but
Answer: inclination of the forearm area distal to the this nerve will innervate… INNERVATION
elbow or trauma – there is a possibility the bicipital ➢ Muscles of your thenar eminences “OAF”,
aponeurosis will contract. The bicipital aponeurosis ➢ lumbricals 1 and 2, and
approaches the ulnar side. Together with the pronator ➢ sensorium at lateral 3 and ½ of palm.
teres, “force padulong” This nerve can be compressed at the the carpal tunnel
Expansion of the tendon of the BB, so it will
approach the ulnar side. If the area has a wound or Note: If you have an Anterior Interosseous Nerve
whatever, as long as it thickens or it contracts, it will Syndrome, you have this three muscles only
impinge or compress the structures below it.
Therefore, the median nerve is affected. So all the
muscles of the median nerve will also be affected.
YET, the difference is that there is Trauma or
inflammation Q: Affected ba ang muscles of the thenar eminence if
you have Anterior Interroseus Nerve?
If there is no trauma or inflammation, there is a A: No
possibility it is TOS. Utilize the maneuvers.
Q: Now if you have carpal tunnel syndrome, are the
If there is no conslessness (idkkk) , no replication of three muscles affected?
signs and symptoms, then it is possible ligament of A: No
struthers
Q: If you have a carpal tunnel syndrome, can you still
If there is conslessness (iddkkk) or replication of do okay sign
signs and symptoms upon implementing the A: Yes, because intact ang muscles, legal muscle
maneuvers. Therefore, it is in the TOS anterior FPL and FDP
For example, retropectoral = stretch the pectoralis Q: If you have pronator teres syndrome, can I do okay
minor so the it can decompress the area sign
(WE NEED TO HAVE A PRECISE DIAGNOSIS) A: No
Q: How will I determine if pronator teres syndrome or
flexor digitorum syndrome? How do you test
A: Pronate forearm and supinate. Makapronate sya
Pronator Teres
because naa pa syay pronator teres.
Pronator Teres syndrome
- If the pronator teres will hypertrophy, then it
can compress the median nerve beneath it Determine Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, (action of
(only the pronator teres is sparred) Flexor digitorum superficialis) flexion of the proximal
interphalangeal joint (so naay gibuhat si sir, I don't
Flexor Carpi Radialis remember what)
Palmaris Longus RADIAL NERVE
(Bare with me pt3)
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Take note: we have Sublimis Arcade or Flexor TOS
Digitorum syndrome
Axilla (before the elbow)
So what will happen here is that, if it is impinge you will
have “Anterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome” Axillary branches. Axillary crutch improper use.
→ because you have 3 nerves that are affected and the If walay radial nerve, then the next is axillary nerve.
➢ first one will be the Flexor Pollicis Longus,
➢ Flexor Digitorum Profundus,
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 8
HUMAN ANATOMY Date discussed: 2 / 23 / 24
LESSON # | CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW
PT13 - C | Maynard Aparicio
All the muscles that the radial nerve will innervate will be
affected. Muscles include:
➢ Long head of biceps
➢ Triceps medial head AFTER INTRAMS UE2
➢ Triceps lateral head Questions that will draw higher order thinking skills
➢ Triceps medial head Bones and muscles (para easier)
➢ Anconeus
➢ Brachialis
Spiral groove - Honeymoon or saturday night Q: If you have Posterior Interosseous Nerve, will you
If you have spiral groove, the triceps long head is lose the sensation of the lateral 3 ½
basically impaired. You can still extend but there is little A: No
weakness
Q: If you have posterior Interosseous Nerve
Brachioradialis Syndrome, can I still do this *IDK the action*
A: Because the muscle need here is the Extensor
ECR Pollicis Longus
ELBOW
Prior to the supinator, Pathognomonic of which Lesion
There is another Superficial radial nerve can be
impinch in the wrist *** Thumbs up sign (can also be wrist drop) - PIN
Supinator (wrist drop - ECU, EDC, ECRB are all affected. Wrist
- You have arcade of FROHSE also known as drop can be 0 - 3. For example, 0 ang strength for
Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome extension, pero naa tay strength sa ulnar deviation
compared to your radial because you still have your
ECRB FCU. On the other side, you still have your ECRL and
FCR; hence, the radial deviation is much stronger
EDC compared to your ulnar deviation in PIN syndrome )
EDM Okay sign and Khion ___ (abnormal okay sign) - AIN
ECU Froment’s test - Ulnar Nerve
- Test for ulnar nerve. If there is a lesion of the
APL ulnar nerve, you can see the froment’s sign.
The froments sign is the flexion of the DIP of
EPB the thumb. You can flex the thumb because it
is the function of the flexor pollicis longus
EPL which is innervated by the median nerve
-
EIP Phalen’s test or Prayer’s test (or Reverse) - Impinge
Median nerve as it passes the carpal tunnel
Wrist drop - Radial nerve
*** → can impinge at the wrist.
If it is impinge at the wrist, you have your “cheralgia
prothetica or wartenberg syndrome
Chestergia prothetica or wartenberg syndrome
- You noticed walay muscle, but you have your
sensorium at dorsum at lateral 3 ½
- If you have, you have no motor deficits (no
weakness). Loss of sensation on the lateral 3
½ of the dorsum of the hand
CLINICAL NOTES + REVIEW | Page 9
You might also like
- Muscle Tables of The Upper Extremities From Netter'sDocument4 pagesMuscle Tables of The Upper Extremities From Netter'sJemarey de RamaNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology of Shoulder ComplexDocument7 pagesKinesiology of Shoulder ComplexAlya Putri KhairaniNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive InsufficiencyDocument25 pagesActive and Passive Insufficiencydina sharafNo ratings yet
- Table of Cranial NervesDocument7 pagesTable of Cranial NervesCoy EnNo ratings yet
- Nasa Khan MRCS A Notes 2018 PDFDocument834 pagesNasa Khan MRCS A Notes 2018 PDFWaqas Haleem100% (5)
- Trigger Points Release Through Scalp AcupunctureDocument112 pagesTrigger Points Release Through Scalp AcupunctureTri Dewi Larasati80% (5)
- 1-SPINE AND LIMBS Print PDFDocument52 pages1-SPINE AND LIMBS Print PDFsaddam hussainNo ratings yet
- Whiplash Certification CDocument229 pagesWhiplash Certification CPedro M. BorgesNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneDocument2 pagesMnemonic For Forearm Muscles and BoneLaura Tapia89% (28)
- Palm MusclesDocument45 pagesPalm MusclesBandarupalli Akash Chowdary100% (1)
- Human Sectional Anatomy Atlas of Body Sections, CT and MRI Images 4ed-127-201Document75 pagesHuman Sectional Anatomy Atlas of Body Sections, CT and MRI Images 4ed-127-201Elei GiNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Mnemonics 2Document8 pagesUpper Limb Mnemonics 2KaiyoorNo ratings yet
- Cervical SpineDocument66 pagesCervical SpineHotnog Madalin100% (1)
- Muscles of Back LectureffDocument28 pagesMuscles of Back LectureffNko NikoNo ratings yet
- 3 ReviewerDocument46 pages3 ReviewerSHINE JASMIN LAXAMANA100% (1)
- Shoulder GirdleDocument47 pagesShoulder GirdleSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesDocument8 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Noteskamie155No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Summary PDFDocument9 pagesCranial Nerves Summary PDFMudassar SattarNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Pain Kiiko Matsumoto Japanese Style PDFDocument4 pagesUpper Extremity Pain Kiiko Matsumoto Japanese Style PDFtito zambrano100% (2)
- Adhesive Capsulitis Full PDFDocument45 pagesAdhesive Capsulitis Full PDFjoanna gurtizaNo ratings yet
- Lab Ana228 - 63Document22 pagesLab Ana228 - 63pachara.p65No ratings yet
- Identify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaDocument7 pagesIdentify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaHARSHDESAI56929640No ratings yet
- Hand Muscles 3Document1 pageHand Muscles 3Shatha AlgahtaniNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionDocument11 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy: Lesson 3: The Structure of Mastication: The Jaws and DentitionMarian AlecsNo ratings yet
- Palm MusclesDocument41 pagesPalm MusclesRealmeNo ratings yet
- Infratemporalfossa PpsDocument7 pagesInfratemporalfossa PpsНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - The Wrist and Hand Regions - Jones - Full Slides PDFDocument77 pagesLecture 9 - The Wrist and Hand Regions - Jones - Full Slides PDFAustin KellyNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Muscles of Hand and Their Nerve SupplyDocument7 pagesIntrinsic Muscles of Hand and Their Nerve SupplyAlNo ratings yet
- Emailing SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES DR JAVERIA PDFDocument28 pagesEmailing SUPERFICIAL REFLEXES DR JAVERIA PDFNoor ZehraNo ratings yet
- Handpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument34 pagesHandpresentation 141020140007 Conversion Gate02 PDFMichael SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Guyon Canal - PhysiopediaDocument1 pageGuyon Canal - Physiopediaashfaqahammadm1mplNo ratings yet
- La Faringe. SNM Del Nervio Glosofaríngeo. Plexo FaríngeoDocument24 pagesLa Faringe. SNM Del Nervio Glosofaríngeo. Plexo FaríngeocristinaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper LimbDocument11 pagesMuscles of The Upper LimbSuman DahalNo ratings yet
- UE and LE AnaDocument123 pagesUE and LE AnaPatrick JohnNo ratings yet
- Infra Temporal FossaDocument7 pagesInfra Temporal FossaНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - UPPER LIMB - 3 Short Muscles of The HandDocument1 pageAnatomy - UPPER LIMB - 3 Short Muscles of The HandAyesha ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Median Nerve Anatomy PDFDocument2 pagesMedian Nerve Anatomy PDFIndra RanteNo ratings yet
- Hand MusclesDocument5 pagesHand MusclesHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 6Document12 pagesAssignment No. 6Regina GambayanNo ratings yet
- 13-Hand & WristDocument10 pages13-Hand & Wristzain juttNo ratings yet
- M.15 The Hand Part 1 by DR LaygoDocument9 pagesM.15 The Hand Part 1 by DR LaygoGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- GIT PhysiologyDocument27 pagesGIT PhysiologyMohamed AdnanNo ratings yet
- Hand and Wrist: Key InformationDocument4 pagesHand and Wrist: Key InformationAmr AbdelghaffarNo ratings yet
- 09 - Upper Limb 1 EditedDocument52 pages09 - Upper Limb 1 Editedshabnam sajidaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Workbook - Intrinsic Hand MusclesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Workbook - Intrinsic Hand MusclesMukt PatelNo ratings yet
- 7 - HandDocument30 pages7 - Handعاصم مروانNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDFDocument12 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDFDejan MilenkovicNo ratings yet
- LAB Forearm and HandDocument15 pagesLAB Forearm and HandnanaNo ratings yet
- Blepharoptosis: Alan A. McnabDocument11 pagesBlepharoptosis: Alan A. Mcnabโสภาพรรณวดี รวีวารNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesDocument10 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Musculosk UL5 Muscles 3Document94 pagesMusculosk UL5 Muscles 3Zaid HamdanNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Essay - Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesNeuroscience Essay - Cranial NervesAkshaya RajangamNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Plastic SurgeryDocument12 pagesEssentials of Plastic SurgeryjoryadelmNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Sonoanatomy - Giải phẫu siêu âm chi dưới (Khoá gây tê vùng dưới hướng dẫn siêu âm ĐHYHN)Document74 pagesLower Limb Sonoanatomy - Giải phẫu siêu âm chi dưới (Khoá gây tê vùng dưới hướng dẫn siêu âm ĐHYHN)Rùa’s Anesthesia HanoiNo ratings yet
- Foot Muscles ChartsDocument6 pagesFoot Muscles ChartsddNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure and Function Basic Structure and Function of The of The Wrist and Hand Wrist and HandDocument54 pagesBasic Structure and Function Basic Structure and Function of The of The Wrist and Hand Wrist and HandJoseNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves (Part III) LectureDocument5 pagesCranial Nerves (Part III) Lectureteam.tell.0qNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Urinary, Foramina, Respiratory: Study Online atDocument2 pagesAnatomy - Urinary, Foramina, Respiratory: Study Online atSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- AP 13 Spinal Cord PNSDocument8 pagesAP 13 Spinal Cord PNSTam BeloNo ratings yet
- Anterior Nerve Syndrome - Morton SpinnerDocument11 pagesAnterior Nerve Syndrome - Morton SpinnerJunji Miller FukuyamaNo ratings yet
- Radial and Ulnar NervesDocument10 pagesRadial and Ulnar NervesZoi PapadatouNo ratings yet
- The Hand Complex NEWDocument11 pagesThe Hand Complex NEWVIRESH VNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModuleDocument38 pagesThe Respiratory System: A Fixed Learning ModulerezaNo ratings yet
- 3 TrigeminalwordDocument26 pages3 TrigeminalwordrajaniNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument2 pagesMnemonicsnogenaogaNo ratings yet
- Interphalangeal Joint (Hand Complex)Document6 pagesInterphalangeal Joint (Hand Complex)VIRESH VNo ratings yet
- 3-2 MP Dislocation Fingers - DIU 2022Document35 pages3-2 MP Dislocation Fingers - DIU 2022Professeur Christian DumontierNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: Pre-MedicalDocument19 pagesSensory Organs: Pre-MedicalvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Muscles, Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesMuscles, Cheat SheetIvan SkoricNo ratings yet
- Kin 4KK3 - L8 Shoulder FoundationsDocument6 pagesKin 4KK3 - L8 Shoulder FoundationsYurNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyDocument7 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Serratus AnteriorDocument33 pagesSerratus AnteriorJuliana BarbosaNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder GirdleDocument6 pagesThe Shoulder GirdlekanevwNo ratings yet
- MMT Scapular Adduction and Downward Rotation by DR M UsamaDocument25 pagesMMT Scapular Adduction and Downward Rotation by DR M UsamaUsama SohailNo ratings yet
- Muscle OIADocument3 pagesMuscle OIAVanessa TumangNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Back 2Document18 pagesMuscles of The Back 2mohammed abidieNo ratings yet
- Medial Vs Lateral Winging of The ScapulaDocument11 pagesMedial Vs Lateral Winging of The ScapulaanjelikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Review of Extreme TiesDocument65 pagesAnatomy Review of Extreme Tiesskihard0404749No ratings yet
- Winged Scapula Caused by Dorsal Scapular.21Document4 pagesWinged Scapula Caused by Dorsal Scapular.21emilio9fernandez9gatNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Scapula in The Rehabilitation of Shoulder InjuriesDocument9 pagesThe Role of The Scapula in The Rehabilitation of Shoulder InjuriesRahees KhanNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder GirdleDocument26 pagesThe Shoulder GirdleVeena VishwanathNo ratings yet
- InserviceDocument27 pagesInserviceapi-216088427No ratings yet
- Superficial Muscles of The BackDocument3 pagesSuperficial Muscles of The BackSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Scapular Region: Figure 17.1 Scapular Muscles (Posterior View)Document12 pagesScapular Region: Figure 17.1 Scapular Muscles (Posterior View)Anjali TanwarNo ratings yet
- Cat Muscles 2Document3 pagesCat Muscles 2nathan3602No ratings yet
- Rehab Grand Rounds: Comprehensive Approach To The Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in The Overhead Throwing AthleteDocument8 pagesRehab Grand Rounds: Comprehensive Approach To The Management of Scapular Dyskinesia in The Overhead Throwing AthletekotraeNo ratings yet