Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Page 005
Page 005
Uploaded by
popsformarchingbandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 005
Page 005
Uploaded by
popsformarchingbandCopyright:
Available Formats
Marcelo Milan I
central banks and governments, which temporarily avoided a similar collapse, there
is some pressure on the currency and financiai global market. The main role played
by the dollar in the global fmancial markets became clear again during the fmancial
criais in 2007. McGuire and Von Peter (2009) discuss the scarcity of dollars at the
international banking market, showing the enormous dependency of financiai
markets and of the global economy on U.S. dollars. On the other hand, financiai
transactions have great sensibility to changes in the value of the U.S. currency,
which may challenge the dollar's hegemonic role. In other words, since the dollar is
the main source of liquidity of these markets, the lack of this currency may lead to a
full rupture on the functioning of these markets. But the very maintenance of this
asymmetry reinforces the problems that led to the crises, and its resolution may
radically change the dollar's role on the world economy. lll
z
Maybe even more important, the financiai cns1s has shattered both
o
neoliberalism as an ideological regime informing national economic policies and the ~
w
world fmancial system that was sustained and expanded based on the adoption of ClJl!
....1
these measures. Any attempts to keep the U .S. hegemony sustained by this ideology <
z
and by the global operation oflarge U.S.- and to a lower scale, European- financiai o
institutions will face great difficulties. Especially due to the fact that countries from
~
zClJl!
the capitalist periphery today have conditions to operate with relative autonomy
from the center. But in which sense the fmancial crisis representa a transition to a w
1-
world order where the dollar and the U .S. economy would play a different, or a less
important role?
-z~
~
w
~
Continuity and rupture of U .S. hegemony
t;;
u..
o
....1
Tavares (1997) and Tavares and Melin (1997) discuss the resumption and <
z
reaffirmation of U.S. hegemony. The authors do not focus on the US' political and ClJl!
=»
economic power, even though the strong dollar diplomacy has played an important
role in the 1980's, focusing instead on the country's capacity to shape political and
economic options in other countries. For instance, the neoliheral policies, imposed as
-oz
<
::i
the only policy option, created the conditions necessary to avoid the German and
J apanese challenges and the rise of a polycentric world. They also allowed the
creation of a new international division of labor based on the internationalization of
U.S. capital. However, the authors do not consider China's rise and the destahilizing
potential of those arrangements, especially regarding the possihility of challenges to
the dollar's role due to the harshness of the of 2007 crisis.
129
You might also like
- Allergy Test ResultDocument10 pagesAllergy Test ResultBabukutty JacobNo ratings yet
- Multipolarity PDFDocument6 pagesMultipolarity PDFNatasha InayyatNo ratings yet
- Dollar ReportDocument26 pagesDollar ReportNirati AroraNo ratings yet
- " Project Charter ": Reading AssignmentDocument26 pages" Project Charter ": Reading AssignmentJankey NdagileNo ratings yet
- Getting Hegemony Right: - G. John IkenberryDocument9 pagesGetting Hegemony Right: - G. John IkenberrybambooinaNo ratings yet
- Sindh Land Revenue Act 1967Document62 pagesSindh Land Revenue Act 1967Tarique Jamali100% (1)
- Great Global Shift WhitepaperDocument20 pagesGreat Global Shift WhitepapermcampuzaNo ratings yet
- Joseph Nye Soft Power JournalDocument20 pagesJoseph Nye Soft Power JournalabdouNo ratings yet
- Financial Crisis, Contagion, and Containment: From Asia to ArgentinaFrom EverandFinancial Crisis, Contagion, and Containment: From Asia to ArgentinaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Page 003Document1 pagePage 003popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Periodising Money and Currency Relations: Part Two - Chapter SixDocument7 pages3.3 Periodising Money and Currency Relations: Part Two - Chapter SixFrancisco MartinezNo ratings yet
- Page 010Document1 pagePage 010popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 007Document1 pagePage 007popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 009Document1 pagePage 009popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- The State of The LandscapeDocument5 pagesThe State of The Landscapegiorgiogarrido6No ratings yet
- Explaining US StrategyDocument6 pagesExplaining US StrategyarchaeopteryxgrNo ratings yet
- The Right Grand Strategy: G. John IkenberryDocument3 pagesThe Right Grand Strategy: G. John IkenberrygregoryperezNo ratings yet
- PC ZD JPF The Threat of Currency Wars A European PerspectiveDocument17 pagesPC ZD JPF The Threat of Currency Wars A European PerspectiveBruegelNo ratings yet
- What Is International Political EconomyDocument4 pagesWhat Is International Political Economyzubair khanNo ratings yet
- Pauly Chap8inravenhillDocument33 pagesPauly Chap8inravenhillJuan Esteban Arratia SandovalNo ratings yet
- International Political Economy Beyond Hegemonic StabilityDocument10 pagesInternational Political Economy Beyond Hegemonic StabilityRaikaTakeuchiNo ratings yet
- Impact of 2008 CrisisDocument9 pagesImpact of 2008 Crisisdoko98No ratings yet
- What Is International Political Economy?Document4 pagesWhat Is International Political Economy?umarNo ratings yet
- HUM 6.1 Final Text SARGENTDocument16 pagesHUM 6.1 Final Text SARGENTChris MacartneyNo ratings yet
- Soft Power by Joseph S NyeDocument19 pagesSoft Power by Joseph S NyemohsinshayanNo ratings yet
- Cooper TurbulenceDocument25 pagesCooper TurbulenceJarrettMoranNo ratings yet
- S1-Latin America Confronting The Asian Crisis (31 P.)Document32 pagesS1-Latin America Confronting The Asian Crisis (31 P.)uchitewaNo ratings yet
- Page 006Document1 pagePage 006popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Bank Crisis 1Document6 pagesBank Crisis 1ghaj2006No ratings yet
- Readings: Reveron and Mahoney Norris CH 8, Zakaria, Bacevich, Ferguson, JoffeDocument13 pagesReadings: Reveron and Mahoney Norris CH 8, Zakaria, Bacevich, Ferguson, Joffednm110No ratings yet
- Europe, The International System and A Generational ShiftDocument4 pagesEurope, The International System and A Generational ShiftIulia ModigaNo ratings yet
- Power and Wall StreetDocument5 pagesPower and Wall StreetDoris SorianoNo ratings yet
- Is China The New America?Document4 pagesIs China The New America?lawrenceNo ratings yet
- Cepal: ReviewDocument10 pagesCepal: ReviewmarceloscarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Washington ConsensusDocument1 pageBeyond The Washington ConsensusRafael Machado Pereira C de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- The American Phoenix: And why China and Europe will struggle after the coming slumpFrom EverandThe American Phoenix: And why China and Europe will struggle after the coming slumpNo ratings yet
- A Partnership With China To Avoid World WarDocument11 pagesA Partnership With China To Avoid World WarCata CataNo ratings yet
- The Hegemony of The US DollarDocument4 pagesThe Hegemony of The US DollarJoey MartinNo ratings yet
- Influence of The Power of Great Powers On Emerging StatesDocument17 pagesInfluence of The Power of Great Powers On Emerging StatesJohn Mauricio Ramos DuqueNo ratings yet
- Melinda Cooper - Turbulent WorldsDocument24 pagesMelinda Cooper - Turbulent WorldsZeynep OguzNo ratings yet
- International Monetary SystemDocument6 pagesInternational Monetary SystemBora EfeNo ratings yet
- Terra Firma - Q2'10 LetterDocument5 pagesTerra Firma - Q2'10 LetterDima MostovoyNo ratings yet
- China and The Return of Great Power Strategic Competition: Executive SummaryDocument11 pagesChina and The Return of Great Power Strategic Competition: Executive SummaryValentina SadchenkoNo ratings yet
- Gelb LeslieDocument4 pagesGelb LeslieStefan TCNo ratings yet
- Understanding The IMF Debate: Homas IllettDocument18 pagesUnderstanding The IMF Debate: Homas Illettharishstud00No ratings yet
- The Crisis of The Early 21st CenturyDocument47 pagesThe Crisis of The Early 21st CenturyicesunnyNo ratings yet
- U.S. Hegemony Today - Peter GowanDocument12 pagesU.S. Hegemony Today - Peter GowanpeterVoterNo ratings yet
- Wade 2000Document28 pagesWade 2000HillarylaCruzNo ratings yet
- Ankel AssessingRMB4!6!07cbgDocument78 pagesAnkel AssessingRMB4!6!07cbgMilanNo ratings yet
- The Credit CrisisDocument13 pagesThe Credit CrisisbowssenNo ratings yet
- Dollar HegemonyDocument30 pagesDollar HegemonyFatihBayezitNo ratings yet
- America's Imperial Ambition Foreign AffairsDocument22 pagesAmerica's Imperial Ambition Foreign Affairssergio tavaresNo ratings yet
- The Immoderate World Economy: Maurice ObstfeldDocument23 pagesThe Immoderate World Economy: Maurice ObstfeldDmitry PreobrazhenskyNo ratings yet
- National Security Strategy: of TheDocument34 pagesNational Security Strategy: of TheAndrei IjacNo ratings yet
- Zhenqiang-The US-Europe China Triangle in An Increasingly Multipolar WorldDocument33 pagesZhenqiang-The US-Europe China Triangle in An Increasingly Multipolar Worldmadus666No ratings yet
- Next Gen Global CurrencyDocument17 pagesNext Gen Global CurrencyShehryar Akhter AliNo ratings yet
- Is This The Beginning of The End of Central Bank Independence?Document40 pagesIs This The Beginning of The End of Central Bank Independence?Anonymous HsoXPyNo ratings yet
- The New International Relations - From Crisis Management To Strategic GovernanceDocument26 pagesThe New International Relations - From Crisis Management To Strategic GovernanceAnonymous 8O9X3QtR4No ratings yet
- Stem Erg Ing PowersDocument25 pagesStem Erg Ing PowersspeedymiguelNo ratings yet
- Hill, C. Foreign Policy in The Twenty-First Century. Cap. 6Document33 pagesHill, C. Foreign Policy in The Twenty-First Century. Cap. 6Flor MartinezNo ratings yet
- The International Monetary System Is Changing: What Opportunities and Risks For The Euro?Document20 pagesThe International Monetary System Is Changing: What Opportunities and Risks For The Euro?BruegelNo ratings yet
- No Development Without Security: The Transatlantic Donor Community Needs To Redesign Aid For Fragile StatesDocument28 pagesNo Development Without Security: The Transatlantic Donor Community Needs To Redesign Aid For Fragile StatesGerman Marshall Fund of the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Page 008Document1 pagePage 008popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 006Document1 pagePage 006popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 020Document1 pagePage 020popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 018Document1 pagePage 018popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 015Document1 pagePage 015popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 017Document1 pagePage 017popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Page 004Document1 pagePage 004popsformarchingbandNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma at 3mDocument13 pagesSix Sigma at 3mAltansukhDamdinsurenNo ratings yet
- English - Direction North South East West - Rosa Dos VentosDocument3 pagesEnglish - Direction North South East West - Rosa Dos VentosBbook One100% (1)
- Upadesha Sahasri: by Adi Sankaracharya, Translated by Swami Jagadananda Published by Sri Ramakrishna Math, ChennaiDocument18 pagesUpadesha Sahasri: by Adi Sankaracharya, Translated by Swami Jagadananda Published by Sri Ramakrishna Math, Chennairichard_kangNo ratings yet
- Polity Questions in Upsc Prelims 2022 26Document6 pagesPolity Questions in Upsc Prelims 2022 26RamdulariNo ratings yet
- MP190E34W: Technical DescriptionsDocument19 pagesMP190E34W: Technical DescriptionsBroCactusNo ratings yet
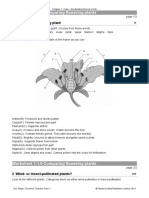
- Worksheet 1.1.9 Comparing Flowering Plants: 1 Parts of The Flowering PlantDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1.1.9 Comparing Flowering Plants: 1 Parts of The Flowering PlantGadgetGlitchKillNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Unit 6 - Probability Sample Spaces, Tree Diagrams and The Fundamental Counting PrincipleDocument3 pagesMath 2 Unit 6 - Probability Sample Spaces, Tree Diagrams and The Fundamental Counting PrincipleKimberly ilonzeNo ratings yet
- Please Tell Me How I AmDocument13 pagesPlease Tell Me How I AmNathalia QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Final PHD Thesis - Abeer AlsalloomDocument374 pagesFinal PHD Thesis - Abeer Alsalloomayunda rizqiNo ratings yet
- Morning Calm Korea Weekly, February 25, 2011Document30 pagesMorning Calm Korea Weekly, February 25, 2011Morning Calm Weekly NewspaperNo ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Thai Movies and Factors Contributing To Becoming Widely Known in International Markets PDFDocument6 pagesThe Characteristics of Thai Movies and Factors Contributing To Becoming Widely Known in International Markets PDFDisneyboiNo ratings yet
- AaDocument1,286 pagesAaRhea AlayonNo ratings yet
- Fix Any Usb, SD, Mini, Micro ''No Format Needed''Document48 pagesFix Any Usb, SD, Mini, Micro ''No Format Needed''sebastienNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Module Science 10Document12 pagesWeek 4 Module Science 10Princess Charisse BautistaNo ratings yet
- Comets, Meteors, Asteriods Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesComets, Meteors, Asteriods Reading ComprehensionJay-ar RiosNo ratings yet
- 5b. Structural Engineering HO CH 04bDocument17 pages5b. Structural Engineering HO CH 04bThompson kayodeNo ratings yet
- Hemendra Rasiklal Ghia Vs Subodh ModyDocument47 pagesHemendra Rasiklal Ghia Vs Subodh Modyckd84100% (1)
- Referat Bladder Trauma: Rizal TriantoDocument28 pagesReferat Bladder Trauma: Rizal TriantoTrianto RizalNo ratings yet
- ICGP Sign Posts To SuccessDocument139 pagesICGP Sign Posts To SuccessJonathanGrahamNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Karad: World Environment DayDocument1 pageGovernment Polytechnic, Karad: World Environment DayAditya GambhireNo ratings yet
- Study Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsDocument45 pagesStudy Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsLORENA AMATIAGANo ratings yet
- U07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingDocument13 pagesU07754QOSM - Project O & M Manual Auditorium SeatingRithesh ShettyNo ratings yet
- Art AprreciationDocument15 pagesArt AprreciationChini ChanNo ratings yet
- Retirement Community ProjectDocument3 pagesRetirement Community ProjectZarin TashnimNo ratings yet
- Be 100% Sure 1 - Group 2Document13 pagesBe 100% Sure 1 - Group 2sunila2310No ratings yet
- Ach145Document23 pagesAch145prettypetNo ratings yet
- Diary of Albigence WaldoDocument1 pageDiary of Albigence Waldowhatguy309No ratings yet