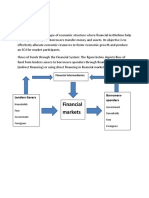
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TA Thuong Mai
Uploaded by
khanhlinh.2504004Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TA Thuong Mai
Uploaded by
khanhlinh.2504004Copyright:
Available Formats
1. How many business factors (yếu tố) are there?
There are four basic factors: land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship (doanh nghiệp)
What do these factors mean?
Land: refers a piece of real estate, sources of raw materials needed for production
Labor (lđ): is the use of mental or physical work to produce goods
Capital (vốn): means not only wealth (tài sản) but all things that workers use in production
and distribution (phân phối) which are purchased with money
Entrepreneurship: is the activity of controlling (kiểm soát) and directing (chỉ đạo) the
other three factors
2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of an entrepreneur?
Advantages:
Keep all profits (for himself)
Start/end his business
Decide to do everything for his business
Disadvantages: Who holds the bag if the business goes bankrupt (phá sản)?
Owner of the business/entrepreneur
Employees (nv) (have to seek work elsewhere)
Customers (look for another place to buy their products)
Creditors (chủ nợ): money lenders (lose money)
Others (friends/relatives)
3. What are the advantages of sole proprietorship, and partnership?
Sole proprietorship
Advantages:
- Start/set up or end his (current) business
- Decide to do everything for his business
- Keep all profits (not share with anyone)
- Follow very few government (chính phủ) and legal regulations (qui định pháp luật)
- Pay personal income taxes (pay no corporate income taxes)
Partnership (is the same with sole proprietorship)
4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a corporation?
Corporation (is owned by many shareholders/stock owners)
Advantages:
- Legal entity (Which is chartered by the state) (thực thể hợp pháp)
- Ownership divided into shares of stocks
- Buying & selling shares without permission from other owners
- Raising capital by selling shares of stock
- Liability of corporation limited to the value of the assets of the company
Disadvantages:
- Follow legal procedures (thủ tục) (forming a corporation is not easy)
- Taxed twice (corporate income taxes / personal income taxes)
5. What are the 4 types of production?
- Analysis (phân tích): process of separating (tách) a raw material into several parts
(petroleum refining) (tinh chế dầu mỏ)
- Synthesis (tổng hợp): process of putting together 2 or more raw materials into one
finished product (glass (thủy tinh) is made by joining together lime (vôi), soda, potash
(kali) and other chemicals)
- Extraction (khai thác): process of removing (lấy) raw materials from the land, sea, air for
the purpose of production
- Fabrication (chế tạo): process of making products of more value from already
manufactured (đã sx) materials (automobiles)
6. What are the characteristics (đặc điểm) of the intermittent production methods?
- Short production runs (production of that item stops and production of another item
begins)
- Low volume (số lượng thấp) (Only a limited number, perhaps only one, of each
specification (chi tiết) are made)
- Custom-made products (goods are made to customer specifications (yêu cầu))
- Adjustable (có thể điều chỉnh) machines (machinery is adjusted for a specific job/ is
taken apart (tháo rời) or reset for a different job)
- Flexibility (tính linh hoạt) (many designs and styles are possible)
- Increased labor (increased labor is necessary)
- Expensive (one of the reasons that custom-made goods (sp làm theo yêu cầu) are popular
is that they are expensive)
7. What are the characteristics of the continuous production methods?
- Long production runs (This method makes one type of product for a long period of time)
- High volume (The volume must be large)
- Standard (chuẩn) goods (the products must be standardized (tiêu chuẩn hóa)/try to please
average taste)
- Specialized machinery (máy móc chuyên dụng) (the company buys specialized
machinery/ automatic (tự động) machines)
- Standardization (standardization is necessary in order to get the greatest benefit)
- Less labor (assembly line (dây chuyền lắp ráp) fixed the number of employees)
- Less cost per unit (production costs are low thanks to the use of the assembly line)
8. What is the concept of marketing in the past?
Produce first, sell later
Two aspects of marketing: sales promotion and distribution
Sales promotion: advertising and personal selling
Distribution: transportation/ storage (dự trữ)/ related services (dv liên quan): financing/
standardization/ grading (sự phân loại)/ related risks
9. Explain the concept of modern marketing.
Modern marketing: see if product will sell first, then produce it.
- Marketing decides what customer wants, designs and produces a product that satisfies
customer (hài lòng khách hàng)
- Desire (nhu cầu) of consumers becomes a factor on production decisions
- Production is an engineering problem (vđ kĩ thuật)
- Marketing involves considering human behaviour
10. What is concentrated market/ Saturated market and their solutions?
Concentrated market (thị trường ứng đọng): situation in which there are very few
customers for the product
Saturated market (thị trường bão hòa): a market situation in which all the customers
have made their purchases and there are no new customers to be found
Their solutions:
11. Describe shopping goods/ convenience goods/ retail store/ channel of distribution.
Shopping goods/ or consumer product: requiring more consideration of price and quality
Convenience goods: products that are usually inexpensive/or have a low price and purchased at
the most convenient locations
Are widely distributed (available for sale at many places/locations such as:
vending machines/ convenience stores/ supermarket)
Retail outlet (cửa hàng bán lẻ)/ store: Full service retail store includes: staff service (available
to explain the features of products to customers)
Channels of distribution: trade channel: the route (con đường) or way (cách thức) that product
travels from manufacturer (nhà sx) to the consumer
12. Write down the difference between franchise store and chain store and the similar
thing/ the advantages both stores enjoy from parent company as well as the services (from
parent company)
The difference b/t a franchise and a chain store
- Franchise store: is independently owned/ under a franchise or license from a parent
company/ pays a fee or a certain percentage of the total sales to the parent company
- Chain store: is owned by parent company/ is vertically integrated (parent company
controls warehouses, trucking lines (transporting service)
Similar things:
- The same merchandise from the parent company
- The same name from the parent company
The parent company supplies:
- Promotion
- Distribution
- Products/ supplies
Both distributors can enjoy from the parent company:
- advertising
- distribution
- name recognition
13. What is a discount house?
=>Retail outlet where products/ goods can be reduced because there is less service and
display of goods
=> receiving discounts from wholesalers by purchasing in quantity
=> selling discontinued models (a product that has become either temporarily or permanently
unavailable for purchase)
=> dealing directly with producers without middlemen
=> lower overhead costs (costs of operation)
14. What includes in personal selling?
- Sales person: tries to convince customers to buy products
- When? Concentrated market for a product
- Industrial goods which are difficult to advertise / custom-made products
- Trade-in: an older or used product which is being exchanged for a newer model
-> Sales staff demonstrates products/ negotiates the price/ designates specifications of products
15. What should the producer do to increase sales of products?
=>Find new markets (by expanding its geographical sales area or try to sell its products to a
different segment of the popular)
You might also like
- TA Thuong MaiDocument5 pagesTA Thuong Maikhanhlinh.2504004No ratings yet
- TATMDocument8 pagesTATMBích TrươngNo ratings yet
- Business ResultDocument9 pagesBusiness Resultkhanhlinh.2504004No ratings yet
- Business StudiesDocument7 pagesBusiness StudiesĐạt VươngNo ratings yet
- Business: Is The Activity of Making & Distributing Goods and Services (To The End-Users)Document18 pagesBusiness: Is The Activity of Making & Distributing Goods and Services (To The End-Users)Anh ThùyNo ratings yet
- Chap 20212223Document6 pagesChap 20212223bẹjamin hoàngNo ratings yet
- Business Economics IDocument22 pagesBusiness Economics ISashaselffNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: The Economic Problem: Needs, Wants, Scarcity and Opportunity CostDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 1: The Economic Problem: Needs, Wants, Scarcity and Opportunity CostHweeNo ratings yet
- Thuật NgữDocument11 pagesThuật NgữVy ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Business Last Minute Information SheetDocument28 pagesBusiness Last Minute Information Sheetkhalt067.309No ratings yet
- ENTREPDocument4 pagesENTREPSittíNo ratings yet
- Business SupleDocument9 pagesBusiness Suplealejandra choezNo ratings yet
- Business Notes For BoardsDocument59 pagesBusiness Notes For BoardsananyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Operations Management?Document11 pagesWhat Is Operations Management?Anjali AngelNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Unit 1 Business and ManagmentDocument20 pagesApuntes Unit 1 Business and Managmentlorena burgaleta delgadoNo ratings yet
- IB Business and Management Chapter 1.1 NotesDocument6 pagesIB Business and Management Chapter 1.1 NotesJiny LeeNo ratings yet
- Mjet Term 2 2018 BST 2 MSDocument6 pagesMjet Term 2 2018 BST 2 MSmartinNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument27 pagesNotesnorhan alaliNo ratings yet
- Note MarketingDocument2 pagesNote MarketingLê Thủy HiềnNo ratings yet
- Ib Diploma Business Summary (SL-HL)Document68 pagesIb Diploma Business Summary (SL-HL)Dolores López CentoNo ratings yet
- Design and Planning of Production Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesDesign and Planning of Production Lecture NotesThijs DrevesNo ratings yet
- BST F2 MS 1Document4 pagesBST F2 MS 1Selifa AbutiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Activity EnglishDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Activity EnglishAlejandra MargaritaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 GlossaryDocument26 pagesUnit 1 GlossaryJoshua WilliamsNo ratings yet
- ERP DataDocument2 pagesERP DataSuprio SahaNo ratings yet
- Etech Midterm ReviewDocument3 pagesEtech Midterm ReviewtheresefleurkythNo ratings yet
- ACCA F1/ CAT FAB - Chapter 6 Organisation Culture and Committees PDFDocument61 pagesACCA F1/ CAT FAB - Chapter 6 Organisation Culture and Committees PDFNick Kai Chong Wong0% (1)
- BIA NotesDocument17 pagesBIA NotespepukayiNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Modified 19 2 27022024 092242amDocument47 pagesLec 1 Modified 19 2 27022024 092242aminshalabdulrehman1No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3Surendran SaravananNo ratings yet
- BM Review Notes 4.6 - 5.6Document22 pagesBM Review Notes 4.6 - 5.6howard.chen0604No ratings yet
- Amit Singh: By:-Asst. Prof. Hpihe, BudaunDocument14 pagesAmit Singh: By:-Asst. Prof. Hpihe, BudaunMina MichealNo ratings yet
- Hrm. Highly Trained Professionals. OM. Process: Complex Requires High Level of TrainingDocument19 pagesHrm. Highly Trained Professionals. OM. Process: Complex Requires High Level of TrainingChiara LupiNo ratings yet
- ngli quản trịDocument3 pagesngli quản trịphnlingNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - RetailDocument8 pagesChap 1 - Retailpink pinkNo ratings yet
- Metrology ClusteredDocument5 pagesMetrology Clusteredshreya rajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Business Market and Business Buyer Behavior B2BDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Business Market and Business Buyer Behavior B2BMinh SinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 Introduction To Business Management Part 1Document54 pagesUnit 1.1 Introduction To Business Management Part 1Shania Florence HarlockNo ratings yet
- Cobecon NotesDocument9 pagesCobecon Noteswill geeNo ratings yet
- Strategy Summary LessonsDocument48 pagesStrategy Summary LessonsNaut van GoorNo ratings yet
- Samenvatting Levy Weitz (Boek)Document10 pagesSamenvatting Levy Weitz (Boek)Richard BuremaNo ratings yet
- Business Review Chapter 1Document20 pagesBusiness Review Chapter 1TanishNo ratings yet
- MKTG Notes MidtermDocument5 pagesMKTG Notes MidtermNatasha Militar0% (1)
- Template - Sales and MarketingDocument11 pagesTemplate - Sales and MarketingRamesh SoniNo ratings yet
- WK#1 Successful Product DevelopmentDocument43 pagesWK#1 Successful Product DevelopmentCarl AriffNo ratings yet
- Resume EnglishDocument23 pagesResume EnglishJulia LimaNo ratings yet
- Managing Products, Product Lines, Brands, PackagingDocument16 pagesManaging Products, Product Lines, Brands, PackagingAbhisek DeyNo ratings yet
- What Is Business ActivityDocument18 pagesWhat Is Business ActivityJulius DennisNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective of The Chapter: Product AND Service Concept Product AND Service ConceptDocument24 pagesLearning Objective of The Chapter: Product AND Service Concept Product AND Service ConceptHibo AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 EntrepreneurshipDocument7 pagesChapter 3 EntrepreneurshipYuyu ComelNo ratings yet
- Name: Cohort: Date: Training Program: Instructor: Describing Products and ServicesDocument8 pagesName: Cohort: Date: Training Program: Instructor: Describing Products and ServicesMABEL XIMENA GONZALEZ PEREZNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument72 pagesInternational BusinessSandesh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Start Coir IndustryDocument7 pagesStart Coir IndustryBalasubramaniam MuruganNo ratings yet
- Today's Topic: Analyzing and Beating The CompetitionDocument60 pagesToday's Topic: Analyzing and Beating The Competitionugan9edsNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesUnit 5 - Operations Managementadriana zugastiNo ratings yet
- All Business NotesDocument63 pagesAll Business Notesantoniosflopes1No ratings yet
- Full SummaryDocument44 pagesFull SummaryKhánh ĐanNo ratings yet
- Mandlo Commercial NotesDocument82 pagesMandlo Commercial Notestinonyahuma923No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Enterprise, Business Growth & SizeDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Enterprise, Business Growth & SizeAayushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Commercial InvoiceDocument1 pageCommercial InvoiceAli SadegaNo ratings yet
- Fin 203 Assignment 1Document12 pagesFin 203 Assignment 1aarzu dangiNo ratings yet
- International Finance NotesDocument42 pagesInternational Finance NotesShilu MNo ratings yet
- IDFC FIRST Bank Credit Card Statement 24052022Document3 pagesIDFC FIRST Bank Credit Card Statement 24052022avisinghoo7No ratings yet
- Foreign Trade University: VocabularyDocument32 pagesForeign Trade University: VocabularyVũ Như NgọcNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Sample Questions Attempt Review 2Document9 pagesFinal Exam Sample Questions Attempt Review 2leieparanoicoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1malak aymanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cash and Cash Equivalents (Student File - Questionnaire)Document147 pagesLecture 1 - Cash and Cash Equivalents (Student File - Questionnaire)JOSCEL SYJONGTIANNo ratings yet
- Beer Game Simulation Moodle BUSI1150Document6 pagesBeer Game Simulation Moodle BUSI1150HanaLeNo ratings yet
- Physical Distribution of Products in The PhilippinesDocument1 pagePhysical Distribution of Products in The PhilippinesReynald CabiasNo ratings yet
- LM Business Finance - Q3 W6-8 - Module 9 FDocument24 pagesLM Business Finance - Q3 W6-8 - Module 9 Fvmin친구No ratings yet
- Banking and Financial InstitutionDocument2 pagesBanking and Financial InstitutionMaricar TabadaNo ratings yet
- GMIT JD193 Sindhu Kumari P.R 21 23Document3 pagesGMIT JD193 Sindhu Kumari P.R 21 23manvi aminNo ratings yet
- Tanzania Single Administrative Document: Component No Item Invoice Price Unit Price 48.model, Specification QuantityDocument1 pageTanzania Single Administrative Document: Component No Item Invoice Price Unit Price 48.model, Specification QuantityHonest consolidationNo ratings yet
- Tax Administration: Bacc 2 Income Taxation Franklin D. Lopez, CPADocument1 pageTax Administration: Bacc 2 Income Taxation Franklin D. Lopez, CPAJaeun SooNo ratings yet
- POCA Assignment #1: Roll 18BM61K16 Name Mayukh MukhopadhyayDocument2 pagesPOCA Assignment #1: Roll 18BM61K16 Name Mayukh Mukhopadhyaymayukh mukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Consignment SD MMDocument65 pagesConsignment SD MMAl-Mahad International SchoolNo ratings yet
- Tuition Fee 2023 - DigitalDocument17 pagesTuition Fee 2023 - DigitalYuva InapalaNo ratings yet
- Super MartDocument3 pagesSuper MartVishal SainiNo ratings yet
- "The Worst of All Worlds:" Oil Sanctions and Italy's Invasion of Abyssinia, 1935-1936Document27 pages"The Worst of All Worlds:" Oil Sanctions and Italy's Invasion of Abyssinia, 1935-1936Connor RhodesNo ratings yet
- Quizlet - SOM CH 8Document25 pagesQuizlet - SOM CH 8Bob KaneNo ratings yet
- List of Non Deposit Accepting Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCS) As On February 28, 2017 Sr. No. Company Name Ahmedabad Regional OfficeDocument446 pagesList of Non Deposit Accepting Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCS) As On February 28, 2017 Sr. No. Company Name Ahmedabad Regional OfficeamandeepNo ratings yet
- Total Pages: 15Document15 pagesTotal Pages: 15sureshdevidasNo ratings yet
- Atharv Gupta A15 SIPDocument42 pagesAtharv Gupta A15 SIPAditya TarasNo ratings yet
- Currency Hedging: Currency Hedging Is The Use of Financial Instruments, Called Derivative Contracts, ToDocument3 pagesCurrency Hedging: Currency Hedging Is The Use of Financial Instruments, Called Derivative Contracts, Tovivekananda RoyNo ratings yet
- Trading SessionDocument3 pagesTrading SessionAmaitem UdohNo ratings yet
- Bill Feb 23 2Document1 pageBill Feb 23 2Irfan JillaniNo ratings yet
- Q2 SSLM3 Principles-Of-Marketing JPestanoDocument6 pagesQ2 SSLM3 Principles-Of-Marketing JPestanoDaniel Guanzon TanNo ratings yet
- Step 1a: Life Pulls Your Money in All Directions. Spend Time Here Before Spending Your CashDocument5 pagesStep 1a: Life Pulls Your Money in All Directions. Spend Time Here Before Spending Your CashRichard MitchellNo ratings yet
- Acct Statement XX8993 30042022Document42 pagesAcct Statement XX8993 30042022Sarvesh JukarNo ratings yet