Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BS 5146 - 1 - 1974
BS 5146 - 1 - 1974
Uploaded by
T Kelvin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views11 pagesOriginal Title
BS 5146_1_1974
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views11 pagesBS 5146 - 1 - 1974
BS 5146 - 1 - 1974
Uploaded by
T KelvinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
BSI BS¥S514— PART*) 74 MM Lb24Gb9 0040987 |
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
UDC 620.1: 621.646 : [622.323 + 662.753 + 665.6]
(Reprinted, incorporating Amendments
No, 1 to No, 3 inclusive)
Inspection and test of valves
Part 1. Specification for steel valves for the
petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries
British Standards Institution
BSI BS*5]4b PART#L 74 MM Mb24b69 0040588 3 mm
‘This British Standard, having been approved by the Petroleum Equipment Industry Standards Committee, was published under
the authority ofthe Executive Hoard on 6 September, 1974,
© British Standards Institution, 1974
ISBN: 0 $80 08448 5
[British Standards Institution
Incorporated by Royal Charter, BSI is the independent national body for the preparation of British Standards. It isthe UK
‘member of the Intemational Organization for Standardization and UK sponsor of the British National Committee of the
International Eleciotechnical Commission,
Copyright
Users of British Standards are reminded that copyright subsists in all BSI publications. No part of this publication may be
reproduced in any form without the prior permission in writing of BSI. This does not preclude the Free uso, in the course of
implementing the standard, of necessary details such as symbols and size, type or grade designations. Enguiies should be
addressed to the Publications Manager, British Standards Institution, Linford Wood, Milton Keynos MK 4 GLE. The number for
telephone enquiries is 0908 320033 and for tlex 825777,
Contract requirements
‘A British Standard does not purport to inelude all the necessary provisions ofa contract Users of British Standards are responsible
Trtheir correct application,
Revision of British Standards
British Standards are revised, when necessary, by the issue either af amendments or of revised editions. It is important that users of
British Standards should ascertain that they are in possession of the latest amendments or editions. Information on all BSI
publications isin the BSY Catalogue, supplemented exch month by BSY News which is available to subscribing members of the
Institution and gives details of new publications, revisions, amendments and withdrawn standards. Any person who, when making
tse of a British Standard, encounters an inaccuracy or ambiguity is requested to notly BSI without delay inorder that the matter
‘may be investigated and appropriate action taken.
Linford Wood, Milton Keynes MK14 GLE (Telephone 0908 220022; Telex 825777),
‘The following BSI references relate fo the work on ths standard:
Committe reference PEE/I Draft for comment 74/37782DC
Co-operating organizations
‘The Petroloum Equipment Industry Standards Committe, undor whose suporvsion this British Standard was propared, consists
of representatives from the following Government departinent and scientific and industrial organizations
British Gas Corporation
British Mechanical Engineering Confederation
British Rubbor Manufacturers Association Lid
‘rts Stet Industry
“Council of British Manufacturers of Petroleum
Equipment
Department of Trade and Industry
"Oil Companies Materials Association
The organizations marked with an asterisk in the above lst, together with tho following, wore dreetly represented on the
Committee entrusted withthe preparation of this standard:
Association of Hydraulic Kaulpment Manufacturers
Brush Chemical Engineering Contractors’ Asoctation
British industrial Measuring and Control Apparatus
Manufactureny Asociation
8804-5056
Uris Patios Pederation
British Valvo Manufacturers’ Association
Engineering Equipment Users’ Assocation
‘Steel Castings Association
BSI BS¥SL4G PARTAL 74 MM Lb24bb9 0040989 5 mm
BS BS 5146 :Part 1:1974
Do ean 62.646 672928 + 062750 656.61
Inspection and test of valves
Part 1. Specification for steel valves for the
petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries
Amendments issued since publication
Amd. No. Date of issue | Text affected
2316 August 1979 | Indicated by a line in the margin
3343 May 1980 Indicated by a line in the margin
71 November 1984 | Indicated by a line in the margin,
British Standards Institution - 2 Park Street - London W1A 2BS
‘Telophone 01-629 9000
Telex 266933
BSI BS*5L44 PART*) 74 MM Lb246b5 0040550 1
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
Contents
Page Page
Co-operating organizations Inside front cover Section three. Pressure tests
Foreword 2 13. General 4
14, Shell test (hydrostatic) 5
15. Seat test (hydrostatic) 5
16. Seat test (air) 6
17, Test duration 6
Section one, Goer 3 18 Tetlgas é
ee 315. Tetanus $
3. Information to be supplied by the a
purchaser 3 Section four. Further tests
21. Fire safe tests 6
22. Anti-static device testing 6
Section two. Inspection
4. Inspection at manufacturer's works 3 Appendix
5. Inspection of purchased components 3A... Prototype tests 7 @
6. Inspection by purchaser 4
7. Inspection of materials 4 Tables
8, Supplementary inspection 4 1. Hydrostatic test pressure (gauge) in bar S
9. Repair of shell defects 4 2. Test durations 6
ence 43. Average leakage rates |
11. Notie of inspection 4 Figure
12. Protective coz 4 1. Typical fire safe test rig 9
Foreword
‘This British Standard is one ofa series of standards for valves prepared under the authority of the Petroleum
‘quipment Industry Standards Committee. I¢ covers the requirements for inspection and testing of valves for the
petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries and is comparable with API Standard 598 ‘Valve Inspection and
Tost’,
‘This standard is published in two Parts: Part 1 ‘Specification for steel valves for the petroleum, petrochemical and
allied industries’ and Part 2 ‘Specification for pressure testing requirements for general purpose valves’,
BSI BSxS14G PART*) 74 MM b24b69 OO4OT9L 3 ml
BS 5146: Part 1: 1974
Inspection and test of valves
Part 1, Specification for steel valves for the petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries
Section one. General
1. Scope
‘This British Standard specifies the requirements for the inspection and test of steel valves, manufactured in
aocordance with the requirements of the following British Standards, for the petroleum, petrochemical and
allied industries:
BS 1414, BS 1570, BS 1868, BS 1873, BS 2080, BS 5351, BS 5352, BS 5353.
Important note. Inspection and test requirements given in thi British Standard shall only apply to the individual
valve types when this is specified in the corresponding individual valve type British Standard.
2. References
‘The titles of the British Standards roferred to in this standard are listed on the inside back cover.
3. Information to be supplied by the purchaser
Certain clauses of this standard permit alternatives and the purchaser shell inform the manufacturer in the
purchase order, and preferably also in the enquiry stage, of the following:
(@) whether normal inspection at the manufacturer's works is required (Gee clauses 4 and 11);
(b) whether any special material tests are required (6eo clause 7),
(©) any supplementary inspection requirements for castings, forgings and fabrications and any associated test
certificates (see clause 8);
@ whether repair of dofects is forbidden (se0 clause 9);
© whether the valve is required to be lined and, ifs, whether a pressure testis required before lining (Gee
clause 12);
(f) whether low pressure air test is required (see clause 16);
() whether a test fluid other than water at ambient temperature is required and, if so, the details (see
clause 18);
(h) whether valve test certificates are required (see clause 20).
Section two. Inspection
4, Inspection at manufacturer's works
If specified in the purchase order, the valve shall be inspected by the purchaser's inspector at the place of
manufacture before despatch, and this inspection shall be so conducted as not to interfore unnecessarily with
the manufacturer's programme. ‘The inspector shall be allowed access at all reasonable times to those parts of the
‘manufacturer's works which are concemed with the manufacture of the valves, and he shall be afforded ll
reasonable facilities for satisfying himself that the valves are manufactured in accordance with the requirements
of the relovant standard and the purchase order.
‘The manufacturer, when so requested, shall supply a certificate stating that the valve and the valve parts
comply in all respects with the relovant standard and the purchase order.
6. Inspection of purchased components
If tho valve manufacturer obtains component parts from some other supplier, similar facilites for inspection of
these components shall be given to the purchaser's inspector by prior arrangement.
BSI BS¥514b PART*L 74 MM 2624669 OOWOTI2 S a
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
6. Inspection by purchaser
Normal inspection by the purchaser shall be limited to the following:
(@) visual examination of any finished components at the assembly stages
(b) visual and dimensional check of the finished valve;
(©) witnessing of shell and seat pressure tests as specified in section three,
‘Any part of the normal inspection procedure may be waived by the inspector.
7. Inspection of materials
Physical tests and chemical composition of materials shall be as specified in the various material specifications
referred to in the relevant individual valve type standard. Requirements for associated certificates shall be
spocified in the purchase order.
8. Supplementary inspection
‘When specified in the purchase order, supplomentary tests on castings, fabrications and forgings, e.g. magnetic
particle, radiographic, shall be carried out by the manufacturer to an agreed procedure or specification. If copies
of the relevant test cotificates are required this should also be stated in the purchase order.
9. Repair of shell defects
Defectsin the shel ofa castle maybe repsved unl otherwise specif in the purchase order. Such pais @
shall be carried out in accordance with the requirements of BS 4570 : Part 1.
10. Rejections
Any completed valves, or rough or finished components (whether made by the valve manufacturer or purchased
from other suppliers) which have been rejected for any reason by the purchaser's inspector shall not be used for
completing the purchase order except as provided for in clause 9.
11. Notice of inspection
When inspection by the purchaser is stipulated, the valve manufacturer shall normally give at least five days’ prior
notice of the availability of valves and components for inspection or test.
12. Protactive coatings
Unpainted surfaces of valves may be protected by an easily removable rust preventive to BS 1133 : Section 6
provides emovel fm stg fs bf to
Valves shall normally be tested before painting but painted valves from stock may be tested without removal
Whore a peaon ining such sls, abbr, ply steorethen (PTFE, te, specie the
purchase y tire sey apres tt on he sel porto ing in ato oe hares on
th sel alowing ning e
Section three. Pressure tests
13, General
‘The pressure tests specified inthis section shall, unless otherwise specified, be carried out by the manufacturer on
cach valve and shall stated in the purchase order, be conducted in the presence of the purchaser's inspector.
“The gauge test pressures shall be as shown in table 1. These pressures are to be maintained for the times given
in table 2
PART#L 74 Ml Lb246b9 0040993 7 Ml
BSI BS*5SL4b
BS 5146 : Part 1:
974
‘Table 1. Hydrostatic test pressure (gauge) in bar*
ha mateial ference in BS 1560: Part 2
cos [incisheand P10 [ratio PES "Tables PE-9 and E12
ind et
seat [eet [oron [seat ‘sha ‘soar
150 | 30 zt | 30 at [30 ‘| 22
300 «| 76 sst—| ot ~~ | art —«| «| aor
40 fio [si a7 @ 1 3s
eo [iso furor iso oar fio | aor
soot [207 fasat five iar ia oor
00 aos ftos usa fut fists
isoo [373 fara [aan—faas— [266 |i6
2500 |ear_— ass saa [an sfaaa’ [20
1 bar= 10 Nin? =10*k
4 he hyo set pre or bal vas hal no exe he ody rating or at eting ae BS S381), whichever
Not applicable to ange vas.
14. Shell test (hydrostatic)
All valves shall be subjected to a hydrostatic test of the shell at the appropriate pressure given in table 1. They
shall remain tight under this pressure when subjected to the full stresses in all directions induced by the test pressure
for the durations given in table 2. For this test disks, wedges and plugs shall be in the open position and balls in the
half-open position. Check valves shall have the pressure applied to the upstream side.
‘When valves with stuffing boxes are being tested, the back seat shall be tested for leakage with the valve fully
‘open and either with the stem packing removed or untightened.
15, Seat test (hydrostatic)
Ail valves (excluding ball valves unless specified by the purchaserq) shal be subjected to hydrostatic seat tests,
during which no external forces which might improve seat scaling shall be applied to the valve ends, at the
appropriate pressure given in table 1. There shall be no visible: leakage during the test (see table 2 for test duration).
‘The pressure is to be applied as follows.
(@) Gate valves: successively to each side of the wedge. In the ease of soft seal valves, the bonnet plug shall be
removed prior to test to prove the double block and bleed facility
(b) Globe valves: under the disk
(6) Check valves: on the downstream side.
(a) Globe stop and check valves: under the disk and also with stem raised and test pressure applied to the
downstream side.
() Plug valves: successively to each side of the plug§.
(f) Ball valves: successively to each side of the ball.
Tn each case the valve shall be in the closed position, except as stated in (4), with the side not under pressure
open to the atmosphere and, where applicable, the shell cavity shall be full of the test liquid during the test.
‘Whee! keys shall be permitted to attain the manufacturer's specified closing torque where gearing is specifically
omitted by the purchaser.
‘€ When specified by the puichaser, soft seated ball valves shall have hydrostatic sat test n accordance with clause 1, It should be
noted, however, that soft seated valves tested to a maximum seat pressure might havea reduced performance capability in some
subsequent services at low diferental pressures, In these cases the manufacturer should be conslted.
'§ The plug is to be moved from fully open to fully closed three times to demonstrate satisfactory mechanieal operation and
continued tightness after operation. With valves relying on a sealing compound to effect a stl Ic is permitted to charge with
scaling compound prio to testing.
11 The ball isto be moved from fully open to fully closed thee times to demonstrate satisfactory mechanlcl operation and
continued tightness after aperation.
5 SSS.
BSI BS*514b PARTS) 74 MM Lb24669 0040994 9 mm
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
In addition (o the above tests, check valves and globe stop and check valves shal also be tested om the
downstream side to 25 % of the seat test pressure given in table 1
16, Seat test (air)
All gate, globe, globe stop and check, plug and ball valves shall be subjected to an air seat test at a minimum
sauge pressure of 6.9 bar® applied as specified in clause 15 with liquid on the side which is not under pressure
and there shall be no visible leekage during the tost (see table 2 for test duration). As an alternative, ball and plug
valves may be tested, when specified and the method agreed with the purchaser, by pressurizing the body cavity
‘with the bal/plug in the closed position and liquid on both sides. This testis not required for check valves (see
clause 15(c)).
If so specified by the purchaser, a low pressure air test on the seats shall be carried out by the manufacturer on
valves intended for low differential pressure or vacuum service; the test pressure shall then be stated by the
purchaser anc! may be witnessed by the purchaser if desi
17. Test duration
‘The specified test pressure foreach type of test shall be maintained for atleast the durations given in table 2.
Table 2, Test durations
Minimum test duration
Set seat
mm min min
Up to and including 50 % %
65 up to and including 1501 1
200 up to and including 300 |2 2
350 and larger Ss 2
18. Test liquid
Hydrostatic tests shall be made with water at ambient temperature unless the use of another liquid is agroed
between the purchaser and the manufacturer. If water is used, it may contain a water-soluble oil or a rust
inhibitor.
19, Test gauges
‘Test gauges shall be calibrated at intervals not exceeding three months and the results shall be recorded.
20. Test certificates e@
‘When specified by the purchaser, the manufacturer shall issuo a test certificate confirming that the valves have
been tested in accordance with the requirements of this standard and stating actual pressures and medium used
in the test.
Section four. Further tests (see appendix A)
21, Fire safe tests
‘When required, these tests shall be carried out as specified in A.1.
22. Anti-static device testing
When requited, these fests shall be carried out as specified in A.2.
#1 ar = 10 Njmn? = 10° kPa
BSI BS*524b PART*L 74 MM Lb24Gb9 OO40S55 O mm
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
Appendix A
Prototype tests
[NOTE. Its recommended that if fire safe testing is being conducted for purposes other than Kitemarking or sina recognized cetifiation
sefuemes, then the sample valves tested shall normally represent a size range of similar valves of nominal bore size not more than 50 mm
‘greater than and not more than SO mm smaller than the nominal bore and size of the sample valve. It is suggested thatthe smallest vale in
the range should be included as sample valve
‘Where valves manufactured by a particular company vary according to material, constructional detail etc, then only limited
programme of testing may be required to cover such additional ranges.
A.L Fire safe testing of soft seated ball valves
A.Lul General The requirements of A.1.2 shall be satisfied for the design of valve to be classified as fire safe. Ths testis
intended only 2s «prototype test and is intended to cover a rango of sizas of valve having the same pressure rating, design
detail and material composition. A valve design or material change which might affect the fire safe aspect may be cause for
retest in order to classify the modified design as fire safe.
‘This test method may also be used as the basis ofa prototype tet for fir safe testing of other types of soft seated valve
‘when specified in the appropriste British Standard.
AL2 Test procedure
(@) The valve shall be mounted in the test rig with the stem vertically upwards (a sketch of a typical rg is given in
figure 1). The valve body and bore of the bal shall be filled with kerosene or diesel fuel prior to commencement of the
test.
(b) The valve shall be exposed to fire with the ballin the open position until the body of the valve reaches a temperature
of at east 600 °C. (The temperature should be measured in the body, as near to the seat ring as possible and remote
from the flame source). This minimum temperature shall be maintained for the period of time recommended by the
valve manufacturer to ensure complete decomposition or disintegration of the soft seats and seals. In to case shall this
period be less than 15 min. Body temperature shall be recorded at 5 min intervals.
During fcing the valve shall be observed for visual signs of leakage to atmosphere from the stem, body joint or
cover joint.
(©) A minimum internal pressure of 2 bac* shall be maintained during exposure to fire.
(@) The valve shall be demonstrated to be operable by shutting and opening it a minimum of three times (leaving the
valve in the open position) within $ min of extinguishing the Sire, If approved by the manufacturer the valve may then
bbe force cooled after cooling naturally to black heat. As soon as practicable thereafter the following additional tests
shall be carried out in the sequence specified.
(1) With water flowing through the valve, commence to close the valve (one single operation) within 10 of.
‘commencement of flow. With the valve closed stabilize the pressure to 1 bar. Measure leakage rate across the
pressure retaining seat and to atmosphere from the stem, body joint or cover joint between 3 min and 13 min after
closing the valves and applying the pressure.
(2) After completing (1), (and without further operations) the valve shall be subjected to a full hydrostatic seat test
pressure (ee table 1). Measure the leakage rate across the pressure retaining seat and to atmosphere from the stem,
body joint or cover joint between 3 and 13 min after applying the pressure.
(©) Bistirectional valves shall be tested in both directions.
(@) No gland adjustment shall be made at any stage of the test procedure.
(g) After completion of the test, the-valve shall be dismantled for inspection to obtain assurance that all soft sealing
components have decomposed or disintegrated.
* Lbar= 10! Ni?
BSI BS¥S14— PARTH) 74 MM Lb24b69 OO4OS9e 2 ml
BS 5146 : Part 1: 1974
AAL.3 Leakage rates, Maximum allowable leakage rates shall be as shown in table 3.
Table 3. Average leakage rates
‘Valve nominal size DN Allowable average leakage rates
Reduced Full Seat Total stem, body
bore bore joint, cover joint
rml/min ml/min
B10 50 81040 20 10
80 so 30 15
100 80 40 20
150 100 60 30
200 150 80 40
250 200 100 so
300 250 120 60
350 300 140 70
400 350 160 80
400 180 90
Leakage rates from the stem, body joint and cover joint during firing which support
either a single flame of a length in excess of 100 min or multiple flames of a total
combined length in excess of 100 mm shall be a cause of rejection
‘A.2 Testing of anti-static device. For those types of valve where an antistatic device is specified in the relevant
British Standard, a prototype test shall be carried out on a new, dry, ‘as built’ valve of each type after pressure
‘esting. The test for continuity shall be cartied out after a valve has been cycled at least five times. It shall then be
demonstrated that the discharge path as defined in the individual valve product standard has electrical continuity
with a resistance not exceeding 10 92 from a power source not exceeding 12 V.
NOTE. THIS TEST IS HAZARDOUS. ALL REASONABLE PRECAUTIONS HAVE TO BE TAKEN FOR THE SAFETY OF
PERSONNEL CONDUCTING THE:
TEST.
BSI BS*5146 PART*) 74 MM Ub24469 OO40597 4 mm
Discharge to sate area
downwind of tir
Valve body and skin
Rel valve~ temperature pyrometers
Set pressure to 0 C-1000°C.
suit valve rating —|
Portable displacer
type hand pump Test valve
‘Thermocouple
‘Manus! bleed valve inserted into. bind
andlor pressure hole in valve body
‘elif valve
0 0
o
@eody city LEE Tresor o rane
Kerosene 1 Foe! supply
re = he
Bleed valve
NOTE 1, Recommended minimum distance downwind from flebox of pump, bleed valve discharges and relit valve vents is 7m.
NOTE 2. Installation for body cavity pressure is optional.
NOTES. All rei pipework to boa minimum of DN 15.
Figure 1. Typical fire safe test rig
BSI publications referred to in this standard:
“This standard makes reference tothe following British Standards:
WS 1133 Packaging code
Section 6 Temporary protection of motal surfaces against corrosion (during transport and storage)
BS 1414 Flanged and buttowrelding end stel outskde-serow-and-yoke wedge gate valves for the petroleum industry
[BS 1560 Steel pipe flanges and Manged fittings (nominal sizes in to 24 in) for the petroleum industry
Part 2 Metric dimensions
BS 1570 Flanged and buttarelding end steel plug valves for the petroleum industry (excluding wellhead and flowline valves)
BS 1868 Flanged stool chock valves forthe petroleum industry
BS 1873 Flanged steel plobo valves for the petroleum industry
[BS 2080 Summary of face-to-face dimensions of Manged ferrous valves for the petroleum industry
[BS 4570 Fusion welding ofstol castings
Part 1 Production, rectification and repale
BS 5351. Stool ball valves for the etréleum, Petrochemical and allied industries,
BS 5352 Specifiation for steel wedge gate, globo and check valves 0 mm and smaller for the petroleum, petrochemical and
allied induseios
BS $353. Specification for plug valves
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Iso 27509 2020Document15 pagesIso 27509 2020T KelvinNo ratings yet
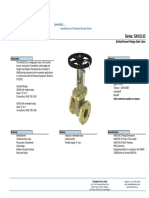
- BrooksBank ButterflyValve ConcentricDoubleFlange NABDocument2 pagesBrooksBank ButterflyValve ConcentricDoubleFlange NABT KelvinNo ratings yet
- BS en 10204-1991Document11 pagesBS en 10204-1991T KelvinNo ratings yet
- UKOOA - Part 1Document19 pagesUKOOA - Part 1T KelvinNo ratings yet
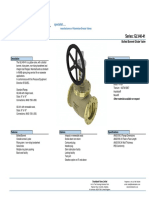
- BrooksBank ButterflyValve ConcentricLug NABDocument2 pagesBrooksBank ButterflyValve ConcentricLug NABT KelvinNo ratings yet
- PFI ES-22 1993 Color Coding of Piping MaterialDocument3 pagesPFI ES-22 1993 Color Coding of Piping MaterialT KelvinNo ratings yet
- Sunway Avila Brochure - LowresDocument13 pagesSunway Avila Brochure - LowresT KelvinNo ratings yet
- T BeamDocument2 pagesT BeamT KelvinNo ratings yet
- BrooksBank GateValve FlangeBelow4Document3 pagesBrooksBank GateValve FlangeBelow4T KelvinNo ratings yet
- BrooksBank CheckSwingValve Below12Document3 pagesBrooksBank CheckSwingValve Below12T KelvinNo ratings yet
- BrooksBank GlobeValve FlangeAbove6Document3 pagesBrooksBank GlobeValve FlangeAbove6T KelvinNo ratings yet
- BrooksBank GateValve ScrewedDocument2 pagesBrooksBank GateValve ScrewedT KelvinNo ratings yet
- Pokemon Heart Gold Wild Pokemon ModifierDocument10 pagesPokemon Heart Gold Wild Pokemon ModifierT KelvinNo ratings yet