Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ncpgasthep 0333
Uploaded by
thaisagoraer10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMelatonin was found to reduce abdominal pain and enhance rectal pain thresholds in IBS patients, but did not significantly improve sleep quality or quantity. Higher activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are involved in liver fibrosis, at 4 months post-transplant was predictive of progression to severe fibrosis within 1-2 years for HCV-infected liver transplant patients. Two studies used markers of HSC activation to identify patients at highest risk of developing advanced fibrosis who may benefit most from antiviral therapy.
Original Description:
Melatonina intestino
Original Title
ncpgasthep0333
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMelatonin was found to reduce abdominal pain and enhance rectal pain thresholds in IBS patients, but did not significantly improve sleep quality or quantity. Higher activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are involved in liver fibrosis, at 4 months post-transplant was predictive of progression to severe fibrosis within 1-2 years for HCV-infected liver transplant patients. Two studies used markers of HSC activation to identify patients at highest risk of developing advanced fibrosis who may benefit most from antiviral therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageNcpgasthep 0333
Uploaded by
thaisagoraer1Melatonin was found to reduce abdominal pain and enhance rectal pain thresholds in IBS patients, but did not significantly improve sleep quality or quantity. Higher activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are involved in liver fibrosis, at 4 months post-transplant was predictive of progression to severe fibrosis within 1-2 years for HCV-infected liver transplant patients. Two studies used markers of HSC activation to identify patients at highest risk of developing advanced fibrosis who may benefit most from antiviral therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
www.nature.com/clinicalpractice/gasthep
Melatonin trial in patients with interferon-based therapies and ribavirin has
irritable bowel syndrome limited efficacy and is poorly tolerated in liver-
transplant patients. The aim of two recent stud-
Sleep disturbance is highly prevalent in ies was to identify a marker for those patients
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients. As at highest risk of fibrosis that might allow more
melatonin has been associated with both effective targeting of therapy. Both studies looked
sleep promotion and the regulation of gastro- at hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the main source
intestinal motility, Song and colleagues carried of extracellular matrix and collagen in the liver.
out a randomized, placebo-controlled study to Activation of HSCs is known to be the earliest
assess its efficacy in treating symptoms of IBS stage of hepatic fibrogenesis, but data are lack-
and sleep disturbance. ing on the association of HSC activation and the
In total, 40 patients with IBS and sleep dis- subsequent development of advanced fibrosis
turbance were randomized 1:1 to receive either and cirrhosis in liver-transplant patients.
14 days treatment with melatonin 3 mg daily at Gawrieh and colleagues used α-smooth-
bedtime, or placebo. Bowel symptoms, sleep muscle actin (αSMA), detected immuno-
disturbance and the psychological status of histochemically, as a marker of HSC activation.
participants were recorded at baseline and after Liver biopsies performed 4 months post-
completion of 14 days of therapy, by means of transplantation were stained for αSMA and
questionnaires: rectal manometry and overnight assessed retrospectively by a pathologist blind to
polysomnography were also performed at these the patients’ clinical and laboratory data. A semi-
two evaluation points. quantitative scoring system was used to give
After 2 weeks, patients receiving melatonin regional and total HSC activation scores. The
had a significantly greater decrease in abdomi- 4-month scores were then correlated with
nal pain and significantly increased sensory the fibrosis score at 1 year post-transplant.
thresholds for urgency and pain, compared with They found that total HSC scores were similar
those receiving placebo. The quality and quan- between patients with severe (fibrosis score
tity of patients’ sleep, however, did not differ sig- ≥2; n = 13) and those with mild (fibrosis score 0;
nificantly between the two groups. In addition, n = 13) HCV infection. Regional scores differed,
there was no significant difference in the anxi- however (parenchymal zones 1, 2 and 3; mesen-
ety and depression scores of patients receiving chymal portal tracts and fibrous septa). Higher
melatonin compared with placebo. mesenchymal scores were predictive of pro-
The authors conclude that melatonin is effec- gression, and mesenchymal activation of HSCs
tive in reducing abdominal pain and enhancing had a specificity and positive predictive value of
rectal pain thresholds in IBS patients, but this 100% for the development of progressive fibro-
effect is independent of its effect on sleep and sis. The authors conclude that assessment of
psychological parameters. HSC activity at 4 months post-transplant could
Katy Cherry help identify a population of patients at particu-
Original article Song GH et al. (2005) Melatonin improves lar risk of cirrhosis who might benefit most from
abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome patients who antiviral therapy.
have sleep disturbances: a randomised, double-blind, placebo Russo and colleagues used the same marker
controlled study. Gut 54: 1402–1407
(αSMA) to detect activated HSCs in their study,
which also assessed HSC activation at 4 months
as a predictor of the subsequent development of
Hepatic stellate cells: early advanced fibrosis. Their study included 46 HCV-
activation predicts fibrosis infected liver-transplant recipients, divided into
in HCV-infected transplant rapid fibrosers (n = 21), defined by the develop-
recipients ment of fibrosis or cirrhosis within 2 years of
transplantation, and slow fibrosers (n = 25). A
End-stage liver disease due to hepatitis C virus computerized image and data analysis sys-
(HCV) infection is an indication for liver trans- tem was used to analyze αSMA retrospectively
plantation. Recurrent HCV infection is universal (expressed as the proportion of cellular area
in these patients, and leads to the development positive on immunohistochemistry) detected in
of fibrosis or cirrhosis in around 20% after 4-month post-transplant biopsy samples. The
2 years and 30% after 5 years. Treatment with authors found that HSC activity was associated
558 NATURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY DECEMBER 2005 VOL 2 NO 12
©2005 Nature Publishing Group
You might also like
- Skinny Liver - A Proven Program To Prevent and Reverse The New Silent Epidemic-Fatty Liver Disease PDFDocument337 pagesSkinny Liver - A Proven Program To Prevent and Reverse The New Silent Epidemic-Fatty Liver Disease PDFSpj Jj100% (5)
- Principles of Liver TransplantationDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Liver TransplantationRajarshi KumarNo ratings yet
- BTK Quick Hits Final PDFDocument24 pagesBTK Quick Hits Final PDFcusom34No ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument21 pagesCirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDan ChicinasNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Hepatitis BDocument24 pagesCase Study For Hepatitis BEmma Mariz Bernas Garcia67% (6)
- The Effect of Photobiomodulation On Chemotherapy-Induced PeripheralDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Photobiomodulation On Chemotherapy-Induced PeripheralLizeth Arce100% (1)
- Michael Chancellor, Royal Oak, MI Pradeep Tyagi, Pittsburgh, PA Jayabalan Nirmal, Don Bui, Kenneth Peters, Royal Oak, MIDocument2 pagesMichael Chancellor, Royal Oak, MI Pradeep Tyagi, Pittsburgh, PA Jayabalan Nirmal, Don Bui, Kenneth Peters, Royal Oak, MIPpa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- Dietrich Et Al-2002-Journal of Ultrasound in MedicineDocument9 pagesDietrich Et Al-2002-Journal of Ultrasound in MedicineErikaMRSiaNo ratings yet
- Bren Bridge 1987Document3 pagesBren Bridge 1987Erlangga D SaputroNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument11 pagesDDDDNejc KovačNo ratings yet
- Muscarinic Cholinergic Receptor Agonist and Peripheral Antagonist For Schizophrenia (2021)Document10 pagesMuscarinic Cholinergic Receptor Agonist and Peripheral Antagonist For Schizophrenia (2021)ShadeLRKNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Fibrosis Evaluation With SemiquantitativeDocument9 pagesHepatic Fibrosis Evaluation With Semiquantitativeehsanulazim50buetNo ratings yet
- It Is Time To Review Concepts On Renal Involvement in Leprosy Pre and Post Treatment Evaluation of 189 PatientsDocument5 pagesIt Is Time To Review Concepts On Renal Involvement in Leprosy Pre and Post Treatment Evaluation of 189 PatientsAdhyt PratamaNo ratings yet
- Vagal Tone Effects On Sensitivity, Motility, and InflammationDocument8 pagesVagal Tone Effects On Sensitivity, Motility, and InflammationGuillermo923No ratings yet
- Tofacitinib As Induction and Maintenance Therapy For Ulcerative ColitisDocument14 pagesTofacitinib As Induction and Maintenance Therapy For Ulcerative Colitismichal ben meronNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Hypersensitivity in IBS and Functional DisordersDocument27 pagesMechanisms of Hypersensitivity in IBS and Functional DisordersJessica NotarioNo ratings yet
- Caac 21599Document8 pagesCaac 21599Kezia TindasNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE PANCREATITIS Chile PDFDocument2 pagesDIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF AUTOIMMUNE PANCREATITIS Chile PDFJesusita AbrigoNo ratings yet
- The Accuracy of Fibroscan in A Real World StudyDocument2 pagesThe Accuracy of Fibroscan in A Real World StudyRaeni Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2589986423000448 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2589986423000448 MainsoylahijadeunvampiroNo ratings yet
- 192 FullDocument6 pages192 FullnaamiiNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersDocument2 pagesGastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersXimenaNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2304286Document11 pagesNejmoa 2304286Elisa ChinchillaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Vagal Tone, Cortisol, TNF-Alpha, Epinephrine and Negative Affects in Crohn's Disease and Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument9 pagesRelationship Between Vagal Tone, Cortisol, TNF-Alpha, Epinephrine and Negative Affects in Crohn's Disease and Irritable Bowel SyndromeAinaNo ratings yet
- 【案例1:2017-Open Forum Infectious Diseases-病毒性脑膜炎- Japanese encephalitis virus】- Central Nervous System Infection Diagnosis by NextDocument3 pages【案例1:2017-Open Forum Infectious Diseases-病毒性脑膜炎- Japanese encephalitis virus】- Central Nervous System Infection Diagnosis by Nextdai shujuanNo ratings yet
- Fecal Calprotectin, Gut Inflammation and Spondyloarthritis: ClinicalDocument6 pagesFecal Calprotectin, Gut Inflammation and Spondyloarthritis: ClinicalPNo ratings yet
- Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (2013)Document1 pageJournal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (2013)Norberto MolloNo ratings yet
- A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Maintenance Interferon Therapy For Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus and PersisDocument9 pagesA Randomized, Controlled Trial of Maintenance Interferon Therapy For Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus and Persisgrace liwantoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Hung, 2004Document4 pages5 - Hung, 2004Henrique MachadoNo ratings yet
- Riginal Research: LucasDocument11 pagesRiginal Research: Lucas'fanny Quenhita'No ratings yet
- MagnascoDocument8 pagesMagnascoMeliana SulistioNo ratings yet
- Metastatic MelanomaDocument8 pagesMetastatic MelanomashokoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease PDFDocument8 pagesHirschsprung Disease PDFAlchemistalazkaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NeurogastroenterologyDocument12 pagesFundamentals of NeurogastroenterologyFlavia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Neurology and NeurosurgeryDocument5 pagesClinical Neurology and NeurosurgeryAffan AdibNo ratings yet
- The Perme Scale Score As A Predictor of Functional Status and Complications After Discharge From The Intensive Care Unit in Patients Undergoing Liver TransplantationDocument6 pagesThe Perme Scale Score As A Predictor of Functional Status and Complications After Discharge From The Intensive Care Unit in Patients Undergoing Liver TransplantationKaren MuñozNo ratings yet
- 5th PortfolioDocument11 pages5th Portfoliotajhussain1100786No ratings yet
- Park DKK 2004Document4 pagesPark DKK 2004Natasya DarrelNo ratings yet
- New England Journal Medicine: The ofDocument11 pagesNew England Journal Medicine: The ofJosé Ignacio Rinaldi CentresNo ratings yet
- 44 Year Old Man With Fatigue, Weight Loss, and LeuDocument5 pages44 Year Old Man With Fatigue, Weight Loss, and LeuRamiro Arraya MierNo ratings yet
- Appi Ajp 2008 07121900Document8 pagesAppi Ajp 2008 07121900jacopo pruccoliNo ratings yet
- Absceso Hepático NeonatalDocument6 pagesAbsceso Hepático NeonatalNabila Peña ZapataNo ratings yet
- HSP 6Document12 pagesHSP 6garethNo ratings yet
- Review Article The Management of Pelvic Floor DisordersDocument15 pagesReview Article The Management of Pelvic Floor DisordersYvonne MedinaNo ratings yet
- Par EnteralDocument4 pagesPar EnteralshalukiriNo ratings yet
- Night Eating Syndrome: How To Treat It?: Review ArticleDocument7 pagesNight Eating Syndrome: How To Treat It?: Review ArticleAna Raíza OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Classificação Do Sono 8Document14 pagesClassificação Do Sono 8Jefferson JuniorNo ratings yet
- 2012 Pall Care For Pancreas CancerDocument6 pages2012 Pall Care For Pancreas CancerFilip IonescuNo ratings yet
- Harrisons Principles of Internal Medicine 21st Edition Vol 1 Vol Split PDF 1694700703964Document73 pagesHarrisons Principles of Internal Medicine 21st Edition Vol 1 Vol Split PDF 1694700703964Clorinda RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Limitation Graft BiopsyDocument11 pagesLimitation Graft BiopsyWEE LENG GANNo ratings yet
- Etanercept in Alzheimer Disease: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 2 TrialDocument8 pagesEtanercept in Alzheimer Disease: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Phase 2 TrialGiuseppe AcanforaNo ratings yet
- Journal Nefro 5 PDFDocument13 pagesJournal Nefro 5 PDFAndhika Aryandhie DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Rovin 2019Document13 pagesRovin 2019hanzelNo ratings yet
- 4323 22520 1 PBDocument4 pages4323 22520 1 PBFreddy Shanner Chávez VásquezNo ratings yet
- 250 Successful Management of Ankylosing SpondylitiDocument1 page250 Successful Management of Ankylosing SpondylitiAananda Raaj V MNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3 Fater 2Document8 pagesJurnal 3 Fater 2ANDIANY CAHYANTY TAHIRNo ratings yet
- ProstatitisDocument32 pagesProstatitisArkam SaleemNo ratings yet
- Biomarkers in Overactive Bladder: Mini ReviewDocument5 pagesBiomarkers in Overactive Bladder: Mini Reviewmardha tillahNo ratings yet
- Other Medical ConditionsDocument2 pagesOther Medical ConditionsThiago CostaNo ratings yet
- Tabrizi An 2009Document4 pagesTabrizi An 2009Dung Tran HoangNo ratings yet
- Population-Based Sleep-Disordered Breathing: StudyDocument7 pagesPopulation-Based Sleep-Disordered Breathing: StudyDiego SolaqueNo ratings yet
- CTS PDFDocument6 pagesCTS PDFBiola DwikoNo ratings yet
- Secretin-Enhanced MRCP: Proceed With Cautious OptimismDocument4 pagesSecretin-Enhanced MRCP: Proceed With Cautious OptimismYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Song 2017Document8 pagesSong 2017Patricia BezneaNo ratings yet
- E-Ahpba 2013 Congress Book Add-OnDocument30 pagesE-Ahpba 2013 Congress Book Add-OnSvet MedicineNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver Failure in Children Management - UpToDateDocument20 pagesAcute Liver Failure in Children Management - UpToDateZeliha TürksavulNo ratings yet
- Orthotopic Mouse Liver Transplantation To Study Liver Biology and Allograft ToleranceDocument12 pagesOrthotopic Mouse Liver Transplantation To Study Liver Biology and Allograft Tolerancepaul00040No ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper TitleDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper TitleFebie Gayap FelixNo ratings yet
- JCM 12 06173Document20 pagesJCM 12 06173Taulant MukaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding in Liver Surgery Prevention and TreatmentDocument10 pagesBleeding in Liver Surgery Prevention and TreatmentMutammamin UlaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Hepatic Liver CirrhosisDocument11 pagesGroup 2 - Hepatic Liver Cirrhosismelba040510No ratings yet
- Living Donor Liver Transplant From An HIV Positive.1Document7 pagesLiving Donor Liver Transplant From An HIV Positive.1Laura Lopez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Contributo - 2017 - Blumgart S Surgery of The Liver Biliary Tract and PancreasDocument17 pagesContributo - 2017 - Blumgart S Surgery of The Liver Biliary Tract and PancreasJoe JoeNo ratings yet
- GEN GallBladderInstrumentsADocument10 pagesGEN GallBladderInstrumentsANeo Rodriguez AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia Copy LNGDocument10 pagesBiliary Atresia Copy LNGlloraoNo ratings yet
- Treating Liver CancerDocument34 pagesTreating Liver Cancermohamed aliNo ratings yet
- Transplant International Special Issue: Abstracts of The 14th Congress of The European Society For Organ Transplantation Volume 22, Issue Supplement s2, Pages 95-222, August 2009Document145 pagesTransplant International Special Issue: Abstracts of The 14th Congress of The European Society For Organ Transplantation Volume 22, Issue Supplement s2, Pages 95-222, August 2009Enrique Moreno GonzálezNo ratings yet
- A Review of Liver Transplantation For The Dentist and Guidelines For Dental ManagementDocument7 pagesA Review of Liver Transplantation For The Dentist and Guidelines For Dental ManagementLujainNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing of Mouse Primary Hepatocytes To Generate 3D Hepatic StructureDocument6 pagesThree-Dimensional (3D) Printing of Mouse Primary Hepatocytes To Generate 3D Hepatic StructuregpaivNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Document7 pagesMed Surg 2 - 7 Malabsorption Syndromes and Nursing Care of Clients With Hepatic Disorders 2Maxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Biliary Atresia UP To DATEDocument21 pagesBiliary Atresia UP To DATECarlos CuadrosNo ratings yet
- Liver Transplant in PuneDocument9 pagesLiver Transplant in PuneDr. Ninad DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Obstructive JaundiceDocument5 pagesAn Approach To Obstructive JaundiceEvediciNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in Adults - Overview of Complications, General Management, and PrognosisDocument24 pagesCirrhosis in Adults - Overview of Complications, General Management, and PrognosisAhraxazel Galicia ReynaNo ratings yet
- The Bio Artificial Liver2Document17 pagesThe Bio Artificial Liver2Sandeep KattiNo ratings yet
- 2017 HepatologyDocument148 pages2017 HepatologyrdLuis1No ratings yet
- Abstract 2005HBP Surgery PDFDocument100 pagesAbstract 2005HBP Surgery PDFDrAmmar MagdyNo ratings yet
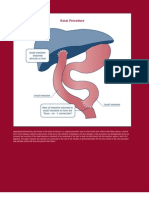
- KasaiDocument7 pagesKasaishalukiriNo ratings yet
- Living Donor Transplantation BrochureDocument13 pagesLiving Donor Transplantation BrochureShani KushwahaNo ratings yet