Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Servlet Architecture in Java
Uploaded by
Vaibhav PandeyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Servlet Architecture in Java
Uploaded by
Vaibhav PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
SERVLET ARCHITECTURE IN JAVA
Servlets are grouped under the Advanced Java tree that is used to create dynamic
web applications. Servlets are robust, well scalable, and are primarily used in
developing server-side applications. If we go a little back in time, we would be able
to witness that before the introduction of servlets, CGI (Common Gateway
Interface) was used. Among several indigenous tasks that a servlet is capable of
doing, dynamically performing client requests and responses are most common.
Other tasks that a servlet can do effectively are:
Can easily manage/control the application flow.
Suitable to implement business logic.
Can effectively balance the load on the server side.
Easily generate dynamic web content.
Handle HTTP Request and Response
Also act as an interceptor or filter for a specific group of requests.
Types of Servlet
Generic Servlets: These are those servlets that provide functionality for
implementing a servlet. It is a generic class from which all the
customizable servlets are derived. It is protocol-independent and provides
support for HTTP, FTP, and SMTP protocols. The class used is
‘javax.servlet.Servlet’ and it only has 2 methods – init() to initialize &
allocate memory to the servlet and destroy() to deallocate the servlet.
HTTP Servlets: These are protocol dependent servlets, that provides
support for HTTP request and response. It is typically used to create web
apps. And has two of the most used methods – doGET() and doPOST()
each serving their own purpose.
There are three potential ways in which we can employ to create a servlet:
Implementing Servlet Interface
Extending Generic Servlet
Extending HTTP Servlet
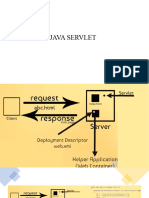
Components of Servlet Architecture
Servlet Architecture contains the business logic to process all the requests made by
client. Below is the high-level architecture diagram of servlet. Let’s see in brief, how
does each component add to the working of a servlet.
1. Client
The client shown in the architecture above is the web browser and it primarily works
as a medium that sends out HTTP requests over to the web server and the web server
generates a response based on some processing in the servlet and the client further
processes the response.
2. Web Server
Primary job of a web server is to process the requests and responses that a user sends
over time and maintain how a web user would be able to access the files that has
been hosted over the server. The server we are talking about here is a software which
manages access to a centralized resource or service in a network. There are precisely
two types of webservers:
Static web server
Dynamic web server
3. Web Container
Web container is another typical component in servlet architecture which is
responsible for communicating with the servlets. Two prime tasks of a web container
are:
Managing the servlet lifecycle
URL mapping
Web container sits at the server-side managing and handling all the requests that are
coming in either from the servlets or from some JSP pages or potentially any other
file system.
How does a Servlet Request flow?
Every servlet should override the following 3 methods namely:
1. init(): To initalize/instantiate the servlet container.
2. service(): This method acts like an intermediatory between the HTTP
request and the business logic to serve that particular request.
3. destroy(): This method is used to deallocate the memory allocated to the
servlet.
These methods are used to process the request from the user.
Following are the steps in which a request flows through a servlet which can be
observed in the architecture diagram:
The client sends over a request.
The request is accepted by the web server and forwarded to the web
container.
In order to obtain the servlet’s address, the web container
traces web.xml file corresponding to the request URL pattern.
By the time above process takes place, the servlet should have been
instantiated and initialized. The init() method is invoked to initialize the
servlet.
By passing ServletRequest and Response object, public service() method is
called by the container.
In the next step, the ServletRequest and ServletResponse objects are type
casted to HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects by
the public service() method.
Now protected service() method is called by the public service() method.
The protected service() method dispatches the request to the correct
handler method based on the type of request.
When servlet container shuts down, it unloads all the servlets and
calls destroy() method for each initialized servlet.
Advantages
Prime functionality of a servlet is that they are independent of server
configuration, and they are pretty much compatible with any of the web
servers.
Servlets are also protocol-independent supporting FTP, HTTP, SMTP, etc.
protocols to the fullest.
Until destroyed manually, servlets can be retained in the memory helping
process several requests over time. Also, once a database connection is
established, it can facilitate process several requests for a database in the
very same database session.
Servlets inherit Java’s property of portability and hence are compatible
with nearly any web server.
Servlets are first converted into byte codes and then executed, which helps
in increasing the processing time.
Disadvantages
Designing a servlet can be pretty laborious.
Exceptions need to be handled while designing a servlet since they are not
thread safe.
Developers may need additional skills to program a servlet.
You might also like
- Servelet and JSPDocument23 pagesServelet and JSPSatyamNo ratings yet
- Java ServletDocument10 pagesJava Servletmsdssr7No ratings yet
- ServletsDocument25 pagesServletsSherril VincentNo ratings yet
- Ervlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Document54 pagesErvlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Chetan ShindeNo ratings yet
- What is a Servlet? Guide to Servlet Technology, Life Cycle & ArchitectureDocument13 pagesWhat is a Servlet? Guide to Servlet Technology, Life Cycle & ArchitectureamritNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document27 pagesUnit 4Vishnu Vardhan HNo ratings yet
- Web Technologies Servlet NotesDocument24 pagesWeb Technologies Servlet NotesKasaragadda MahanthiNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 1441118342chapter-7 ServletsDocument8 pagesLecturenote - 1441118342chapter-7 ServletsChalew ZeynuNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets: Powerful Server-Side ComponentsDocument5 pagesJava Servlets: Powerful Server-Side ComponentsVivek AnanthNo ratings yet
- JAVA NotesDocument42 pagesJAVA NotesSuvarna GowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 2-Java Servlets: I) IntroductionDocument11 pagesModule 2-Java Servlets: I) IntroductionAkshay ChinnanNo ratings yet
- Servlet Interface in Java: Servlet Life Cycle StepsDocument23 pagesServlet Interface in Java: Servlet Life Cycle StepsFike FikirNo ratings yet
- WT Unit 3Document112 pagesWT Unit 3Bhure VedikaNo ratings yet
- What Is A ServletDocument21 pagesWhat Is A Servletrajdeep_chakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3swarajpatil180No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document14 pagesUnit 5Kavya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Java AssignmntDocument9 pagesJava AssignmntSahil ChauahanNo ratings yet
- ServletqbDocument17 pagesServletqbAmol AdhangaleNo ratings yet
- Servlet Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesServlet Interview QuestionsksgdbaNo ratings yet
- Servlet NotesDocument13 pagesServlet NotesseetharamNagesh AppeNo ratings yet
- Servlet and JSPDocument21 pagesServlet and JSP1da21cs137.csNo ratings yet
- Servlet Side Scripting Using Servlets-1Document52 pagesServlet Side Scripting Using Servlets-1Niranjan Prabhu k sNo ratings yet
- Ass 3Document18 pagesAss 3yashthummar003No ratings yet
- Ip Unit IiiDocument45 pagesIp Unit Iiiiyyanarappan aNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets Complete Reference GuideDocument35 pagesJava Servlets Complete Reference GuideSudhanshu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document25 pagesUnit 2Shaheena BegumNo ratings yet
- Servlet interview QuestionsDocument48 pagesServlet interview QuestionssubhabirajdarNo ratings yet
- Servlet Interview Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesServlet Interview Questions and AnswersrajinishNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Java Server ProgrammingDocument9 pagesUnit 6 - Java Server Programmingaashika shresthaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: Servlets, JSP S.No. Question/Answers 1. What Is Difference Between Servlets and CGI Servlets CGIDocument16 pagesTOPIC: Servlets, JSP S.No. Question/Answers 1. What Is Difference Between Servlets and CGI Servlets CGIKishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ServletDocument39 pagesChapter 6 ServletAshlesha AdhatraoNo ratings yet
- ServletsDocument10 pagesServletsGon FrecsNo ratings yet
- Servlets 170833Document6 pagesServlets 170833np05cp4a220052No ratings yet
- Unit III ServletsDocument18 pagesUnit III ServletsroshnibijuNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets: Dynamic Web PagesDocument81 pagesJava Servlets: Dynamic Web PagesJencyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Servletppt 1Document75 pagesChapter 06 Servletppt 1IF 06 Anjali BhamareNo ratings yet
- Servlet Are Java ProgramsDocument27 pagesServlet Are Java ProgramsmasoomrezaNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets: What Is Server-Side Programming?Document18 pagesJava Servlets: What Is Server-Side Programming?PrinceRajDKilerNo ratings yet
- Servlets PPTDocument129 pagesServlets PPTanchaliaaryanNo ratings yet
- Serv LetsDocument30 pagesServ LetsPreeti JawalkarNo ratings yet
- UNit 4 CompleteDocument3 pagesUNit 4 CompleteAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ServletDocument105 pagesUnit 5 ServletSagar PithadiaNo ratings yet
- Servlets Training Session, CGI, Hyderabad Date: 14 MAR 2011 - 15 MAR 2011Document33 pagesServlets Training Session, CGI, Hyderabad Date: 14 MAR 2011 - 15 MAR 2011tmhNo ratings yet
- Servletsintroduction Life CycleDocument73 pagesServletsintroduction Life Cyclejajupreetam100% (2)
- What Is Servlet: History of Web ApplicationDocument7 pagesWhat Is Servlet: History of Web ApplicationAnonymous rcmeSfj5No ratings yet
- 1.JAVA MODULE6 ServletDocument59 pages1.JAVA MODULE6 Servletsuyash agarwalNo ratings yet
- New Rich Text DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Rich Text Documentdeveshyadav11No ratings yet
- Unit7 Servlets and Java Server PageDocument20 pagesUnit7 Servlets and Java Server PagePrabesh KarkiNo ratings yet
- UNIT III - Web Servers and ServletsDocument23 pagesUNIT III - Web Servers and Servletsneed qNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets: The Servlet Life CycleDocument13 pagesJava Servlets: The Servlet Life CycleSheikh Azam AliNo ratings yet
- Servlet Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesServlet Interview QuestionsDurga SantuNo ratings yet
- Java ServletDocument71 pagesJava ServletTarjani ShahNo ratings yet
- Java Servlets: Replacement of CGIDocument34 pagesJava Servlets: Replacement of CGImaurya_asu3426No ratings yet
- JavaServlet TechnologyDocument27 pagesJavaServlet TechnologyMuKuLGaNo ratings yet
- Servlet NotesDocument21 pagesServlet NotesSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Servlets: RelationshipDocument95 pagesServlets: Relationshipstudy materialNo ratings yet
- SERVLETSDocument9 pagesSERVLETSCHINMAY SONINo ratings yet
- ServletsDocument33 pagesServletsShaheena BegumNo ratings yet
- JSP-Servlet Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandJSP-Servlet Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Lab Wireshark Packet Capture Assignment TutorialDocument8 pagesLab Wireshark Packet Capture Assignment TutorialHaseeb RazaNo ratings yet
- Current LogDocument10 pagesCurrent LogJuli MachucaNo ratings yet
- All Browser ElockClientNSE Installation GuideDocument9 pagesAll Browser ElockClientNSE Installation Guidenidhi jhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- A64 Datasheet V1.1 PDFDocument64 pagesA64 Datasheet V1.1 PDFpedisoj465No ratings yet
- Os Lab-11 PDFDocument27 pagesOs Lab-11 PDFTanveerNo ratings yet
- IFM ProfinetDocument15 pagesIFM ProfinetTapfumanei ZhouNo ratings yet
- Infinera-7100-Series-0169-SN-RevB-0122Document2 pagesInfinera-7100-Series-0169-SN-RevB-0122manhhaibcvtNo ratings yet
- Liang, Introduction To Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (C) 2011 Pearson Education, IncDocument43 pagesLiang, Introduction To Java Programming, Eighth Edition, (C) 2011 Pearson Education, IncAwadAyoubNo ratings yet
- Online Art Gallery Project ReportDocument25 pagesOnline Art Gallery Project ReportBnks SdfdsfsNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Ideapad L340 15IWL SpecDocument1 pageLenovo Ideapad L340 15IWL SpecTimuçinNo ratings yet
- Riverbed White PaperDocument10 pagesRiverbed White PaperSaqib GhaniNo ratings yet
- Item Description & QuantitiesDocument5 pagesItem Description & QuantitiesYoutube MeNo ratings yet
- 11 CSS Module Week 3Document23 pages11 CSS Module Week 3Alexander IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Major Report On Website Of: Submitted ByDocument46 pagesMajor Report On Website Of: Submitted BysaNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Smart Glove PRO 2Document23 pagesArduino Based Smart Glove PRO 2faisal aminNo ratings yet
- Perforce Users GuideDocument166 pagesPerforce Users GuideVijaya Lakshmi Bhupathi RajuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument48 pagesComputer Science NotesaDEOlu AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Control Lab To Study P Pi and Pid Temperature Controller For An Oven and Compare Their PerformanceDocument6 pagesLab Manual Control Lab To Study P Pi and Pid Temperature Controller For An Oven and Compare Their PerformanceVikasNehraNo ratings yet
- Transdutor de Força Oes 202M23Document6 pagesTransdutor de Força Oes 202M23Cristiano CezaraniNo ratings yet
- ValSpeQ33-L User ManualDocument90 pagesValSpeQ33-L User Manualvidaurre_89No ratings yet
- Working Effectively with Oracle's Public APIsDocument21 pagesWorking Effectively with Oracle's Public APIsappsloaderNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Wireless Biomedical Parameter Monitoring System Using ZigbeeDocument5 pagesArduino Based Wireless Biomedical Parameter Monitoring System Using ZigbeeBA BIaNo ratings yet
- Console Control Surface Simplifies Station OperationsDocument2 pagesConsole Control Surface Simplifies Station OperationsmelonmixNo ratings yet
- Lab Report DiodeDocument11 pagesLab Report DiodeMuhammad Hilmi0% (1)
- SkillDocument2 pagesSkillahoo125No ratings yet
- BS 5TH OS Lec19Document18 pagesBS 5TH OS Lec19ayman noreenNo ratings yet
- X-4046 VcoDocument8 pagesX-4046 VconirulfenNo ratings yet
- System Software Module 3: Machine-Dependent Assembler FeaturesDocument28 pagesSystem Software Module 3: Machine-Dependent Assembler Featuresvidhya_bineeshNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Hueber Planet 2 Lehrerhandbuch Tests Planet 2 Lehrerhandbuch Tests Please OverchargeDocument3 pagesDokumen - Tips Hueber Planet 2 Lehrerhandbuch Tests Planet 2 Lehrerhandbuch Tests Please OverchargeNathalia MeiNo ratings yet
- Load Dependent Interference Margin For Link Budget Calculations of OFDMA NetworksDocument3 pagesLoad Dependent Interference Margin For Link Budget Calculations of OFDMA NetworksMitikuNo ratings yet