Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Variance Formulas
Uploaded by
khanmohnoor550Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Variance Formulas
Uploaded by
khanmohnoor550Copyright:
Available Formats
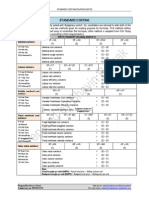
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
COST VARIANCES
1) Material variances (single raw material)
Case - I Material quantity purchased = Material quantity consumed
(i) Total material cost variance Here:
= SC x SQ – AC x AQ SC = Standard cost per Kg
OR AC = Actual cost per Kg
= MPV + MQV AQ = Actual total quantity used for actual output
(ii) Material price variance [MPV] SQ = Standard total quantity which should have been used
= AQ x SC – AQ x AC for actual output
(iii) Material usage/quantity variance [MQV]
= SC x SQ – SC x AQ
Case - II Material quantity purchased ≠ Material quantity consumed
(a) If inventory is measured at standard cost (i.e. MPV is recorded at the time of purchase)
(i) Total material cost variance
= SC x SQ – [SC x Opening RM + AC x AQ(purchased) – SC x Closing RM]
OR
= MPV + MQV
(ii) Material price variance
= AQ(purchased) x SC – AQ(purchased) x AC
(iii) Material usage variance
= SC x SQ – SC x AQ(used)
(b) If inventory is measured at actual cost (i.e. MPV is recorded at the time of issuance)
[If nothing is mentioned even then assume this case in question]
(i) Total material cost variance
= SC x SQ – AC x AQ(used)
OR
= MPV + MQV
(ii) Material price variance
= AQ(used) x SC – AQ(used) x AC
(iii) Material usage variance
= SC x SQ – SC x AQ(used)
2) Direct labor variances (single type of labor)
Case - I No separate record of idle time is kept OR Hours worked = hours paid
(i) Total labor cost variance Here:
= SR x SH – AR x AH SR = Standard rate per hour
OR AR = Actual rate per hour
= LRV + LEV AH = Actual total hours used for actual output
(ii) Labor rate variance [LRV] SH = Standard total hours which should have been used
= SR x AH – AR x AH for actual output
(iii) Labor efficiency variance [LEV]
= SR x SH – SR x AH
NASIR ABBAS FCA Page 1 of 5
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
Case - II Separate record of idle hours is kept OR Hours worked ≠ hours paid
(a) Idle time is not part of standard cost (i.e. ignored in standard card) (default case in exam)
(i) Total labor cost variance
= SR x SH – AR x AH(paid)
OR
= LRV + LEV + Idle time variance
(ii) Labor rate variance
= AH(paid) x SR – AH(paid) x AR
(iii) Idle time variance
= SR x AH(worked) – SR x AH(paid)
(iii) Labor efficiency variance
= SR x SH – SR x AH(worked)
(b) Idle time is made part of standard cost as a separate element
(i) Total labor cost variance
= SR x SH(paid) – AR x AH(paid) Here:
OR SH (paid) = Standard total hours which should have been
= LRV + LEV + Idle time variance paid for actual output
(ii) Labor rate variance SH (idle) = Standard total hours which should have been
= AH(paid) x SR – AH(paid) x AR remained idle for actual output
(iii) Idle time variance SH (worked) = Standard total hours which should have been
= SH (idle) x SR – AH (idle) x SR worked for actual output
(iv) Labor efficiency variance
= SR x SH(worked) – SR x AH(worked)
3) VOH variance
(i) Total variable OH cost variance
= SR x SH – AR x AH Here:
OR SR = Standard rate per hour (machine or labor)
= Spending variance + Efficiency variance AR = Actual rate per hour (machine or labor)
(ii) VOH expenditure / spending variance AH = Actual total hours (machine or labor) used for
= AH x SR – AH x AR actual output
(iii) VOH efficiency variance SH = Standard total hours (machine or labor) which
= SR x SH – SR x AH should have been used for actual output
NASIR ABBAS FCA Page 2 of 5
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
4) Fixed OH variance
(i) Total fixed OH cost variance
= Applied fixed OH – Actual fixed OH Here:
AH = Actual total hours (machine or labor) used
OR for actual output
= Spending variance + volume variance SH = Standard total hours (machine or labor) which
(ii) Fixed OH expenditure / spending variance should have been used for actual output
= Budgeted fixed OH – Actual fixed OH BH = Standard total hours (machine or labor) which
would be used for budgeted output
(iii) Fixed OH volume variance Applied fixed OH = SR x SH
= Applied fixed OH – Budgeted fixed OH Budgeted fixed OH = SR x BH
Volume variance can be further analyzed into:
(a) Fixed OH efficiency variance
= SR x SH – SR x AH
(b) Fixed OH capacity variance
= SR x AH – BH x SR
Notes - In case of marginal costing, there is NO fixed OH volume variance
SALE VARIANCE
1) Sales price variance
= AQ (sale) x Actual price – AQ (sale) x Standard price
2) Sales volume variance
(a) Sales profit volume variance [used in case of absorption costing]
= [AQ (sale) – BQ (sale)] x standard profit per unit
(It is used if SCC is prepared on absorption costing)
(b) Sales contribution volume variance [used in case of marginal costing]
= [AQ (sale) – BQ (sale)] x standard contribution per unit
Exam notes:
- If not given in question, students should prepare a detailed standard cost card first from
information given in question. It will help in calculating variances.
- If standard cost card is not given but budgeted P&L is given in question, then “per unit costs” from
budgeted P&L will be the standard costs.
- All above formulas are designed so that “positive” answer shows “favorable variance” and
“negative” answer shows “adverse variance”.
- All cost variances are calculated for actual FG production for the period instead of sales.
- If process costing is mixed, then SH/AH and SQ/AQ will be based on "equivalent produced FG
units for the period calculated using FIFO basis" instead of "actual FG units produced for the
period"
NASIR ABBAS FCA Page 3 of 5
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
OPERATING STATEMENT [i.e. Reconciliation of budgeted profit and actual profit]
Rs. Rs.
Budgeted GP X
Sale variances:
Sale price variance X
Sale volume variance X X
Cost variances:
Material price variance X
Material usage variance X
Labor rate variance X
Labor efficiency variance X
Labor Idle time variance X
VOH spending variance X
VOH efficiency variance X
FOH spending variance X
FOH volume variance [Only for absorption costing] X X
Actual profit X
Exam notes:
- Add all “favorable variances” and deduct all “adverse variances” in above format.
- Replace "fixed OH efficiency and capacity variances" with "fixed OH volume variance" and
"Material yield and mix variances" with "material usage variance" if separately required in
question.
- If FG and WIP stocks are valued at actual cost then an adjustment is required as follows:
[Actual cost of closing stock - Standard cost of closing stock] XXX
[Standard cost of opening stock - Actual cost of opening stock] XXX
ADVANCED VARIANCE ANALAYSIS
1) Material mix and yield variances
If a product uses more than one type of direct materials and such materials are substitutable (i.e. less of one type
of material can be compensated by more of another material), then material usage variance is further analyzed
into:
- Material mix variance
- Material yield variance
The total of these two variances is equal to material usage variance.
(i) Mix variance
- Following formula is applied to each RM individually and then totaled:
= [AQ in SM – AQ in AM] x SC
here:
AQ in SM = Actual total, of all material quantities used, split in standard mix
AQ in AM = Actual material quantities used
NASIR ABBAS FCA Page 4 of 5
VARIANCE ANALYSIS
(ii) Yield variance
- Following formula is applied to each RM individually and then totaled:
= [SQ in SM – AQ in SM] x SC
here:
AQ in SM = Actual total, of all material quantities used, split in standard mix
SQ in SM = Standard material quantity of each material to be used for actual output
Exam notes:
If losses are also incorporated as a part of standard card then “SQ in SM” column is calculated as
follows:
If FG is given units:
SQ in SM = standard material (kg) x Actual FG production (units) / FG units for which standard is
set
If FG is given Kgs:
SQ in SM = standard material (kg) x Actual FG production (Kgs) / FG Kgs of which standard is set
NASIR ABBAS FCA Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Chap 11 - Variance AnalysisDocument10 pagesChap 11 - Variance AnalysisNehal OmarNo ratings yet
- Mas 07Document14 pagesMas 07Christine Jane AbangNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing FormulaDocument2 pagesStandard Costing FormulaAce Erguiza50% (2)
- 5-Standard Costing and GP Variance AnalysisDocument16 pages5-Standard Costing and GP Variance AnalysisMelybelle LaurelNo ratings yet
- MAS-42G (Standard Costing With GP Variance Analysis)Document14 pagesMAS-42G (Standard Costing With GP Variance Analysis)Bernadette PanicanNo ratings yet
- 06 Standard Costing PDFDocument5 pages06 Standard Costing PDFMarielle CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Variance ANALYSISDocument10 pagesVariance ANALYSISWaseim khan Barik zaiNo ratings yet
- P 15 5. Standard Costing ChartDocument1 pageP 15 5. Standard Costing ChartHari MNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4mark fernandezNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING and Variance AnalysisDocument30 pagesSTANDARD COSTING and Variance AnalysisAlthon JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Advanced VariancesDocument27 pagesChapter - 12 Advanced Variancesthakkert25No ratings yet
- Overhead and Other Variances PDFDocument26 pagesOverhead and Other Variances PDFAnuruddha RajasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Module 005 Standard CostingDocument12 pagesModule 005 Standard CostinggagahejuniorNo ratings yet
- ACC2008 - Lec 3 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead CostsDocument29 pagesACC2008 - Lec 3 - Flexible Budgeting and Analysis of Overhead CostsSu-Kym TanNo ratings yet
- Formula List of Basic Variance PDFDocument4 pagesFormula List of Basic Variance PDFShi Yan LNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Chapter 6Document3 pagesLecture Notes - Chapter 6Saint BakemonoNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING - Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesSTANDARD COSTING - Cost AccountingDarwin DionisioNo ratings yet
- Costing Notes Chapter - Standard Costing: MCV Muv + MPV and Muv Myv + MMVDocument12 pagesCosting Notes Chapter - Standard Costing: MCV Muv + MPV and Muv Myv + MMVSocial SectorNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: Output (Eg. Pieces Per Unit)Document4 pagesStandard Costing: Output (Eg. Pieces Per Unit)glcpaNo ratings yet
- Formula For Calculating Variances - UpdatedDocument3 pagesFormula For Calculating Variances - UpdatedNikita ConatyNo ratings yet
- Operating Statement (Absorption Costing) Sales VariancesDocument2 pagesOperating Statement (Absorption Costing) Sales VariancesHushnak AliNo ratings yet
- Advanced VariancesDocument7 pagesAdvanced Variancesthakkert25No ratings yet
- Standart Costing PDFDocument3 pagesStandart Costing PDFVIHARI DNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: QUANTITY Standard - Indicates The Quantity of Raw Materials orDocument19 pagesStandard Costing: QUANTITY Standard - Indicates The Quantity of Raw Materials orMarielle Mae Burbos100% (2)
- Variances: 1) Material VarianceDocument21 pagesVariances: 1) Material Variancedosani90No ratings yet
- Answer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Document5 pagesAnswer:: Managerial Accounting Quiz (Online)Zia UddinNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 MNGT Acctng PDFDocument4 pagesChap 4 MNGT Acctng PDFRose Ann YaboraNo ratings yet
- Synth 1 (STD COSTING)Document11 pagesSynth 1 (STD COSTING)Hassan AdamNo ratings yet
- Costing FormulasDocument4 pagesCosting FormulasAlkaNo ratings yet
- MAS 2 - Standard CostingDocument13 pagesMAS 2 - Standard CostingLovely Mae Lariosa100% (1)
- Standard Costing FormulaeDocument1 pageStandard Costing FormulaeMUSTHARI KHANNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument8 pagesSummarySittiehaina GalmanNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument2 pagesStandard CostingJon LeinsNo ratings yet
- Variable Production Overhead Variance (VPOH)Document9 pagesVariable Production Overhead Variance (VPOH)Wee Han ChiangNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis As Applied ToDocument39 pagesStandard Costing and Variance Analysis As Applied TorhearomefranciscoNo ratings yet
- STCM06 Standard CostingDocument31 pagesSTCM06 Standard Costingdin matanguihanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Varians Dan Standar Products CostsDocument4 pagesAnalisis Varians Dan Standar Products CostsAhad KamisNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing & Variance AnalysisDocument10 pagesStandard Costing & Variance AnalysisMariella Antonio-NarsicoNo ratings yet
- Formulas in CostDocument3 pagesFormulas in CostHappyPurpleNo ratings yet
- Formula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointDocument24 pagesFormula:: High Low Method (High - Low) Break-Even PointRedgie Mark UrsalNo ratings yet
- Block 4 MCO 5 Unit 2Document32 pagesBlock 4 MCO 5 Unit 2Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Variance AnalysisDocument15 pages7 - Variance AnalysisRakeysh RakyeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Standard Costing - SynopsisDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Standard Costing - SynopsissajedulNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets, Overhead Cost Variances, and Management ControlDocument30 pagesFlexible Budgets, Overhead Cost Variances, and Management ControlabeeraNo ratings yet
- Summary Standard CostingDocument2 pagesSummary Standard CostingMaria Callista LovinaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing: SUPER SUMMARY (Reading Method 1) Material VarianceDocument5 pagesStandard Costing: SUPER SUMMARY (Reading Method 1) Material VarianceWinnieOngNo ratings yet
- MAS - Variance AnalysisDocument6 pagesMAS - Variance AnalysisJohn Mahatma Agripa100% (1)
- VariancesDocument45 pagesVariancesanonNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions: Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument54 pagesCost Accounting Foundations and Evolutions: Standard Costing and Variance AnalysismarieieiemNo ratings yet
- AH Accounting FormulaeSheetVarianceAnalysis PDFDocument2 pagesAH Accounting FormulaeSheetVarianceAnalysis PDFAditi SInghNo ratings yet
- Overhead Variance - PinnacleDocument2 pagesOverhead Variance - PinnacleMagadia Mark JeffNo ratings yet
- Javier Danna Assignment IM17.1 17.4 17.5 17.7Document14 pagesJavier Danna Assignment IM17.1 17.4 17.5 17.7Danna ClaireNo ratings yet
- Disposition of VariancesDocument12 pagesDisposition of VariancesNors PataytayNo ratings yet
- SCM Discussion 6Document10 pagesSCM Discussion 6M4ZONSK1E OfficialNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Summary For CA Inter, CMA Inter, CS ExecutiveDocument5 pagesStandard Costing Summary For CA Inter, CMA Inter, CS Executivecd classes100% (1)
- Cost Accounting Formula'sDocument7 pagesCost Accounting Formula'sdigital_darwaish82% (38)
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)