Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week5 Thyroid
Week5 Thyroid
Uploaded by
riverabeanico0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views33 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views33 pagesWeek5 Thyroid
Week5 Thyroid
Uploaded by
riverabeanicoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
THYROID DISORDERS
Thyroid Gland Disorder
THYROID GLAND:
● Secretes the following hormones
● T3 (Triidothyronine)
● Metabolism and growth
● T4 (Thyroxine, tetra
iodothyronine)
● Catabolism and body heat
production
● Thyrocalcitonin
● bring down the blood
Ca++ level
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● T3/ T4 levels
● ⭡ level: hyperthyroidism
● ⭡ level: hypothyroidism
● PBI (Protein-bound Iodine)
● Preparation
● No foods, drugs, test
dyes with iodine 7-10
days before the test
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● RAIU (Radioactive Iodine Uptake)
● Tracer dose of I131 is used P.O. & at 2°, 6°, and
24° ⭡ exposure to scintillation camera is done
● No foods, drugs, test dyes with iodine 7-10 days
before the test, temporarily discontinue
contraceptive pills (these may ⭡metabolic rate)
● Result:
●⭣ iodine uptake: hyperthyroidism
● ⭣ iodine uptake: hypothyroidism
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● RAIU (Radioactive Iodine Uptake)
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● Thyroid Scan
● Radioisotope Iodine is injected IV
● Exposure to scintillation camera
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● FNB (Fine Needle Biopsy)
● Cytology (detection of malignant cells)
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate)
● Measures O2 consumption
at the lowest cellular activity
● Oxygen uptake is measured
as an indirect measurement
of metabolic rate
● increased utilization O2
(hyperthyroid)
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Diagnostic Tests:
● Reflex Testing (Kinemometry)
● Tendon of Achilles Reflex (TAR)
Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism
(Hypocalcemia) (Hypercalcemia)
Hyperactive TAR Hypoactive TAR
Thyroid Gland Disorder
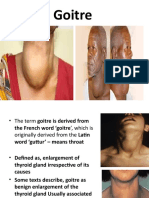
● Goiter
● Enlargement of
the thyroid gland
associated with
hyperthyroidism,
hypothyroidism or
euthyroidism
● A hyperthyroid goiter
toxic
is called
goiter
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis)
● Grave’s Disorder
● Parry’s Disorder
● Basedow’s Disorder
● Exophthalmic Goiter
● Toxic Diffuse Goiter
● common in female, below 40 y/o
● Causes:
● Severe emotional stress
● Autoimmune Disorder
● Thyroid inflammation
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Assessment Findings
● Restlessness, nervousness, irritability, agitation,
fine tremors, tachycardia, hypertension,
voracious appetite to eat, weight loss,
diaphoresis, diarrhea, heat intolerance,
amenorrhea, fine silky hair, pliable nails
● Exophthalmos
● Due to accumulation of fluids at the fat-pads behind
the eyeballs
● It can lead to corneal ulceration, opthalmitis,
blindness
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Assessment Findings
● Dermopathy
● Warm, flushed sweaty
skin
● Thickened hyper-
pigmented skin at the
pretibial area
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
● Rest (non-stimulating cool environment)
● Diet
● HIGH Calorie, HIGH protein; vitamin and mineral
supplement
● Increased fluid intake (if with diarrhea)
● Replace F&E losses
● Avoid stimulants like coffee, tea and nicotine
● Promote safety
● Protect the eyes
● Artificial tears at regular intervals
● Wear dark sunglasses when going out under the
sun
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Pharmacotherapy
● ß-blockers: Propranolol
● Ca++ channel blockers
● These drugs are given to control
tachycardia and HPN
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Pharmacotherapy
● Iodides : Lugol’s solution
● SSKI (Saturated Solution of Potassium Iodide)
● Are given to inhibit release of thyroid hormone
● Mix with fruit juice with ice or glass of water to
improve its palatability
● Provide drinking straw to prevent permanent
staining of teeth
● Side effects:
● Allergic reaction, Increased salivation, colds
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Pharmacotherapy
● Thioamides
● PTU (Propylthiouracil) & Tapazole (Methimazole)
● inhibit synthesis of thyroid hormones
● Side effects of PTU
● AGRANULOCYTOSIS / NEUTROPENIA
● This is manifested by unexplained Fever, Sore
throat, Skin rashes
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Pharmacotherapy
● Paracetamol for fever
● Aspirin must be avoided because
it can displace the T3/T4 from the
albumin in the plasma causing
increased manifestations
● Dexamethasone
● inhibit the action of thyroid
hormones
● prevent the conversion of T4 to
T3 in the peripheral tissues
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Radiation therapy (Iodine131)
● Need isolation for few days; body
secretions are radioactive
contaminated
● NOT recommended in pregnant
women because of potential
teratogenic effects. Pregnancy
should be delayed for 6 months
after therapy
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Subtotal Thyroidectomy- Usually about 5/6
of the gland is removed
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Pre-op Care
● Promote euthyroid state
● Control of thyroid disturbance
● Stable VS
● Administer Iodides as ordered
● To reduce the size & vascularity of thyroid
gland, thereby prevent post-op hemorrhage and
thyroid crisis
● ECG
● Heart failure/ cardiac damage results from HPN/
tachycardia
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Post-op Care
● Position : Semi-fowler’s with head, neck &
shoulder erect
● Prevent Hemorrhage: ice collar over the neck
● Keep tracheostomy set available for the first 48°
post-op
● Ask the patient to speak every hour (to assess for
recurrent laryngeal nerve damage)
● Keep Ca++ gluconate readily available
● Tetany occurs if hypocalcemia is present. This may be
secondary to the removal of the parathyroid gland
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Post-op Care
● Monitor Body Temperature: hyperthermia is an
initial sign of thyroid crisis
● Monitor BP (hypertension may be a manifestation of
thyroid storm)
● assess for Trousseau’s sign (hypocalcemia)
● Steam inhalation to soothe irritate airways
● Advise to support neck with interlaced fingers when
getting up from bed
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Post-op Care
● Observe for signs and symptoms of potential
complications
● Hemorrhage
● Airway obstruction
● Tetany
● Recurrent laryngeal nerve damage
● Thyroid crisis / storm / thyrotoxicosis
● Myxedema
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hyperthyroidism: Management
Surgery
● Post-op Care
● Client Teaching
● ROM exercises of the neck 3 to 4 days after
discharge
● Regular follow – up care
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism
● results from deficiency of thyroid hormones
Myxedema (adult) Cretinism (children)
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism
● Causes
● Autoimmune
● Hashimoto’s disease or chronic lymphocytic
thyroiditis - an autoimmune disorder in which
your immune system inappropriately attacks your
thyroid gland causing an inflammation
● after surgery (thyroidectomy)
● after radiation therapy (radioactive iodine)
● antithyroid drugs
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism
Assessment:
● Slowed physical, mental
reactions, apathy
● Dull, expressionless, mask-like
face
● Anorexia
● Obesity
● Bradycardia
● Hyperlipidemia & atherosclerosis
● Cold intolerance, subnormal
temperature
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism
Assessment:
● Constipation
● Coarse, dry, sparse
hair
● Brittle nails
● Irregular
menstruation
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism: Management
● Monitor vital signs
● Be alert for signs and symptoms of
cardiovascular disorders
● Monitor the weight daily
● Diet:
● LOW Calorie
● High fiber (constipation)
● Provide warm environment during cold
climate
Thyroid Gland Disorder
Hypothyroidism: Management
Pharmacotherapy
● Thyroid hormonal replacement
● Proloid (Thyroglobulin)
● Synthroid (Levothyroxine)
● Dessicated Thyroid Extract
● Cytomel (Liothyronine)
● Before administration, the nurse should
monitor BP & PR
● Start with low dose and gradually increase
You might also like
- Hyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- My Ray Peat NotesDocument24 pagesMy Ray Peat NotesIoannis Bravos100% (5)
- Thyroid Gland DisordersDocument64 pagesThyroid Gland DisordersFaisal RavifNo ratings yet
- Talking Thyroid FactsDocument6 pagesTalking Thyroid FactsVegan Future100% (4)
- Head & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFDocument113 pagesHead & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFPranavNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands: Ms TeamDocument36 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands: Ms TeamShy Dela PuertaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument11 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersLesley GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument97 pagesPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismMarie Joyce SablanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidismaasin100% (1)
- Gold Standard For NclexDocument113 pagesGold Standard For NclexMaria Margarita87% (30)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemJumaimah BauloNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine NotesDocument32 pagesFamily Medicine Noteslalee704100% (8)
- Thyroid Disorders: Tapan A. Patel Cuong Nguyen Mona JamaldinianDocument41 pagesThyroid Disorders: Tapan A. Patel Cuong Nguyen Mona Jamaldiniansheila_kohNo ratings yet
- THYROID Disorders For PB BSCDocument81 pagesTHYROID Disorders For PB BSCchetankumarbhumireddy67% (3)
- Endocrine DiseasesDocument170 pagesEndocrine DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Test 4Document11 pagesMedsurg Test 4Tori RolandNo ratings yet
- SK Singh Lab Report 09042018Document8 pagesSK Singh Lab Report 09042018Iasam Groups'sNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument78 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Endocrine Disordershenny1620100% (1)
- Diseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument72 pagesDiseases of The Thyroid Gland PDFKay BristolNo ratings yet
- The Silver Lining PlaybookDocument4 pagesThe Silver Lining PlaybookJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Surgery Sixer For NBEDocument60 pagesSurgery Sixer For NBEamr elfaresy100% (6)
- Diabetes MellitusDocument18 pagesDiabetes Mellitusrajirajesh100% (1)
- Endocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notes - Part 2Document10 pagesEndocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notes - Part 2grad_nurse_2015100% (1)
- Staphylococcus Aureus and Other Staphylococci Are TheDocument3 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus and Other Staphylococci Are TheRaphael Reyes EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2011Document30 pagesHyperthyroidism 2011Elyza MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid Storm: Tintinalli Chapter 215 12/15/05Document44 pagesHyperthyroidism and Thyroid Storm: Tintinalli Chapter 215 12/15/05Charith KumaraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument23 pagesThyroid Stormsadiq0% (1)
- HashimotoDocument9 pagesHashimotoFrinkooFrinkoBNo ratings yet
- Iodine Deficiency DisordersDocument7 pagesIodine Deficiency DisordersEndocrinology IndiaNo ratings yet
- Yoga and Hyperthyroidism PDFDocument16 pagesYoga and Hyperthyroidism PDFRaushan Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- HipertiroidDocument31 pagesHipertiroidEdo Pramana PutraNo ratings yet
- CCDocument9 pagesCCFritzie BlancheNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument66 pagesThyroid DisordersJOY SANDHYA JOSEPH (RA2123003011002)No ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument1 pageThyroidsharu4291No ratings yet
- Askep GGN ThyroidDocument26 pagesAskep GGN ThyroidTsaalits MuharrorohNo ratings yet
- Tyroid DiseasesDocument40 pagesTyroid DiseasesValentina MilovaNo ratings yet
- Grave's Disease NCLEX ReviewDocument5 pagesGrave's Disease NCLEX ReviewhaleyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesThyroid StormAnjelika Eurelle Caliboso MapiliNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease PDFDocument44 pagesThyroid Disease PDFSuhazeli AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Thyroid Surgery....Document46 pagesAnaesthesia For Thyroid Surgery....Parvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Diseases in Children-1Document36 pagesThyroid Gland Diseases in Children-1Jeffrey EkaNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneDocument4 pagesHypothyroidism: Regulation of Thyroid HormoneAmer Abdulla SachitNo ratings yet
- Mardinthyroid 141212101640 Conversion Gate02Document42 pagesMardinthyroid 141212101640 Conversion Gate02NiyaNo ratings yet
- U World Endocrine FinalDocument12 pagesU World Endocrine Finalsean blazeNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism ReportDocument3 pagesHyperthyroidism ReportLevi Rae CLerigo EstiponaNo ratings yet
- HIPERTIROIDDocument30 pagesHIPERTIROIDNandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders: Submitted By: Jho Ann Labor Submitted To: Mrs. Daphny HatudDocument19 pagesEndocrine Disorders: Submitted By: Jho Ann Labor Submitted To: Mrs. Daphny HatudjhoanNo ratings yet
- RNSG 1533 Raising The Bar For Success Concept: Metabolism: Diabetes Type 1/diabetes Type 2Document4 pagesRNSG 1533 Raising The Bar For Success Concept: Metabolism: Diabetes Type 1/diabetes Type 2katrinasdNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseaseDocument32 pagesThyroid DiseaseAhmadAuliaFadlyRafNo ratings yet
- Prognosis Kiris TiroidDocument3 pagesPrognosis Kiris TiroidTeguh R PerkasaNo ratings yet
- Thyroiddisorders PDFDocument51 pagesThyroiddisorders PDFIslam ShoukryNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: Prevalence Women 2% Men 0.2% 15% of Cases Occur in Patients Older Than 60 Years of AgeDocument54 pagesHyperthyroidism: Prevalence Women 2% Men 0.2% 15% of Cases Occur in Patients Older Than 60 Years of AgeMegan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hperthyroidism 1Document4 pagesHperthyroidism 1Salwa KaramanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders1Document67 pagesThyroid Disorders1AzeemNo ratings yet
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument33 pagesEndocrine EmergenciesbetyahNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument12 pagesHyperthyroidismShoppe 'n ShoppersNo ratings yet
- Hyper and Hypo FunctionDocument19 pagesHyper and Hypo FunctionkasjdkasNo ratings yet
- HPERTHYROIDISMDocument4 pagesHPERTHYROIDISMSalwa KaramanNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidDocument5 pagesHyperthyroidJameston BostreNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument54 pagesHyperthyroidismAsiah JelitaNo ratings yet
- Hyper OfficeDocument4 pagesHyper Officeshakib33001No ratings yet
- Hyperthyoidism: Anaesthetic ManagementDocument11 pagesHyperthyoidism: Anaesthetic ManagementerzaraptorNo ratings yet
- Thyroid LectureDocument65 pagesThyroid LectureAndres TabaresNo ratings yet
- SC2 2015 HyperthyroidismDocument38 pagesSC2 2015 HyperthyroidismShafern TanNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesHypothyroidism: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsMarkWeberNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism and Thyrotoxicosis: Practice EssentialsDocument39 pagesHyperthyroidism and Thyrotoxicosis: Practice Essentialssyl viNo ratings yet
- Sumant Sharma MD CIC. Regional Lab Nejran. KKSADocument58 pagesSumant Sharma MD CIC. Regional Lab Nejran. KKSADr Sumant SharmaNo ratings yet
- '3'hyperthyroid and HypothyroidDocument42 pages'3'hyperthyroid and Hypothyroidafriskha bulawanNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument71 pagesHyperthyroidismAli Murtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- Hypertyroidism: Overview of The DiseaseDocument8 pagesHypertyroidism: Overview of The DiseaseCj UritaNo ratings yet
- By Talha Anwar: HyperthyroidismDocument8 pagesBy Talha Anwar: HyperthyroidismFalah NadeemNo ratings yet
- MX Thyroid DisordersDocument52 pagesMX Thyroid Disorderstarakeeshbai1802No ratings yet
- Specific Disorders of The Thyroid GlandDocument8 pagesSpecific Disorders of The Thyroid Glandgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!From EverandThyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!No ratings yet
- DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS - Docx-1-3Document3 pagesDEPRESSIVE DISORDERS - Docx-1-3Janine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Eye Dxtics and Eye DisordersDocument53 pagesEye Dxtics and Eye DisordersJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource WasJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Mental Illness and Defense Mechanism - Janine Dela CruzDocument2 pagesFactors Influencing Mental Illness and Defense Mechanism - Janine Dela CruzJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Cu12 EndocrineDocument84 pagesNCMB 316 Cu12 EndocrineJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderDocument74 pagesNCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Cu14 AdrenalDocument39 pagesNCMB 316 Cu14 AdrenalJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 21 - Thyroid Function TestsDocument2 pages21 - Thyroid Function Testshamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Hipo - Hiper SubDocument123 pagesHipo - Hiper SubdankouzielNo ratings yet
- Hypothyrodism in PregnancyDocument32 pagesHypothyrodism in Pregnancymohammed makki0% (1)
- The Thyroid ReviewDocument2 pagesThe Thyroid Reviewwest alabamaNo ratings yet
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicDocument2 pagesHashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicPetraNo ratings yet
- Biological Special Programs - Overview: Organs Controlled From The BrainstemDocument19 pagesBiological Special Programs - Overview: Organs Controlled From The BrainstemYogesh Kharche100% (1)
- Thyroid Disorders Part I Hyperthyroidism Little 2006Document9 pagesThyroid Disorders Part I Hyperthyroidism Little 2006Jing XueNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriDocument7 pagesBibliografie: Vizitati WWW - Tocilar.ro ! Arhiva Online Cu Diplome, Cursuri Si Referate Postate de UtilizatoriAndrutza AndraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Total T3Document3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Total T3Chandu Chan LyristNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesKatherine Joy MaderajeNo ratings yet
- Patho Final 2019 CSDocument77 pagesPatho Final 2019 CSSimina ÎntunericNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Eye Disease: Aka Thyroid Associated OphthalmopathyDocument25 pagesThyroid Eye Disease: Aka Thyroid Associated OphthalmopathyYuriko FerisNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism: Case Presentation and DiscussionDocument7 pagesHyperthyroidism: Case Presentation and DiscussionCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Anatomy and PhysiologyJojo JustoNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument20 pagesGoitreSuma100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism in PregnancyDocument3 pagesHyperthyroidism in PregnancyroyNo ratings yet