0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views2 pagesHeart Murmurs: Types and Significance
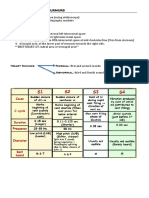
The document discusses the differences between physiological and pathological heart murmurs. It provides details on the origin, causes, clinical significance, treatment, and auscultation location of each type. It also compares characteristics of systolic and diastolic murmurs such as timing, sound, causes, and associated symptoms.
Uploaded by
khantasleema196Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
55 views2 pagesHeart Murmurs: Types and Significance
The document discusses the differences between physiological and pathological heart murmurs. It provides details on the origin, causes, clinical significance, treatment, and auscultation location of each type. It also compares characteristics of systolic and diastolic murmurs such as timing, sound, causes, and associated symptoms.
Uploaded by
khantasleema196Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd