Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Denu.2024.51.1.66a.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.66a
Denu.2024.51.1.66a.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.66a
Uploaded by
Fatima AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Denu.2024.51.1.66a.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.66a
Denu.2024.51.1.66a.pdf Filename UTF-8''denu.2024.51.1.66a
Uploaded by
Fatima AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Letters
Letters to the Editor
Troublesome tauri
I thought I would share an interesting case of
troublesome mandibular tauri.
This 54-year-old patient attended the oral
and maxillofacial outpatients department
complaining of bony growths in his lower
jaw affecting his speech and causing food
impaction. These growths had been present as
long as he could remember, but recently had
increased in size. The patient was otherwise fit
and well.
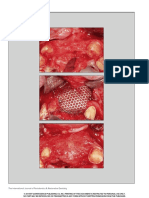
Examination revealed extensive bilateral
lingual tauri of the mandible, almost meeting
in the midline (Figure 1). The bony growths
were raising his tongue, affecting his speech,
and acting as a reservoir for food impaction.
Treatment options of conservative
measures versus surgical management were Figure 1. Pre-operative picture of the tauri in situ.
offered, and given the ongoing symptoms, the
patient was keen for removal and consented
appropriately for damage to the lingual nerve
and submandibular ducts.
The patient underwent bilateral tauri
removal under local anaesthetic by the author.
Mucosal incisions were made over the bony
growths to expose, a groove was made along
the length of the exostosis using a cooled
surgical burr and subsequent controlled
fracture of the growth from the lingual
aspect of the mandible was carried out using
Coupland’s elevators. Underlying sharp edges
of lingual plate were then smoothed with a
cooled surgical burr, and the mucosal flap was
closed using resorbable sutures. The procedure
was uneventful, and the patient returned home
with antiseptic mouthwash and analgesia.
The patient was reviewed in clinic 4
months later, and despite a turbulent post- Figure 2. Post-operative outcome.
operative period with significant pain and
temporary paraesthesia to the left side of
the tongue, was delighted with the result.
His speech was audibly improved, and he Matt Smith top-quality scientific evidence with clinical
no longer experienced food impaction. Specialty Doctor, Oral and Maxillofacial expertise and patient values to enhance
Examination revealed the area to have healed Department, Mid-Cheshire NHS Hospitals clinical decision-making.1 Given that medical
well with no damage to the underlying Foundation Trust knowledge is being constantly updated,
submandibular ducts and full sensation to his C Shaw streamlining the search process is imperative.
tongue (Figure 2). RGN, Mid-Cheshire NHS Hospitals Finding high-quality clinical care evidence is
Not only has this procedure made vast Foundation Trust a demanding task. In recent years, artificial
improvements to the patient’s current quality intelligence (AI) has shown great potential in
of life, the author also acknowledges that enhancing EBD by uncovering patterns and
The role of AI in advancing connections in medical data, big data analysis
future dental prosthetic management has also
been made more straightforward. Although evidence-based dentistry and evidence synthesis, and aiding clinical
the majority of mandibular tauri are managed Evidence-based dentistry (EBD) is widely decision support.2–4
conservatively, in the right circumstances regarded as the gold standard in global AI can automate time-consuming tasks
surgical management can be of great benefit oral healthcare owing to the increasing such as literature searching and screening.
for patients. complexity of clinical dentistry. EBD integrates Machine learning approaches, for instance, can
66 DentalUpdate January 2024
pg66-67 Letters.indd 66 11/01/2024 12:20
Letters
enhance the efficiency and accuracy of high- trials. Artif Intell Med 2021; 118: 102098. https:// damaged dental tissues like dentin, pulp,
quality clinical evidence retrieval in biomedical doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102098. and periodontal tissues. MSCs produced
literature, allowing rapid evidence synthesis.5 7. Huang J, Tan M. The role of ChatGPT in scientific from the dental pulp and periodontal
Additionally, natural language models can communication: writing better scientific review ligament have been demonstrated to
extract key data from texts, automating articles. Am J Cancer Res 2023; 13: 1148–1154. have the ability to differentiate into
evidence collection and providing quick access Mojtaba Mehrabanian various dental cell types and contribute to
to up-to-date information, thereby enhancing Alumnus of University of Debrecen, tissue regeneration.
clinical decision-making and improving patient Hungary Implantation of tooth: Stem cell-
outcomes.6 Moreover, AI tools like ChatGPT Aisan Eskandari-Yaghbastlo based techniques have the potential
can improve scientific writing by facilitating Alumnus of Gulf Medical University, UAE to significantly improve the success
and accelerating the creation of high-quality rate of tooth implantation procedures.
literature reviews and research articles. They Stem cell therapy in Regenerating supporting tissues around
assist in data management, error identification, dental implants, such as the periodontal
and offer diverse perspectives. It is essential, dentistry: the future for oral ligament and alveolar bone, can be
however, to review and edit generated text to tissue regeneration achieved using stem cells, leading to
avoid issues, such as plagiarism.7 In the last period in medicine, including the enhanced implant stability and longevity.
Yet, AI has limitations affecting its field of dentistry, extensive research has been In addition, with the application of tissue
performance and accuracy. These include conducted on the regenerative ability of engineering, it may be possible to completely
training data quality issues, the model’s lack stem cells. Currently, therapies for oral health regenerate teeth in the near future, replacing
of common sense or intuition, vulnerability diseases can permit certain clinical parameters the placement of traditional dental implants.
to adversarial attacks, and accountability during the diagnosis and development of Moreover, dental stem cell storage services in
challenges.4 Overcoming these limitations diseases, but cannot regenerate lost tissue. various developing countries, which can serve
through advancements in machine reasoning, In light of this, researchers are increasingly patients for medical treatment in later years,
knowledge representation, and AI governance interested in achieving proper regeneration of are increasing.5
is critical as these technologies become lost dental tissues as technology develops.1 Although the potential applications of
more prevalent. Dental-related stem cells are attractive stem cell therapy in dentistry are promising,
In conclusion, AI should complement, sources of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells further research and clinical studies are
not replace, the expertise and judgement (MSCs), which can be isolated from the dental needed to fully understand the safety, efficacy,
of dentists. With careful development and pulp, primary teeth, dental follicles, and and long-term outcomes of these treatments.
validation, AI has immense potential to periodontal ligaments.2 Dental pulp should
make EBD more efficient, personalized, and However, available research suggests that
be only from healthy teeth, and ideally from dental stem cells, including MSCs, have the
proactive, significantly improving clinical donors younger than 30 years old because
decision-making and ultimately leading to potential to revolutionize dental treatments
the cells lose their ability to regenerate. There and contribute to regenerative dentistry.
enhanced treatment outcomes and greater
are many potential applications for stem cell
patient satisfaction.
therapy in dentistry, and it holds promise for References
a wide range of clinical outcomes, although 1. Paul K, Islam A, Volponi AA. Future horizons:
References
everything is still in at an in vitro experimental embedding the evolving science of regenerative
1. Kishore M, Panat SR, Aggarwal A et al. Evidence
stage. The following are some noteworthy dentistry in a modern, sustainable dental
based dental care: integrating clinical expertise
areas where stem cell therapy has shown curriculum. Br Dent J 2022; 232: 207–210.
with systematic research. J Clin Diagn Res
potential in dentistry.3,4 2. Li Y, Duan X, Chen Y et al. Dental stem cell-
2014; 8: 259–2562. https://doi.org/10.7860/
JCDR/2014/6595.4076 Treatment of periodontal disease: derived extracellular vesicles as promising
2. Schwendicke F, Samek W, Krois J. Artificial Stem cell therapy has the potential to therapeutic agents in the treatment of diseases.
intelligence in dentistry: chances and cure periodontal diseases including Int J Oral Sci 2022; 14: 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/
challenges. J Dent Res 2020; 99: 769–774. periodontitis. MSCs can be used to s41368-021-00152-2
https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034520915714 repair periodontal tissues, stimulate 3. Srijaya T C, Sriram S, Sugii S, Kasim N H A. Stem
3. Chen YW, Stanley K, Att W. Artificial intelligence tissue healing, and modify immune cells in dentistry: potential applications and
in dentistry: current applications and future responses, thus providing a unique perspectives in clinical research. In: Pham P
perspectives. Quintessence Int 2020; 51: 248– therapeutic method for the treatment of (ed.) Bone and Cartilage Regeneration. Stem
257. https://doi.org/10.3290/j.qi.a43952 periodontal disease. Cells in Clinical Applications. Cham, Switzerland:
4. Ding H, Wu J, Zhao W et al. Artificial intelligence Reconstruction of maxillofacial defects: Springer, 2016.
in dentistry: a review. Front Dent Med 2023; 4: Dental stem cells, particularly those 4. Soudi A, Yazdanian M, Ranjbar R et al. Role and
1085251. generated from the dental pulp and application of stem cells in dental regeneration:
5. Abdelkader W, Navarro T, Parrish R et al. periodontal ligament, have shown a comprehensive overview. EXCLI J 2021; 20:
Machine learning approaches to retrieve promise in stimulating bone regeneration 454–489.
high-quality, clinically relevant evidence from and correcting maxillofacial bone 5. Zeitlin BD. Banking on teeth – stem cells and
the biomedical literature: systematic review. defects. These stem cells may develop the dental office. Biomed J 2020; 43: 124–133.
JMIR Med Inform 2021; 9: e30401. https://doi. into osteoblasts and induce bone tissue https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2020.02.003
org/10.2196/30401 growth, providing a restorative therapy for Enis Veseli
6. Mayer T, Marro S, Cabrio E, Villata S. Enhancing individuals with bone deficiencies. Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School,
evidence-based medicine with natural Regeneration of dental tissue: Stem cell- Faculty of Medicine, University of Pristina,
language argumentative analysis of clinical based treatments may help to regenerate Pristina, Kosovo
January 2024 DentalUpdate 67
pg66-67 Letters.indd 67 11/01/2024 12:20
You might also like
- Treatment Planning of Teeth With Compromised Clinical Crowns Endodontic, Reconstructive, and Surgical StrategyDocument20 pagesTreatment Planning of Teeth With Compromised Clinical Crowns Endodontic, Reconstructive, and Surgical Strategyfloressam2000No ratings yet
- Baptism EventDocument37 pagesBaptism Eventsharmaine ella guittap68% (19)
- Vital Pulp Ricucci PDFDocument12 pagesVital Pulp Ricucci PDFBeto O Rivero100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in General Physics 2Document5 pagesLesson Plan in General Physics 2Mafeth JingcoNo ratings yet
- J Esthet Restor Dent - 2023 - Pedrinaci - Multifunctional Anatomical Prototypes MAPs Treatment of Excessive GingivalDocument10 pagesJ Esthet Restor Dent - 2023 - Pedrinaci - Multifunctional Anatomical Prototypes MAPs Treatment of Excessive Gingivaljuan.vanegas.a1No ratings yet
- Expert Consensus On Regenerative Endodontic ProceduresDocument13 pagesExpert Consensus On Regenerative Endodontic Procedures朱嘉琪No ratings yet
- Int J Paed Dentistry - 2021 - Jiang - Continued Root Development of Immature Permanent Teeth After Regenerative EndodonticsDocument10 pagesInt J Paed Dentistry - 2021 - Jiang - Continued Root Development of Immature Permanent Teeth After Regenerative EndodonticsPedro AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Policy On Using Harvested Dental Stem CellsDocument2 pagesPolicy On Using Harvested Dental Stem CellsمعتزباللهNo ratings yet
- Clin Adv Periodontics - 2023 - Mallappa - Novel Biomaterial Advanced Platelet Rich Fibrin Plus Block For Multiple GingivalDocument7 pagesClin Adv Periodontics - 2023 - Mallappa - Novel Biomaterial Advanced Platelet Rich Fibrin Plus Block For Multiple GingivalNikit DixitNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells in OrthodonticsDocument4 pagesStem Cells in OrthodonticsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Dental Traumatology - 2015 - Mohadeb - Effectiveness of Decoronation Technique in The Treatment of Ankylosis A SystematicDocument9 pagesDental Traumatology - 2015 - Mohadeb - Effectiveness of Decoronation Technique in The Treatment of Ankylosis A SystematicSitiKhadijahNo ratings yet
- Peri-Implantitis: A Curse To ImplantsDocument11 pagesPeri-Implantitis: A Curse To ImplantsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Interceptive Orthodontic Treatment in Reducing MalocclusionsDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Interceptive Orthodontic Treatment in Reducing MalocclusionsAriana de LeonNo ratings yet
- Article7 13 4 PDFDocument6 pagesArticle7 13 4 PDFbadar_aqNo ratings yet
- Has Biology Changed With Clear Aligners?: Readers' ForumDocument2 pagesHas Biology Changed With Clear Aligners?: Readers' ForumAndré DrumondNo ratings yet
- 2021 Does The Timing of 1-Stage Palatoplasty With Radical Muscle Dissection Effect Long-Term Midface Growth A Single-Center Retrospective AnalysisDocument7 pages2021 Does The Timing of 1-Stage Palatoplasty With Radical Muscle Dissection Effect Long-Term Midface Growth A Single-Center Retrospective AnalysisDimitris RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Voice Activated Charting SystemsDocument1 pageVoice Activated Charting SystemsNishanth SudharsonNo ratings yet
- Biologia Art 2Document38 pagesBiologia Art 2Sandry marquezNo ratings yet
- Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial ResearchDocument9 pagesJournal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial ResearchCyber MagicNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Treatment Planning Current Practice Principles and TechniquesDocument4 pagesProsthodontic Treatment Planning Current Practice Principles and TechniquesZiad RabieNo ratings yet
- Ijcpd-15-S103 MetanalysisDocument11 pagesIjcpd-15-S103 MetanalysisGabriela ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Reviving Immature Permanent Teeth: A Case Report On Regenerative Endodontic Treatment As A Retreatment OptionDocument3 pagesReviving Immature Permanent Teeth: A Case Report On Regenerative Endodontic Treatment As A Retreatment OptionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tratamientos Restauradores Atraumáticos en Dientes DeciduosDocument13 pagesTratamientos Restauradores Atraumáticos en Dientes DeciduosNéstor Ricardo Guardado ToledoNo ratings yet
- IEJ - Revitalization in EndodonticsDocument7 pagesIEJ - Revitalization in Endodonticssoho1303No ratings yet
- Panda 2022 Clinical Outcome and Comparison ofDocument35 pagesPanda 2022 Clinical Outcome and Comparison ofTavinn SGNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022391302002998 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S0022391302002998 MainManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Eramo2017 RegenrationDocument15 pagesEramo2017 Regenrationrasagna reddyNo ratings yet
- Surgical Reconstruction of Interdental PDocument11 pagesSurgical Reconstruction of Interdental PMaria Jose GodoyNo ratings yet
- Autologus Fibroblast InjectionsDocument14 pagesAutologus Fibroblast InjectionsDr. DeeptiNo ratings yet
- 软组织相关的并发症风险Document15 pages软组织相关的并发症风险xiaoxin zhangNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Procedures For Deficient Interdental Papillae: A ReviewDocument9 pagesMinimally Invasive Procedures For Deficient Interdental Papillae: A ReviewRodolfoDamásioNunesNo ratings yet
- CCR3 11 E7714Document6 pagesCCR3 11 E7714memo.09navNo ratings yet
- Success Criteria For Dental Implant - A Literature Review: Research ArticleDocument5 pagesSuccess Criteria For Dental Implant - A Literature Review: Research Articlehimanshu vadherNo ratings yet
- Over Sem EsplintarDocument9 pagesOver Sem EsplintarClaudia BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- Management of The Developing Dentition and Occlusion in Pediatric DentistryDocument18 pagesManagement of The Developing Dentition and Occlusion in Pediatric DentistryPAULA ANDREA RAMIREZ ALARCONNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Augmentation Procedures For Mucogingival Defects in Esthetic SitesDocument31 pagesSoft Tissue Augmentation Procedures For Mucogingival Defects in Esthetic Sitesilich sevillaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Fixed Implant Supported Prostheses in Edentulous Patients: Protocol For A Systematic ReviewDocument4 pagesImpact of Fixed Implant Supported Prostheses in Edentulous Patients: Protocol For A Systematic ReviewAngelaBaleaNo ratings yet
- Conservative Managing ofDocument9 pagesConservative Managing ofsystematic reviewNo ratings yet
- New Paradigms in Prosthodontic Treatment PlanningDocument8 pagesNew Paradigms in Prosthodontic Treatment PlanningNanda Iswa MaysferaNo ratings yet
- Int Endodontic J - 2022 - Murray - Review of Guidance For The Selection of Regenerative Endodontics ApexogenesisDocument12 pagesInt Endodontic J - 2022 - Murray - Review of Guidance For The Selection of Regenerative Endodontics ApexogenesisEdward AbadiaNo ratings yet
- Contents - 2021 - Dental Clinics of North AmericaDocument4 pagesContents - 2021 - Dental Clinics of North Americaash shahNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Endodontics: A New Era For Pulpotomy in Mature Permanent TeethDocument7 pagesMinimally Invasive Endodontics: A New Era For Pulpotomy in Mature Permanent TeethEdinam GavehNo ratings yet
- Titanium Mesh Ridges RecontructionDocument11 pagesTitanium Mesh Ridges RecontructionМилутинМићићNo ratings yet
- BP DevelopdentitionDocument18 pagesBP DevelopdentitionShakh ShakhNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Wound Healing Around Teeth and Dental ImplantsDocument17 pagesSoft Tissue Wound Healing Around Teeth and Dental ImplantsDavid CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Jcpe 12206 PDFDocument17 pagesJcpe 12206 PDFrozh rasulNo ratings yet
- Jcpe 12206 PDFDocument17 pagesJcpe 12206 PDFrozh rasulNo ratings yet
- Jcpe 12206 PDFDocument17 pagesJcpe 12206 PDFrozh rasulNo ratings yet
- Chen 2019Document9 pagesChen 2019Tiara HapkaNo ratings yet
- Journal Dental Implant 1Document5 pagesJournal Dental Implant 1Faiqotul KumalaNo ratings yet
- Bilhan 2012Document7 pagesBilhan 2012laur112233No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Patient Satisfaction in Precision Attachment-Supported Overdentures and Conventional Overdentures Through Verbal Rating SystemDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Patient Satisfaction in Precision Attachment-Supported Overdentures and Conventional Overdentures Through Verbal Rating SystemIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 39 TH JC - SindhuDocument11 pages39 TH JC - SindhuDadi SindhuNo ratings yet
- Oktawati 2020Document3 pagesOktawati 2020Mariatun ZahronasutionNo ratings yet
- GOBBATODocument11 pagesGOBBATOBianca MarcheziNo ratings yet
- DR Neha ArticleDocument7 pagesDR Neha ArticleVinod ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Vital InflamDocument15 pagesClinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Vital InflamMihaela TuculinaNo ratings yet
- EBD Nature Journal-Clinical Outcomes of Implant Supported-2023Document8 pagesEBD Nature Journal-Clinical Outcomes of Implant Supported-2023NARESHNo ratings yet
- Retrieve 4Document8 pagesRetrieve 4dreneanastriNo ratings yet
- Int Endodontic J - 2022 - Matoug ElwerfelliDocument17 pagesInt Endodontic J - 2022 - Matoug Elwerfelliالحب الابديNo ratings yet
- J Esthet Restor Dent - 2023 - Eggmann - Deep Margin Elevation Present Status and Future DirectionsDocument22 pagesJ Esthet Restor Dent - 2023 - Eggmann - Deep Margin Elevation Present Status and Future DirectionsNador AbdennourNo ratings yet
- Graftless Solutions for the Edentulous PatientFrom EverandGraftless Solutions for the Edentulous PatientSaj JivrajNo ratings yet
- Act-06-Possessive AdjectivesDocument1 pageAct-06-Possessive Adjectivesconscientious.citizen29No ratings yet
- Survey ReportDocument14 pagesSurvey ReportKamila KuźniarNo ratings yet
- Part 1) Pre-Industrial Experience LogbookDocument17 pagesPart 1) Pre-Industrial Experience LogbookMohamed IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Shape Type DESIGNATION (IMPERIAL) Weight (LBF/FT) Area (In2) Depth (In) Moment Inertia (In4) Designation (Metric)Document60 pagesShape Type DESIGNATION (IMPERIAL) Weight (LBF/FT) Area (In2) Depth (In) Moment Inertia (In4) Designation (Metric)MonicaLilianaRiveraNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary TestDocument20 pagesVocabulary TesttimenetsolutionsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Payment System Digital Cash, Plastic Card, PSO and PSP Sept 2023Document16 pagesElectronic Payment System Digital Cash, Plastic Card, PSO and PSP Sept 2023Meraj TalukderNo ratings yet
- CV of HASAN MAHAMUDDocument3 pagesCV of HASAN MAHAMUDMuhammad Azharul HannanNo ratings yet
- SILICON C05 Refractory Anchors Concrete Lining Corrugated H System Technical Drawing PDFDocument6 pagesSILICON C05 Refractory Anchors Concrete Lining Corrugated H System Technical Drawing PDFkartsoftNo ratings yet
- 151005#LinkDesign20220821-203024Document5 pages151005#LinkDesign20220821-203024jemal yahyaaNo ratings yet
- Inverter Heat Pumps: Heat Pumps For Private and Public Swimming PoolsDocument4 pagesInverter Heat Pumps: Heat Pumps For Private and Public Swimming PoolsAinars VizulisNo ratings yet
- Delco Remy - Manual de DiagnósticoDocument32 pagesDelco Remy - Manual de Diagnósticosanches pita100% (1)
- Silencerco Catalog 2011Document28 pagesSilencerco Catalog 2011Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- 5S Routine Audit FormDocument8 pages5S Routine Audit Formblackbarby100% (3)
- Cement Industry - Group19Document28 pagesCement Industry - Group19swati100% (1)
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsDocument44 pagesRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsKrupakl Gowda100% (8)
- INTRODUCTION - To BackpackDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION - To BackpackMohammad Afnan BugtiNo ratings yet
- Mystery About Number and Longitude of Each Nadi ExplainedDocument10 pagesMystery About Number and Longitude of Each Nadi Explainedpm plassanalNo ratings yet
- Leader End of Financial Catalogue Apr-Jun 2020 - LowRez - FinalDocument16 pagesLeader End of Financial Catalogue Apr-Jun 2020 - LowRez - Finaltim chambersNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document3 pagesActivity 1Daisy Soriano PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Carmudi Inspection Report 40Document5 pagesCarmudi Inspection Report 40Alberto Valdecanas (AlbertCVal)No ratings yet
- Moorish Lebanese CedarDocument19 pagesMoorish Lebanese CedarLews MatinNo ratings yet
- Progress Record TemplateDocument12 pagesProgress Record TemplatenickcnNo ratings yet
- Annual Budget CY 2023Document180 pagesAnnual Budget CY 2023robertson builderNo ratings yet
- Universal Preschool Is No Golden Ticket: Why Government Should Not Enter The Preschool Business, Cato Policy Analysis No. 333Document31 pagesUniversal Preschool Is No Golden Ticket: Why Government Should Not Enter The Preschool Business, Cato Policy Analysis No. 333Cato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Aries LagnaDocument1 pageAries LagnaKapil KhedekarNo ratings yet
- Presentation To TBSB - 30 June 2015 PDFDocument13 pagesPresentation To TBSB - 30 June 2015 PDFMuzhaffar AzizNo ratings yet
- Star Method Interview Prep Packet 2020Document11 pagesStar Method Interview Prep Packet 2020snvales92No ratings yet
- Cause & Effect WorksheetDocument2 pagesCause & Effect WorksheetAh Gone67% (3)