Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 May/June 2019
Uploaded by
fredmelly663Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 May/June 2019
Uploaded by
fredmelly663Copyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge Assessment International Education
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
BIOLOGY 0610/62
Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2019
MARK SCHEME
Maximum Mark: 40
Published
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of the
examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the
details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking began, which would have
considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for
Teachers.
Cambridge International will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge International is publishing the mark schemes for the May/June 2019 series for most
Cambridge IGCSE™, Cambridge International A and AS Level and Cambridge Pre-U components, and
some Cambridge O Level components.
This syllabus is regulated for use in England, Wales and Northern Ireland as a Cambridge International Level 1/Level 2 Certificate.
This document consists of 7 printed pages.
© UCLES 2019 [Turn over
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Generic Marking Principles
These general marking principles must be applied by all examiners when marking candidate answers. They should be applied alongside the
specific content of the mark scheme or generic level descriptors for a question. Each question paper and mark scheme will also comply with these
marking principles.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 1:
Marks must be awarded in line with:
• the specific content of the mark scheme or the generic level descriptors for the question
• the specific skills defined in the mark scheme or in the generic level descriptors for the question
• the standard of response required by a candidate as exemplified by the standardisation scripts.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 2:
Marks awarded are always whole marks (not half marks, or other fractions).
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 3:
Marks must be awarded positively:
• marks are awarded for correct/valid answers, as defined in the mark scheme. However, credit is given for valid answers which go beyond the
scope of the syllabus and mark scheme, referring to your Team Leader as appropriate
• marks are awarded when candidates clearly demonstrate what they know and can do
• marks are not deducted for errors
• marks are not deducted for omissions
• answers should only be judged on the quality of spelling, punctuation and grammar when these features are specifically assessed by the
question as indicated by the mark scheme. The meaning, however, should be unambiguous.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 4:
Rules must be applied consistently e.g. in situations where candidates have not followed instructions or in the application of generic level
descriptors.
© UCLES 2019 Page 2 of 7
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 5:
Marks should be awarded using the full range of marks defined in the mark scheme for the question (however; the use of the full mark range may
be limited according to the quality of the candidate responses seen).
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 6:
Marks awarded are based solely on the requirements as defined in the mark scheme. Marks should not be awarded with grade thresholds or
grade descriptors in mind.
© UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 7
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Guidance
1(a)(i) table drawn with minimum two columns and a header line ; 3
appropriate column headings with units in heading only ;
both times records in seconds (warm) 233 and (cool) 565 ; i.e. test-tube / temperature with warm and cool in the data cell
OR temperature / °C, and time / s
1(a)(ii) at high(er) temperatures the methylene blue became, 1
colourless / disappeared, more quickly / AW ; ora
1(a)(iii) 1
temperature at temperature at
beaker
start / °C end / °C
warm water 45 35
cool water 20 15
;
1(a)(iv) temperature ; 1
1(a)(v) volume / amount / type of yeast (suspension) ; 2
number of drops / concentration / amount / type, of methylene
blue / indicator / AW ;
idea of equilibration time in water-bath / beaker ;
depth / amount / type, of oil ;
© UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 7
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Guidance
1(b)(i) error step 6 2
subjective / difficult to judge when the colour had
disappeared / qualitative ;
improvement
compare to, a test-tube containing yeast with no methylene
blue / test-tube that had already changed colour / use a
colorimeter / colour standard ;
OR
error step 6
idea that both tubes are observed at the same time ;
improvement
idea that they should conduct each experiment at different
times ;
1(b)(ii) error from Table 1.1 2
temperature (of the water-bath) not controlled / temperature
changes / AW ;
improvement
(thermostatically) controlled water-bath / insulation of the
beaker ;
1(c) hydrogencarbonate / bicarbonate ; 2
yellow / orange ;
OR
limewater ;
goes cloudy / milky / white ;
© UCLES 2019 Page 5 of 7
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Guidance
1(d) independent variable: 6 A suitable alternative methods
at least two different concentrations of ethanol ;
dependent variable:
measuring the time taken for methylene blue to decolourise ;
constant variables:
two from ;;
• same temperature
• same pH
• same volume of ethanol (solution)
• same volume / amount / concentration of sugar
one from ;
• same volume / amount / concentration / type, of yeast
• same volume / amount / concentration, of methylene
blue / indicator
• same volume / depth of oil
methodology
idea of leaving to equilibrate at set temperature ;
use of a water-bath / insulation to maintain one temperature ;
detail of a comparison / control e.g. test with no
ethanol / yeast, present ;
two or more repeats / three or more trials ;
safety
relevant safety e.g. gloves / goggles / no flames ;
© UCLES 2019 Page 6 of 7
0610/62 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks Guidance
2(a)(i) outline – clear continuous line around stigmatic disc ; 4
size – larger than 70 mm ;
details:
nine stigmatic rays shown as double lines ;
circle approximately one third of the way out from the
centre of the stigmatic disc ;
2(a)(ii) length of line PQ 26 mm / 2.6 cm ±1 mm ; 3
16 mm / 2 cm ;;
2(b)(i) 60(%) ;; 2
2(b)(ii) A(xes) – labelled ; pH and percentage germination 4
S(cale) – suitable scale and plots occupy at least half the grid
in both directions ;
P(lot) – correct plots ± half a small square ;
L(ine) – suitable line ;
2(b)(iii) percentage (germination) increases and then decreases ; 2
peaks at pH 6 / highest percentage of germination is at A optimum at pH 6
pH 6 ;
2(b)(iv) (test at pH values at) smaller intervals ; 2
between pH 5 and 7 / 5–6 / 6–7 ;
2(c) grind up seeds / AW ; 3
add Benedict’s (reagent/solution) ;
heat ;
red / orange / yellow / green, if reducing sugars present ;
© UCLES 2019 Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Aws C3.4 (1999)Document16 pagesAws C3.4 (1999)luisNo ratings yet
- Melane Zintle Prac 1Document3 pagesMelane Zintle Prac 1Zintle MelaneNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Industrial Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesHandbook of Industrial Water TreatmentArunish Mangla0% (2)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 May/June 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 May/June 2019Ahmed GamerNo ratings yet
- 0610 s18 Ms 62 PDFDocument9 pages0610 s18 Ms 62 PDFTesterNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 October/November 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 October/November 2019Okd TiabNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2019Hana GABERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 May/June 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 May/June 2019fredmelly663No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/52 March 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/52 March 2019TIGER IS LITNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/31 May/June 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/31 May/June 2019Mohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 May/June 2019srividhyaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/41 May/June 2019Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/41 May/June 2019srividhyaNo ratings yet
- Published Answer Marks Guidance 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 7Document4 pagesPublished Answer Marks Guidance 3: © UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 7Mariam EkramyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/62 May/June 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/62 May/June 2019Mohammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/41 May/June 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/41 May/June 2019Kristina FilipovićNo ratings yet
- November 2019 (v3) MS - Paper 4 CIE Biology IGCSEDocument11 pagesNovember 2019 (v3) MS - Paper 4 CIE Biology IGCSEanasmalikelkhatebNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/33 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/33 May/June 2019Benedict EdwardNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2019Tiyané ChigavaziraNo ratings yet
- 0610 s18 Ms 63 PDFDocument8 pages0610 s18 Ms 63 PDFTesterNo ratings yet
- 0610 s18 Ms 61 PDFDocument9 pages0610 s18 Ms 61 PDFTesterNo ratings yet
- November 2018 (v3) MS - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDocument10 pagesNovember 2018 (v3) MS - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEInfinite BlazeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 March 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/62 March 2019Hendry RaoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2018Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/61 October/November 2018Ziyad NabilNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 May/June 2019Alex ScienceNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 October/November 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 October/November 2019Mohamed MuhajireenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 8 Printed PagesDocument8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 8 Printed PagesPrishaaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 October/November 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/42 October/November 2019k12engtutNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 March 2018K KNo ratings yet
- 201combined Science Paper 6 AnswerDocument9 pages201combined Science Paper 6 AnswerfreddyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Biology 0610/63 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Biology 0610/63 May/June 2020bali yunNo ratings yet
- 0610 s18 Ms 42 PDFDocument11 pages0610 s18 Ms 42 PDFTheNether ManiacNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2018Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/31 May/June 2018Last MadanhireNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/43 October/November 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/43 October/November 2019k12engtutNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/53 October/November 2019Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/53 October/November 2019Rainy DaysNo ratings yet
- 0610 s18 Ms 31 PDFDocument13 pages0610 s18 Ms 31 PDFTesterNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/63 October/November 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/63 October/November 2019Samuel de BaizeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 March 2018Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 March 2018Imran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 May/June 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 May/June 2019SimonaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 May/June 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 May/June 2019Nyasha MtemeriNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/61 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/61 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/41 May/June 2020Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/41 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/51 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/51 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Physics 0625/63 May/June 2019Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Physics 0625/63 May/June 2019Hayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™ (9-1) : Co-Ordinated Sciences (9-1) 0973/62 May/June 2022Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™ (9-1) : Co-Ordinated Sciences (9-1) 0973/62 May/June 2022t.dyakivNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/62 March 2018Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/62 March 2018equakeroatsNo ratings yet
- Number 2 (0654 - s20 - Ms - 43)Document13 pagesNumber 2 (0654 - s20 - Ms - 43)Muhammad Luthfansyah PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Physical Science 0652/51 October/November 2020Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Physical Science 0652/51 October/November 2020Inaarah KavadiasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2018abilasha rajenNo ratings yet
- CambridgetestDAnswers PDFDocument12 pagesCambridgetestDAnswers PDFBeatriz ColioNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/43 October/November 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/43 October/November 2019Dada LimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 October/November 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/22 October/November 2019Faariya AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/42 October/November 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/42 October/November 2019Rudra KumarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/32 May/June 2020Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/32 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 0654 - s20 - Ms - 41 Mark SchemeDocument14 pages0654 - s20 - Ms - 41 Mark Schemek12engtutNo ratings yet
- 0625 w19 Ms 63Document7 pages0625 w19 Ms 63Harshi kalaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/63 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/63 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 0620 m18 Ms 62Document6 pages0620 m18 Ms 62Richie TangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/53 May/June 2018Document6 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 0620/53 May/June 2018Aaa IiiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/41 October/November 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Combined Science 0653/41 October/November 2019keyzainbNo ratings yet
- downloadBiologyGCSEPast PapersCIEPaper 4november20201820 (v1) 20MS20 20paper2042Document11 pagesdownloadBiologyGCSEPast PapersCIEPaper 4november20201820 (v1) 20MS20 20paper2042Joyce AmirNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/31 October/November 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/31 October/November 2019081166No ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYFrom EverandLABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Management and Technologies of Water, Wastewater, Waste and Cir-cular Economy: WWW&CEFrom EverandManagement and Technologies of Water, Wastewater, Waste and Cir-cular Economy: WWW&CENo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationfredmelly663No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/33 October/November 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/33 October/November 2019fredmelly663No ratings yet
- About Support Legal Social: SearchDocument1 pageAbout Support Legal Social: Searchfredmelly663No ratings yet
- 04 0862 02 6RP AFP tcm143-686153Document22 pages04 0862 02 6RP AFP tcm143-686153fredmelly663No ratings yet
- PAST YEAR PAPERS - Exam-Mate.Document3 pagesPAST YEAR PAPERS - Exam-Mate.fredmelly663No ratings yet
- 662459-2024-2026-Syllabus (Egypt Centres ONLY)Document24 pages662459-2024-2026-Syllabus (Egypt Centres ONLY)fredmelly663No ratings yet
- A Quantitative Starch-Iodine Method For MeasuringDocument4 pagesA Quantitative Starch-Iodine Method For MeasuringMohammad AadilNo ratings yet
- Ni in SteelDocument3 pagesNi in Steelpayal_joshi_14No ratings yet
- DTW 1239Document16 pagesDTW 1239GANESH GNo ratings yet
- Igcse Past PaperDocument12 pagesIgcse Past PaperSalwa A.haiNo ratings yet
- Phase Change and Phase DiagramDocument65 pagesPhase Change and Phase Diagramryanyann2122No ratings yet
- Model Paper-7Document13 pagesModel Paper-7Anonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Address: Brgy. Gredu, Panabo City Telephone No.: (084) 628-4830Document2 pagesAddress: Brgy. Gredu, Panabo City Telephone No.: (084) 628-4830Mickoy D. EbagagNo ratings yet
- ChemistryReview27 2 PosterDocument1 pageChemistryReview27 2 PosterShruthiNo ratings yet
- Zirconium Alloys Rev1 1Document19 pagesZirconium Alloys Rev1 1Christian AganoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3. SEMEN SEMINAL STAIN and OTHER STAINSDocument5 pagesTopic 3. SEMEN SEMINAL STAIN and OTHER STAINSJack Miller DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan Science 9Document24 pagesLearning Plan Science 9joyNo ratings yet
- Astm E716-94 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm E716-94 PDFRaúl100% (1)
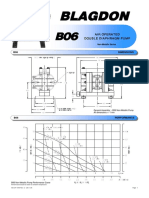
- BLAGDON B06 - Non-Metallic - DatasheetDocument2 pagesBLAGDON B06 - Non-Metallic - DatasheetJose Miguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergerticsDocument24 pagesChemical EnergerticsAnotidaishe ChakanetsaNo ratings yet
- BLA FTP I DS 00 001 Rev.1ADocument14 pagesBLA FTP I DS 00 001 Rev.1Asugeng wahyudiNo ratings yet
- L33A - Power CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesL33A - Power CharacteristicsArshpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Unitherm Oil 303s Pds (E) - Universal Oils Co., Ltd.Document2 pagesUnitherm Oil 303s Pds (E) - Universal Oils Co., Ltd.Nguyễn Hữu Thiện NhtNo ratings yet
- Caie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1Document10 pagesCaie A2 Biology 9700 Practical v1ARMANI ROYNo ratings yet
- Glycated Hemoglobin (Hba1C) : Prepared By: Basalingappa.B.G. 2 M.Sc. Medical Biochemistry JSS Medical College MysoreDocument46 pagesGlycated Hemoglobin (Hba1C) : Prepared By: Basalingappa.B.G. 2 M.Sc. Medical Biochemistry JSS Medical College MysoreYuniati ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Series DS-1 Dry-Type Sprinklers 5.6K Pendent, Upright, and Horizontal Sidewall Quick Response, Standard Coverage General DescriptionDocument10 pagesSeries DS-1 Dry-Type Sprinklers 5.6K Pendent, Upright, and Horizontal Sidewall Quick Response, Standard Coverage General DescriptionRoobertho AthhondoNo ratings yet
- F4 PAT AmaliDocument3 pagesF4 PAT AmaliShi Kai TengNo ratings yet
- Introductory Analytical Chemistry CurriculumDocument4 pagesIntroductory Analytical Chemistry CurriculumAcidri AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Jitendra Hirwani: Problem Solving Techniques of Physical Chemistry For NeetDocument16 pagesJitendra Hirwani: Problem Solving Techniques of Physical Chemistry For NeetabhishekNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica Aplique Luz F02724EN-00Document2 pagesFicha Técnica Aplique Luz F02724EN-00fxavierNo ratings yet
- Generalized Correlations For Gases (Lee-Kesler)Document10 pagesGeneralized Correlations For Gases (Lee-Kesler)amir loloNo ratings yet
- Zmoq : Narjmwu H$Mos H$Mo Cîma NWPÑVH$M Ho$ - Wi N Ð Na Adí' (Bio & Amob ZDocument19 pagesZmoq : Narjmwu H$Mos H$Mo Cîma NWPÑVH$M Ho$ - Wi N Ð Na Adí' (Bio & Amob ZRavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Edexcel RevisionDocument3 pagesChemistry Edexcel RevisionchogoNo ratings yet