Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dhvani Chauhan Task 2
Uploaded by
dhvanichauhan476Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dhvani Chauhan Task 2
Uploaded by
dhvanichauhan476Copyright:
Available Formats
PRAEDICO GLOBAL RESEARCH PVT.
LTD
Name :- DHVANI CHAUHAN
Task 2:- INDIAN ECONOMY ON 5 DIFFERENT ECONOMIC
FACTORS
5 Economic Factors are :
1. Inflation
2. Gross Domestic product (GDP)
3. Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Wholesale Price Index
(WPI)
4. Per Capita Income
5. Forex Reserves
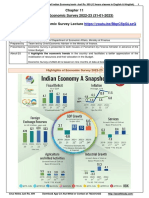
1. Inflation:-
Inflation is crucial to determine one’s purchasing power. In other words,
inflation is a measure that causes the prices of both goods and services to
rise over time and buyers will feel the pinch as it affects their personal
finance, particularly spending and buying habits.
The country’s retail inflation, which is measured by the consumer price
index (CPI), slipped 16-month low to 5.66% in Mar. 2023. Inflation data on
the wholesale Price Index (WPI), which calculates the overall prices of
goods before selling at retail prices, eased 1.34% during the period.CPI hit
the highest of 7.79% in Apr. 2022, and WPI reached 15.88% in May 2022.
Compared to inflation in Mar. 2020, CPI is down 0.18%, and WPI is up
0.34%.The impact of inflation is felt across different sectors of the economy
which are favourable to some and unfavourable to others.
2. Gross Domestic Product:-
GDP or “Gross Domestic Product” refers to the monetary value of all goods
and services produced in a nation during a given year. A higher GDP
indicates that the country is financially strong and growing at a stable rate.
According to the World GDP Ranking 2023 list, India is the fifth largest
economy in the world. Other prominent countries like the United States of
America, China, Japan, Germany, etc., have a significant presence in this
GDP Ranking list. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) projects growth in
India’s gross domestic product (GDP) to moderate to 6.4% in fiscal year (FY)
2023 ending on 31 March 2024 and rise to 6.7% in FY2024, driven by
private consumption and private investment on the back of government
policies to improve transport infrastructure, logistics, and the business
ecosystem.
3. Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Wholesale Price Index
(WPI):-
Consumer Price Index or CPI is the measure of changes in the price level
of a basket of consumer goods and services bought by households. CPI is a
numerical estimation calculated using the rates of a sample of representative
objects the prices of which are gathered periodically. The country’s retail
inflation, which is measured by the consumer price index (CPI), accelerated to
6.50% in Jan. 2023. The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) reports the change in the
price of goods sold by wholesalers across India. The higher this number is the
stronger the affect on consumer inflation. A reading that is stronger than forecast
is generally supportive (bullish) for the INR, while a weaker than forecast reading
is generally negative (bearish) for the INR. The annual rate of inflation based on all
India Wholesale Price Index (WPI) number is 4.73% (Provisional) for the month of
January, 2023 (over January, 2022) against 4.95% recorded in December, 2022.
4. Per Capita Income:-
Per capita income is the measurement of money earned per
person in a certain zone. In layman terms, we can say that “Per Capita
income is the Income supposedly earned by a single person in a country.” It
is calculated by dividing country’s national income by its population. It
should not be misunderstood by average income (because it includes non-
employed and kids population), rather it serves as a pointer to a country’s
living standards. It can be applied to the average per-person income of a
village, city, state or country. It can be used as a means of gauging the living
circumstances and quality of life of citizens. The current per capita income
represents a rise of 15.8 per cent over the previous year. It was estimated
at Rs.1,27,065 and Rs.1,48,524 for 2020-21 and 2021-22, respectively
5. Forex Reserves:-
As of September 2021, the foreign exchange reserves of the
Indian economy stood at around USD 639.46 billion. These reserves are
held by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and comprise foreign currencies,
gold, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) with the International Monetary Fund
(IMF), and the RBI's position with the IMF.Foreign exchange reserves are an
important indicator of a country's economic strength and ability to meet its
international obligations. India's foreign exchange reserves have been
steadily increasing over the years, thanks to various measures taken by the
RBI and the government to attract foreign investment and maintain a stable
exchange rate.The RBI uses these reserves to intervene in the foreign
exchange market to maintain the value of the Indian rupee against other
major currencies. These reserves also provide a cushion against external
shocks and can be used to finance imports or pay off foreign debt in times
of crisis.
You might also like
- Assignment 1-IAPM-19BMS0218Document8 pagesAssignment 1-IAPM-19BMS0218KenanNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Imp Facts & InstitutionsDocument17 pagesGlossary of Imp Facts & InstitutionskolkatacareerlauncherNo ratings yet
- Market Cap To GDP RatioDocument8 pagesMarket Cap To GDP RatiokalpeshNo ratings yet
- Market Outlook 2024 - Kotak SecuritiesDocument36 pagesMarket Outlook 2024 - Kotak Securitiesgg1512100% (1)
- Macro Economic Concepts NewDocument10 pagesMacro Economic Concepts Newshreyas babariaNo ratings yet
- Kanav Malhotra ME AssignmentDocument6 pagesKanav Malhotra ME AssignmentKanav Malhotra1039No ratings yet
- GBP ReportDocument24 pagesGBP ReportSurolla GouthamNo ratings yet
- Governor's Statement - August 6, 2020: TH TH TH THDocument13 pagesGovernor's Statement - August 6, 2020: TH TH TH THThe QuintNo ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2023Document3 pagesEconomic Survey 2023GRAMMAR SKILLNo ratings yet
- Rbi Monetary Policy 2021Document4 pagesRbi Monetary Policy 2021Yuseer AmanNo ratings yet
- Aye Kyu Kyu Khin: Fundamental of EconomicDocument11 pagesAye Kyu Kyu Khin: Fundamental of EconomicHtoo Wai Lin AungNo ratings yet
- Indicators of Economic Growth LEEBDocument12 pagesIndicators of Economic Growth LEEBNischay RathiNo ratings yet
- Report On GDP KadirDocument33 pagesReport On GDP KadirRohit ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of Axis and ICICI BankDocument18 pagesFundamental Analysis of Axis and ICICI BankAnu100% (2)
- Union Budget 2023Document13 pagesUnion Budget 2023RomaNo ratings yet
- How Is CPI Calculated (CPI Formula) ?Document3 pagesHow Is CPI Calculated (CPI Formula) ?hukaNo ratings yet
- Wholesale Price Index & Consumer Price IndexDocument7 pagesWholesale Price Index & Consumer Price IndexfeelfreetodropinNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of Airtel ReportDocument29 pagesFundamental Analysis of Airtel ReportKoushik G SaiNo ratings yet
- Crux of Economic Survey 2023Document8 pagesCrux of Economic Survey 2023Raja S100% (1)
- What Is Inflation?Document6 pagesWhat Is Inflation?Shamoil ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Monthly Economic Review January 2024 - 0Document30 pagesMonthly Economic Review January 2024 - 0guru prasadNo ratings yet
- Compendium: Economics and FinanceDocument16 pagesCompendium: Economics and FinanceAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- TATA AIA Annual Report March 2020Document22 pagesTATA AIA Annual Report March 2020SantoshNo ratings yet
- Impact of Various Policies of Financial MarketDocument12 pagesImpact of Various Policies of Financial MarketNeel KanakNo ratings yet
- 1611757163basics of Indian EconomyDocument338 pages1611757163basics of Indian EconomyashiNo ratings yet
- Invesco Factsheet July 2023Document56 pagesInvesco Factsheet July 2023Akhilesh ksNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Initiatives Since 2008-09 and Its Effectiveness in Containing Inflation"Document31 pagesMonetary Policy Initiatives Since 2008-09 and Its Effectiveness in Containing Inflation"Arpit PangasaNo ratings yet
- Investment Banking Industry Analysis Report PDFDocument46 pagesInvestment Banking Industry Analysis Report PDFricky franklinNo ratings yet
- Inflation Measures in IndiaDocument11 pagesInflation Measures in Indiapradeep3673No ratings yet
- Bandhan Debt-Market-Monthly-Outlook-Nov-2023Document3 pagesBandhan Debt-Market-Monthly-Outlook-Nov-2023Shivani NirmalNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of India and Industry Analysis of Chemical IndustryDocument28 pagesEconomic Analysis of India and Industry Analysis of Chemical IndustrySharanyaNo ratings yet
- Macro Session 15 - 16 InflationDocument37 pagesMacro Session 15 - 16 InflationSHRESTI ANDENo ratings yet
- PR1043MP0Document15 pagesPR1043MP0Shivam SisodiaNo ratings yet
- In Ation in India: July 2014Document14 pagesIn Ation in India: July 2014Dhairya JainNo ratings yet
- RBI Governor Statement 1702090413Document9 pagesRBI Governor Statement 1702090413Jyotiraditya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Business Line JulyDocument7 pagesBusiness Line JulyRaj KishoreNo ratings yet
- Governor's StatementDocument11 pagesGovernor's Statementvipulpandey005No ratings yet
- Ajay Pillai Finanacial Report-1Document10 pagesAjay Pillai Finanacial Report-1Ajay PillaiNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics CIADocument7 pagesMacroeconomics CIASahil IqbalNo ratings yet
- Eco104 - Assignment 2Document4 pagesEco104 - Assignment 2zilani ahmedNo ratings yet
- LinkDocument24 pagesLinkDhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- WEO DataDocument11 pagesWEO Datapremium info2222No ratings yet
- India Monthly Investment Outlook and Strategy: January 2013Document13 pagesIndia Monthly Investment Outlook and Strategy: January 2013saikumarmohinderNo ratings yet
- Mircoeconomics CIADocument6 pagesMircoeconomics CIAsarayuNo ratings yet
- Statement by Governor - First Bi-Monthly Monetary Policy, 2019-20, April 4, 2019Document8 pagesStatement by Governor - First Bi-Monthly Monetary Policy, 2019-20, April 4, 2019Valter SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Invesco Factsheet June 2022Document56 pagesInvesco Factsheet June 2022ADARSH GUPTANo ratings yet
- How To Analyze The Stock MarketDocument9 pagesHow To Analyze The Stock MarketantumanipadamNo ratings yet
- Monthly Economic Review July 2023 - 1Document26 pagesMonthly Economic Review July 2023 - 1H SNo ratings yet
- Inflation in India For SSC Bank ExamsDocument8 pagesInflation in India For SSC Bank ExamsJames K AngamNo ratings yet
- Economic TermsDocument7 pagesEconomic Termsanupkumar55No ratings yet
- Advance Estimates: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) EstimatesDocument3 pagesAdvance Estimates: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Estimates14skreamNo ratings yet
- Prof.R.Srinivasan Department of Management Studies, Indian Institute of Science, BangaloreDocument24 pagesProf.R.Srinivasan Department of Management Studies, Indian Institute of Science, BangaloreSamanth GodiNo ratings yet
- Monthly Beepedia August 2022Document129 pagesMonthly Beepedia August 2022Sakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- India Synopsis-UpdatedDocument33 pagesIndia Synopsis-UpdatedAbhishek pathangeNo ratings yet
- Monthly Beepedia August 2022Document129 pagesMonthly Beepedia August 2022Rahul AnandNo ratings yet
- Economics Case StudyDocument2 pagesEconomics Case StudyDevz NambiarNo ratings yet
- Problems With InflationDocument3 pagesProblems With InflationgagansinghNo ratings yet
- Economic Survey 2022: Why in News?Document15 pagesEconomic Survey 2022: Why in News?Sourav KumarNo ratings yet
- RBI Monetary Policy Statement - Must Read For The Class Now and TodayDocument4 pagesRBI Monetary Policy Statement - Must Read For The Class Now and TodayAnanya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bank of Jamaica Brief HistoryDocument5 pagesBank of Jamaica Brief HistoryTechnicianccnaNo ratings yet
- Annual Report BNM2004.complete PDFDocument341 pagesAnnual Report BNM2004.complete PDFAli FarhanNo ratings yet
- Ie 3 2020 PDFDocument13 pagesIe 3 2020 PDFMANISHA GARGNo ratings yet
- Public Borrowing 4Document14 pagesPublic Borrowing 4Corpuz Tyrone0% (1)
- Dominican Republic Special ReportDocument16 pagesDominican Republic Special ReportNelson MuñizNo ratings yet
- Politics of Foreign Direct Investment in South Asia: Sojin ShinDocument16 pagesPolitics of Foreign Direct Investment in South Asia: Sojin ShinRenata FaizovaNo ratings yet
- Money and Capital Market AssignmentDocument51 pagesMoney and Capital Market Assignmenttanj-wp21No ratings yet
- BNK 601 - Tutorial 1 Solutions 2020Document5 pagesBNK 601 - Tutorial 1 Solutions 2020Inoke RawaigagaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Policy PDFDocument47 pagesIndustrial Policy PDFAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Act MCQDocument12 pagesCentral Bank Act MCQJemima LalaweNo ratings yet
- Assignment4Document2 pagesAssignment4Laiba EjazNo ratings yet
- July - Current AffairsDocument89 pagesJuly - Current AffairsHimanahuNo ratings yet
- Oct 20 - Oct 23 NewsDocument156 pagesOct 20 - Oct 23 NewsBig ShowNo ratings yet
- Fear of Flying Why Is Sustaining Reform So Hard in VietnamDocument22 pagesFear of Flying Why Is Sustaining Reform So Hard in Vietnamnvh92No ratings yet
- CaseDocument19 pagesCaseSara MalikNo ratings yet
- Kashif Et Al., 2024Document10 pagesKashif Et Al., 2024KashifNo ratings yet
- Birritu Magazine 114Document32 pagesBirritu Magazine 114geta beleteNo ratings yet
- Quality Circle ReportDocument45 pagesQuality Circle ReportAkanksha Gupta100% (3)
- The Globalization of World EconomicsDocument3 pagesThe Globalization of World EconomicsRicson Drew100% (1)
- Prelim Test 2023 Paper I General Studies G.S - V2 1Document39 pagesPrelim Test 2023 Paper I General Studies G.S - V2 1MP FITNESSNo ratings yet
- Press Release Aro Granite Industries Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Document4 pagesPress Release Aro Granite Industries Limited: Details of Instruments/facilities in Annexure-1Ravi BabuNo ratings yet
- Banking & Economy PDF - January 2020 by AffairsCloud PDFDocument141 pagesBanking & Economy PDF - January 2020 by AffairsCloud PDFAjith DivakaranNo ratings yet
- Self-Paced Lesson On GDP, GNP, Balance of Payments and TradeDocument14 pagesSelf-Paced Lesson On GDP, GNP, Balance of Payments and TradeJeno GonoNo ratings yet
- Bot & Bto ContractsDocument65 pagesBot & Bto ContractsWalid GradaNo ratings yet
- Bcog 172 2Document1 pageBcog 172 2ACS DersNo ratings yet
- Economy Book IndexDocument14 pagesEconomy Book Indexraanaar0% (2)
- IFM 02 Exchange Rate SystemsDocument53 pagesIFM 02 Exchange Rate SystemsTanu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation - A-Level EconomicsDocument15 pagesGlobalisation - A-Level EconomicsjannerickNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - BOP (International Finance)Document6 pagesUnit 2 - BOP (International Finance)undesastreordenadoNo ratings yet
- CAF 2 Past PapersDocument110 pagesCAF 2 Past PapersAaraiz Hassan BtNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateFrom EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (349)
- Slow Burn: The Hidden Costs of a Warming WorldFrom EverandSlow Burn: The Hidden Costs of a Warming WorldRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsFrom EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationFrom EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityFrom EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailFrom EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (239)
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsFrom EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismFrom EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Land of Promise: An Economic History of the United StatesFrom EverandLand of Promise: An Economic History of the United StatesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaFrom EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNo ratings yet
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- The Profit Paradox: How Thriving Firms Threaten the Future of WorkFrom EverandThe Profit Paradox: How Thriving Firms Threaten the Future of WorkRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenFrom EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNo ratings yet
- Economics 101: How the World WorksFrom EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Bad Samaritans: The Myth of Free Trade and the Secret History of CapitalismFrom EverandBad Samaritans: The Myth of Free Trade and the Secret History of CapitalismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (158)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- The Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyFrom EverandThe Lords of Easy Money: How the Federal Reserve Broke the American EconomyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Economics for Dummies: 3rd EditionFrom EverandEconomics for Dummies: 3rd EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (39)
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingFrom EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)