Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiple Reflections: Iris Is A Dark Muscular Diaphragm That Controls The Size of The Pupil
Multiple Reflections: Iris Is A Dark Muscular Diaphragm That Controls The Size of The Pupil
Uploaded by
Trishna AryalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multiple Reflections: Iris Is A Dark Muscular Diaphragm That Controls The Size of The Pupil
Multiple Reflections: Iris Is A Dark Muscular Diaphragm That Controls The Size of The Pupil
Uploaded by
Trishna AryalCopyright:
Available Formats
Multiple reflections
Two mirrors inclined to each other give multiple images, due to multiple reflections.
When an object is kept between two parallel plane mirrors, infinite images are formed.
Dispersion of light
The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion.
Example: Rainbow
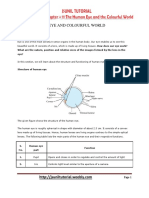
Human Eye
The human eye is a spherically shaped sense organ (diameter about 2.3 cm) that gives the sense of sight
and helps us perceive colours and depth.
Functions of different organs in the human eye
Light enters the eye through a thin membrane that forms a transparent bulge on the front of the
eye, called the cornea.
Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil.
The pupil is the small opening in the centre of the iris.
The lens which is behind the pupil helps to adjust the focal length required to clearly focus on
objects at various distances.
The retina is the screen where the images get formed. It is a delicate membrane with a large
number of photosensitive cells called rods and cones.
Cones are sensitive to bright light and rods are sensitive to dim light.
The optic nerve transmits the electrical signals from the eye to the brain.
Visual defects
Visual defects include the inability to see near objects, or the inability to see far objects.
In old people the lens becomes cloudy, a condition called cataract that impairs vision.
Seeing Sans Eyes
Braille system
Braille is a system to read and write for visually impaired people.
Consists of 63 dot patterns or characters.
These patterns are embossed in braille sheets that can be recognized on touch.
The dots are raised in order to make it easier to touch.
You might also like
- Eyes AnatomyDocument2 pagesEyes AnatomyAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The EyesDocument5 pagesStructure and Function of The EyesPreeti ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Biology Eye NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Eye NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument34 pagesAnatomy of The EyeHarsh DesaiNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Eye and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsFrom EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsNo ratings yet
- 6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Document35 pages6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Eyes Explained: Actions For This PageDocument3 pagesEyes Explained: Actions For This PageAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- 937 Anatomy of The EyeDocument34 pages937 Anatomy of The EyeThariqNo ratings yet
- (Anatomy of The Eye) STUDY!!!Document1 page(Anatomy of The Eye) STUDY!!!Analisa LacaranNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Human Eye and Colourful World - NotesDocument10 pagesCH 11 Human Eye and Colourful World - NotesPankaj PaithankarNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument21 pagesThe Human EyeMichel ThorupNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up An EyeDocument3 pagesWhat Makes Up An EyenandhantammisettyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EyeDocument11 pagesAnatomy of EyeAbi Nan ThanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Eye !Document11 pagesStructure of Eye !Leonora KadriuNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Eye and VisionDocument3 pagesPhysics of The Eye and VisionhusseinNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World NotesDocument13 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World NotesSreejith SurendranNo ratings yet
- Eye NotesDocument21 pagesEye NotesViswaNo ratings yet
- Light - Class NotesDocument6 pagesLight - Class Noteskirankarnawat29No ratings yet
- CH 11 Human Eye and Colourful World - Notes-MergedDocument17 pagesCH 11 Human Eye and Colourful World - Notes-MergedPankaj PaithankarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of The Human EyeAljhon DelfinNo ratings yet
- The Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionDocument5 pagesThe Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Creating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesCreating 3D Eyes: One: The Anatomy of The Human Eyekora_c995No ratings yet
- The EyeDocument6 pagesThe EyeDebiprasad GhoshNo ratings yet
- Eye Lecture GuideDocument46 pagesEye Lecture Guidemaj0% (1)
- Anatomy of The Visual SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Visual SystemMahrukhNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument10 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- CSS Everyday Science Notes PDFDocument50 pagesCSS Everyday Science Notes PDFWaqas Gul100% (1)
- Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful WorldSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- OLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesOLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldRadhika GargNo ratings yet
- HUMAN EYE Class XDocument25 pagesHUMAN EYE Class Xsai projectNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Eyesen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- 1.6 Sense of SightDocument10 pages1.6 Sense of SightFidah MadNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument22 pages11.human Eye and Colourful WorldMalancha high school HSNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Handout No 13 The EyeDocument7 pagesIntegrated Science Handout No 13 The EyeTianna LivanNo ratings yet
- Human Eye 1Document13 pagesHuman Eye 1GUNJAN SHARMANo ratings yet
- The Sense Organs - The EyeDocument1 pageThe Sense Organs - The EyeKarol PeñaNo ratings yet
- Vision:: 1-Outer LayerDocument3 pagesVision:: 1-Outer LayerAimal IhsasNo ratings yet
- Sec 8 BDocument3 pagesSec 8 BShiela Marie RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument11 pagesHuman EyeblehblehdadaNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument3 pagesThe Human EyeKajetano GraucosNo ratings yet
- EYE Notes IgcseDocument3 pagesEYE Notes IgcseTay HermyNo ratings yet
- Keep Reading To Find Out What These Parts of The Human Eye Do and How They Contribute To Us Being Able To SeeDocument6 pagesKeep Reading To Find Out What These Parts of The Human Eye Do and How They Contribute To Us Being Able To SeeAirlangga kusuma HartoyoNo ratings yet
- Windows To The World - Unveiling The Wonders of The Human EyeDocument2 pagesWindows To The World - Unveiling The Wonders of The Human EyeYienNo ratings yet
- Our Sense of Sight and LightDocument6 pagesOur Sense of Sight and LightCikgu EzanNo ratings yet
- Presenttion in ScienceDocument6 pagesPresenttion in ScienceJinky Recelestino YacubNo ratings yet
- Coordination: NotesDocument6 pagesCoordination: Notesyuki soraNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument1 pageHuman EyeKirti GargNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument54 pagesHuman EyeRadu VisanNo ratings yet
- SENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Document5 pagesSENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Said SakerNo ratings yet
- CL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDocument12 pagesCL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDeepanshu BindalNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESDocument12 pagesUNIT 6 Sensory System Vision AND Perception NOTESKristine Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- Basic Eye Anatomy: CorneaDocument6 pagesBasic Eye Anatomy: CorneaGayatri Gaur100% (1)
- Ch.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheDocument17 pagesCh.11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World: The Human Eye: It Is A Natural Optical Instrument Which Is Used To See TheIshi SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteJay MakiNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X For 2017 18Document22 pagesPhysics Class X For 2017 18KalaiNo ratings yet
- How Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Can My Eyes See? Sight and the Eye - Biology 1st Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet