Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Prokaryote Is A Single
A Prokaryote Is A Single
Uploaded by
Jemima TapioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Prokaryote Is A Single
A Prokaryote Is A Single
Uploaded by
Jemima TapioCopyright:
Available Formats
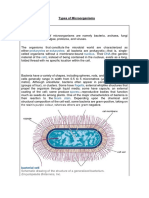
A prokaryote is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
This class of organisms includes all of the bacteria. Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells
lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the
bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most
prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure.
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth.
Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include
cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis. A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane
and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm.
Although invisible to the naked eye, prokaryotes are an essential component of the earth's
biota. They catalyze unique and indispensable transformations in the biogeochemical cycles of
the biosphere, produce important components of the earth's atmosphere, and represent a large
portion of life's genetic diversity.
Escherichia coli.
Streptococcus.
Nostoc.
Anabaena.
Cyanobacteria.
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a
membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes
store their genetic information.
You might also like
- Lesson Overview 20.2 ProkaryotesDocument38 pagesLesson Overview 20.2 ProkaryotesConnie Gomez100% (1)
- Archebacteia and EubacteriaDocument4 pagesArchebacteia and Eubacteriasannidhim123No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument5 pagesProkaryotes Vs Eukaryotesapi-235347129No ratings yet
- Overview of Microbial LifeDocument9 pagesOverview of Microbial LifeQuan ThieuNo ratings yet
- Raven06 34 PDFDocument15 pagesRaven06 34 PDFAbdullah DiefNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, S-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesMicrobiology, S-WPS OfficejoanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of BacteriaDocument15 pagesIntroduction of BacteriaAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- The World of OrganismsDocument30 pagesThe World of Organismsvuminhtut66No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic CellsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- MikrobaDocument35 pagesMikrobaYanuariafitrianaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: Lesson 5 - Five Kingdoms, Three DomainsDocument3 pagesLesson 5: Lesson 5 - Five Kingdoms, Three DomainsKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- 20160624120627topic 2 - CellsDocument30 pages20160624120627topic 2 - CellshilmanNo ratings yet
- Aster Ace A e FamilyDocument25 pagesAster Ace A e FamilyMuh ArzadNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes vs. EukaryotesChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Diversity'of PlantsDocument299 pagesDiversity'of PlantsAbubakkar SaddiqueNo ratings yet
- ZH Core IV - Cell BiologyDocument95 pagesZH Core IV - Cell Biologysahib100% (1)
- Unit 2Document22 pagesUnit 2NAVEENNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument2 pagesClassification of Organismsjocelynmillano115No ratings yet
- Components of A Cell and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesComponents of A Cell and Their FunctionsAnonymous Gv1oiPaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 pagesProkaryotic vs. EukaryoticJaniya KellyNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic BiodegradationDocument19 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic BiodegradationENSO Plastics, LLC100% (1)
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Study of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument42 pagesStudy of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotesali raza100% (1)
- Bio101 Lec1 Prokaryotes 19 09 2019Document43 pagesBio101 Lec1 Prokaryotes 19 09 2019Owusu GideonNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document23 pagesEarth and Life Science 11Red LopezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology UNIT 1Document43 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology UNIT 1Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Types of MicroorganismsDocument2 pagesTypes of MicroorganismsIgnacio condoriNo ratings yet
- Las q3 Week-2 Gen - Bio-1 Viros SnsDocument10 pagesLas q3 Week-2 Gen - Bio-1 Viros SnsFranzhean Balais CuachonNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiologycoolinkenanatamNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 IntroductionDocument22 pagesLec 1 IntroductionAmmara MalikNo ratings yet
- 1.5 ProkaryotesDocument17 pages1.5 ProkaryotesKate Rashell SevillaNo ratings yet
- MCB 211 NoteDocument20 pagesMCB 211 NoteTemidayo OwadasaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1102K Chapter 13 NotesDocument24 pagesBIOL 1102K Chapter 13 NotesAmber Mason TurnerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Handout-4Document47 pagesMicrobiology Handout-4cherishkathy123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Prokaryotes, EukaryotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Prokaryotes, EukaryotesMetchie Rico RafaelNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaDocument4 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Quiapo, ManilaKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- MBC AssignmentDocument6 pagesMBC AssignmentTemp TempNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument1 pageMitochondriaRavin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- BiologyRSMouhamad Converted1 PDFDocument44 pagesBiologyRSMouhamad Converted1 PDFKatie priceNo ratings yet
- Microworld and You 1Document71 pagesMicroworld and You 1Alyssa Mae Navales100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument21 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellskenNo ratings yet
- Eukaryote BiologyDocument9 pagesEukaryote BiologyKrizzy EstoceNo ratings yet
- Structured Assignment of Plant In-Vitro Culture: Review Lecture For Mid-TermDocument7 pagesStructured Assignment of Plant In-Vitro Culture: Review Lecture For Mid-TermLukman Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- BiologyRSMouhamad Converted1Document44 pagesBiologyRSMouhamad Converted1Johnson IdowuNo ratings yet
- Ori Bchet 149Document72 pagesOri Bchet 149Chandan SahNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells: Lecture Number 2: TopicsDocument2 pagesStructure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells: Lecture Number 2: Topicsalex zhangNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology PDFDocument226 pagesBacteriology PDFWaseem Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Lab Prep Aidan BrueschDocument2 pagesBacterial Lab Prep Aidan BrueschAidan BrueschNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Lab Prep Aidan BrueschDocument2 pagesBacterial Lab Prep Aidan BrueschAidan BrueschNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 OutlineDocument3 pagesChapter 7 OutlineRyan SolomonNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Bio Sel Bab 1-4Document92 pagesBahan Ajar Bio Sel Bab 1-4Maychel Arientawira JohannisNo ratings yet
- Bacteria - Definition, Shapes, Characteristics, Types & ExamplesDocument2 pagesBacteria - Definition, Shapes, Characteristics, Types & ExamplesBaikuntha SabarNo ratings yet
- Archaea and BacteriaDocument3 pagesArchaea and BacteriaMartin ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Topic: Bacteria: EtymologyDocument28 pagesTopic: Bacteria: EtymologyVINDHYA SHANKERNo ratings yet
- GERMICIDALDocument19 pagesGERMICIDALVillacrusis, Abegail C.No ratings yet
- Parker 2001Document6 pagesParker 2001Chinasa EkejiubaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic - Origins. BIOMOLDocument4 pagesEukaryotic - Origins. BIOMOLMarcia Iguarán GarzónNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12Jemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Module-5-Accounting-2-Partnership-Liquidation-by-InstallmentDocument9 pagesModule-5-Accounting-2-Partnership-Liquidation-by-InstallmentJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 RecruitmentDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 3 RecruitmentJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 RecruitmentDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2 RecruitmentJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- ENTREPRENEURSHIPDocument18 pagesENTREPRENEURSHIPJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RecruitmentDocument5 pagesChapter 1 RecruitmentJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Team Sports HandoutDocument2 pagesTeam Sports HandoutJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 6 7Document20 pagesChapter 5 6 7Jemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Entrep G 2 ReportDocument33 pagesEntrep G 2 ReportJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ManagementDocument7 pagesChapter 7 ManagementJemima TapioNo ratings yet
- CH 1 ManagementDocument17 pagesCH 1 ManagementJemima TapioNo ratings yet